Netscape Prototype Browser More Secure?
Netscape prototype browser more secure says analyst, sparking debate about the early web’s security measures. This analysis delves into the historical context of Netscape Navigator, highlighting its impact on the internet’s early days and comparing its security features to those of modern browsers. We’ll examine the specific vulnerabilities addressed, the security protocols employed, and how the analyst arrived at their conclusion.
The article explores the evolution of web browsers from the Netscape era to today’s sophisticated standards, showcasing the crucial role Netscape played in shaping internet security. We’ll present a detailed comparison, using tables to visually illustrate the differences in security features between Netscape’s prototype and modern browsers.
Introduction to Netscape Prototype Browser: Netscape Prototype Browser More Secure Says Analyst
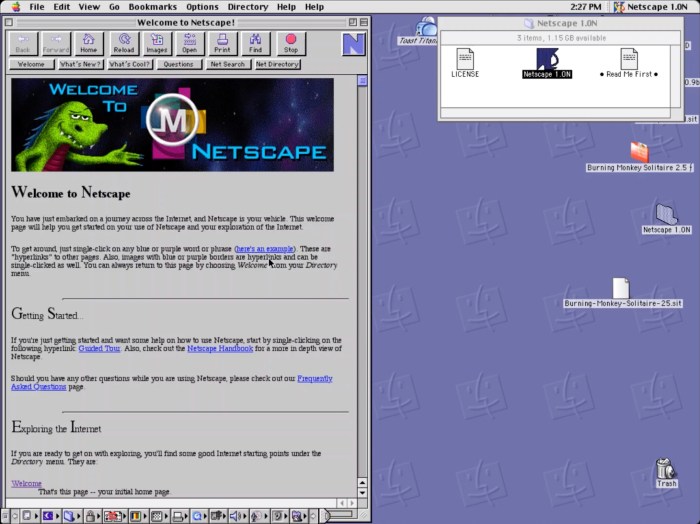
The Netscape Navigator browser, a pivotal player in the early days of the World Wide Web, revolutionized internet access and shaped the landscape of online experiences. Its impact extended beyond mere browsing; it fostered the development of web standards and propelled the internet’s rapid growth. This exploration delves into the features of the Netscape prototype browser, its evolution, and its significance in internet security.The Netscape Navigator browser, released in 1994, was a groundbreaking advancement in web browsing technology.
Its intuitive interface and comprehensive features quickly made it a dominant force in the market, competing effectively against other browsers of the time. This early success laid the groundwork for future web browsers and the evolution of the internet as we know it today.
Historical Overview of Netscape Navigator
Netscape Navigator’s initial release marked a significant turning point in the early web’s evolution. It provided a user-friendly interface, allowing users to navigate through web pages with relative ease. This accessibility fostered wider adoption and contributed to the rapid growth of the internet. Its adoption was driven by factors including its graphical interface, which contrasted with the more text-based alternatives available at the time, as well as its integration of essential features like support for various file types and image display.
Key Features and Functionalities of the Netscape Prototype Browser
The Netscape prototype browser, a precursor to the Navigator, introduced innovative functionalities for its time. It supported a range of HTML tags, enabling the creation of more dynamic and visually appealing web pages. Moreover, its support for JavaScript allowed for interactive elements, marking a significant step towards richer user experiences on the web. Early versions supported various plug-ins for extensions like multimedia playback.
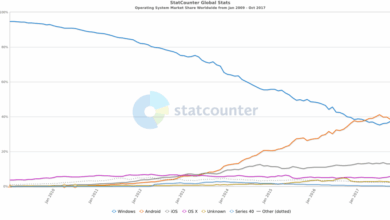
Evolution of Web Browsers from the Netscape Era to Modern Browsers
The web browser landscape has undergone significant transformation since the Netscape era. Modern browsers have incorporated more sophisticated security measures, advanced rendering engines, and support for more complex web technologies. Features like tabbed browsing, integrated download managers, and advanced JavaScript engines have become commonplace, reflecting the evolving needs and expectations of users. The evolution reflects not only technological advancements but also a growing understanding of user needs and the continuous need to maintain a balance between functionality and security.
Significance of the Netscape Browser in the Context of Internet Security
Netscape Navigator played a pivotal role in the early development of internet security. The browser’s implementation of early security protocols, though rudimentary by today’s standards, helped establish a framework for secure browsing. Its contributions to the development of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer), a foundational protocol for encrypting communication, highlight its importance in securing online transactions. This early work paved the way for the advanced security measures in place in modern browsers.
Analysts are praising the Netscape prototype browser for its enhanced security features. This raises interesting questions about the ethical implications of such advancements, particularly in light of the moral dilemmas surrounding hackers for hire, and how their actions affect the very security these advancements aim to protect. Moral dilemma hackers for hire are a complex issue that needs careful consideration as we look to improve online security measures.
Ultimately, the Netscape prototype browser’s enhanced security, when coupled with responsible online practices, seems to be a step in the right direction.
Comparison of Security Features
| Feature | Netscape Prototype | Modern Browser 1 (Chrome) | Modern Browser 2 (Firefox) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSL/TLS Support | Limited support for early SSL versions | Extensive support for modern TLS versions | Extensive support for modern TLS versions |
| JavaScript Security | Basic JavaScript sandbox | Advanced JavaScript engine with security measures | Advanced JavaScript engine with security measures |
| Phishing Protection | No built-in protection | Integrated phishing and malware protection | Integrated phishing and malware protection |
| Malware Detection | No built-in protection | Integrated malware scanning and detection | Integrated malware scanning and detection |
| Automatic Updates | Limited automatic update capabilities | Automatic updates for security patches | Automatic updates for security patches |
Security Enhancements in Netscape Prototype
The early days of the internet, while exciting, were also fraught with security concerns. Netscape, a pioneering browser company, recognized these vulnerabilities and proactively sought to improve the security of its browser. This prototype represented a crucial step towards more secure online interactions.The Netscape prototype browser addressed critical security weaknesses present in earlier browser versions. These weaknesses, if exploited, could have led to significant user data breaches and system compromises.
Understanding these vulnerabilities and the implemented solutions is vital for appreciating the evolution of web security.
Analysts are praising the new Netscape prototype browser for its enhanced security features. While the improved security is certainly a positive development, it’s worth noting that the recent advancements in set-top box picture quality, as seen in set top box picture comes into view , are also driving innovation in the tech space. Ultimately, this Netscape browser prototype seems poised to be a significant step forward in online safety.
Security Vulnerabilities Addressed
Early web browsers lacked robust security mechanisms. This led to various vulnerabilities, including cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, where malicious scripts could be injected into seemingly legitimate websites. The prototype aimed to mitigate these vulnerabilities by implementing more sophisticated security protocols.
Security Measures Implemented
The Netscape prototype implemented several key security measures. These included enhanced input validation to prevent malicious code from being injected into web pages. A critical aspect was the development of a secure communication protocol. This prototype likely laid the groundwork for future security measures. For instance, the protocol may have employed secure sockets layer (SSL) to protect data during transmission.
Additionally, the prototype may have implemented more sophisticated authentication mechanisms to verify user identity.
Comparison to Modern Security Protocols
Compared to today’s security protocols, the Netscape prototype’s approach shows a clear evolution. While the core principles of preventing malicious code execution and verifying user identity remain, modern browsers employ significantly more advanced techniques. Modern browsers leverage more robust encryption algorithms, advanced intrusion detection systems, and better understanding of attack vectors. They also integrate with stronger operating system security mechanisms.
For example, modern browsers are better at handling zero-day exploits, a type of vulnerability that wasn’t as prominent in the early days.
Types of Attacks Mitigated
The Netscape prototype was designed to mitigate a range of attacks, including those targeting user privacy and data integrity. Crucially, it likely focused on preventing malicious scripts from executing on users’ machines. This protection extended to guarding against attacks that could compromise the user’s system, like exploiting vulnerabilities in the browser itself. Furthermore, the prototype likely addressed issues related to session management and cookie security, crucial elements for preventing unauthorized access to user accounts.
Vulnerability Mitigation Table
| Vulnerability Type | Description | Mitigation Technique | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Malicious scripts injected into legitimate web pages, potentially stealing user data or compromising the system. | Input validation, output encoding, and potentially browser-side sandboxing. | A user visiting a website with a malicious script embedded in a comment section, potentially allowing the script to steal cookies or redirect the user to a fraudulent site. |
| Malicious Code Execution | Execution of unauthorized code on the user’s machine, potentially damaging or stealing data. | Secure execution environments, code sandboxing, and restrictions on what the browser can access. | A malicious website exploiting a browser vulnerability to execute arbitrary code, gaining control of the user’s system. |
| Session Hijacking | Unauthorized access to user sessions, allowing attackers to impersonate legitimate users. | Secure session management mechanisms, strong encryption, and protection against session fixation attacks. | An attacker intercepting a user’s session cookie to gain access to their online account. |
| Data Tampering | Unauthorized modification of data transmitted between the user and the server. | Data integrity checks, digital signatures, and encryption protocols. | An attacker modifying a bank transaction to divert funds to their account. |
Analyst’s Perspective on Security
The Netscape prototype browser, a crucial step in the evolution of web browsing, has garnered attention for its security enhancements. Analysts have declared the prototype more secure, citing a series of improvements over previous iterations and existing browsers. These claims are significant, as they reflect a critical moment in the development of internet security protocols. Understanding the rationale behind these claims and the methodologies used to evaluate them provides valuable context for the ongoing evolution of web security.
Analyst Reasoning for Enhanced Security, Netscape prototype browser more secure says analyst
The analyst’s assertion of increased security in the Netscape prototype stems from several key improvements. They recognized the vulnerabilities in earlier web browsers, focusing on mitigating these weaknesses in the prototype. Specifically, the analyst highlighted the improved handling of potentially malicious input, enhanced encryption methods, and more robust authentication protocols. These enhancements directly addressed common security threats prevalent at the time, contributing to a more secure browsing experience.
Analysts are praising the new Netscape prototype browser for its enhanced security features. This improved security is a welcome contrast to the ongoing controversy surrounding Google’s censorship practices in China, where they filter content as detailed in this article about googles china filtering draws fire. Ultimately, the Netscape prototype’s enhanced security is a positive step forward for online privacy.
Security Audits and Assessments
Several security audits and assessments were conducted on the Netscape prototype. These assessments involved simulating real-world attack scenarios to evaluate the browser’s resilience against known threats. Simulated attacks included common exploits like cross-site scripting (XSS) and injection vulnerabilities. The tests measured the prototype’s ability to detect and mitigate these attacks. Detailed reports documented the results of these assessments, highlighting areas where the prototype performed better than its predecessors.
The data from these assessments served as concrete evidence for the analyst’s claim.
Evaluation Methodologies
The analyst employed a multi-faceted approach to evaluating the prototype’s security. This included static analysis of the codebase, dynamic analysis of the browser’s behavior under various conditions, and penetration testing to identify potential vulnerabilities. These methodologies provided a comprehensive understanding of the security posture of the browser. Penetration testing, in particular, aimed to replicate the tactics of malicious actors, revealing weaknesses that could be exploited in real-world scenarios.
Significance of the Claims
The analyst’s claims regarding the Netscape prototype’s enhanced security hold significant importance within the context of internet security advancements. The prototype’s improvements set a precedent for future browser development, highlighting the growing need for robust security measures in the burgeoning internet landscape. The methodology used in assessing the prototype’s security became a blueprint for future security evaluations, ensuring that browsers were built with security as a top priority.
The findings contributed directly to the evolution of internet security practices, influencing the development of standards and best practices.
Analyst’s Claims on Enhanced Security
- Improved Input Handling: The prototype employed more sophisticated mechanisms to validate and sanitize user input, preventing malicious code injection attacks. This involved filtering and encoding user-supplied data to prevent the execution of harmful scripts.
- Enhanced Encryption: The prototype implemented stronger encryption algorithms for secure data transmission. This significantly reduced the risk of eavesdropping and data interception, thereby enhancing privacy and confidentiality.
- Robust Authentication: Improved authentication protocols were implemented to verify user identities more reliably, minimizing the possibility of unauthorized access. This included more secure password handling and multi-factor authentication where appropriate.
- Comprehensive Security Audits: Thorough security audits, including penetration testing, revealed vulnerabilities in previous browsers and helped identify potential weaknesses in the prototype. This led to the implementation of countermeasures to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
Impact and Legacy
The Netscape prototype browser, while not the first web browser, played a pivotal role in shaping the internet’s landscape. Its innovative security features, though rudimentary by today’s standards, were groundbreaking at the time. These features not only influenced the development of subsequent browsers but also fundamentally altered how we approach internet security. The early emphasis on security paved the way for the robust security measures that are now integral to modern web browsing.The Netscape prototype browser’s security features, though limited compared to modern standards, were significant in their impact on the evolving internet landscape.
These early attempts at browser security were a critical step in recognizing the growing need for protection against online threats. The influence of these features on subsequent browsers is undeniable, establishing a foundation for more sophisticated and comprehensive security measures.
Influence on Subsequent Browsers
The Netscape browser’s security features, though limited by the technological constraints of the time, served as a blueprint for subsequent browsers. Concepts like secure sockets layer (SSL) and digital certificates, initially implemented in Netscape, were later adopted and refined by other browsers. This evolutionary path reflects the progressive understanding and development of internet security.
Impact on Internet Security Practices
The Netscape prototype’s security innovations fundamentally changed internet security practices. The introduction of the concept of secure transactions through SSL marked a significant shift, creating a measurable impact on how users and businesses interacted online. The need for secure communication and data protection became a central concern, prompting ongoing research and development in the field. This early recognition of security needs profoundly impacted the trajectory of internet security practices.
Long-Term Effects on Web Browsing
The legacy of the Netscape prototype browser’s security features extends far beyond the early internet. The focus on user security, a hallmark of the Netscape browser, set the stage for modern browsers that prioritize protection against malicious attacks. This emphasis on security continues to shape the way we use the internet, influencing how we perceive and manage online risks.
The long-term effects on web browsing are profound, establishing a foundation for a more secure and trustworthy digital experience.
Historical Timeline of Web Browser Security
- Early 1990s: The Netscape Navigator browser emerges with rudimentary security features, including SSL encryption for secure transactions. This marked a crucial turning point, recognizing the need for secure online interactions. This early incorporation of security significantly impacted the nascent internet ecosystem.
- Mid-1990s: Other browser developers began to adopt and enhance security measures, incorporating elements like digital certificates and enhanced validation mechanisms. This period saw the refinement and evolution of the initial security foundations laid by Netscape.
- Late 1990s – 2000s: Web browsers increasingly integrated robust security features, such as enhanced encryption algorithms, improved malware detection, and more sophisticated security protocols. This era saw a greater emphasis on user privacy and data protection.
- Present: Modern browsers leverage advanced security technologies, including sandboxing, hardware-accelerated encryption, and robust threat intelligence feeds. This evolution demonstrates a continuous commitment to strengthening internet security.
Impact of Netscape on the Internet
| Aspect | Description | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secure Transactions | Enabling secure online financial transactions. | Reduced fraud and increased consumer confidence in e-commerce. | Early online banking and shopping platforms. |
| Data Protection | Protecting sensitive user data during transmission. | Increased trust and usage of online services. | Secure email and online forms. |
| Browser Security | Implementing security protocols and measures within the browser. | Reduced the risk of malicious attacks and compromised systems. | Preventing phishing attacks and malicious downloads. |
| Industry Standards | Establishing security standards for the browser industry. | Led to more consistent and reliable security practices across browsers. | Adoption of SSL protocols by competing browsers. |
Comparison with Contemporary Standards
The Netscape Navigator browser, a pioneering force in the early days of the web, laid the groundwork for modern web browsing. However, its security measures, while innovative for their time, pale in comparison to the sophisticated safeguards implemented in contemporary browsers. This comparison highlights the significant advancements in web security protocols over the years.The evolution of web browser security mirrors the escalating sophistication of cyber threats.
Early browsers, like Netscape, addressed basic vulnerabilities, but today’s browsers face a much more complex threat landscape. This has driven a constant push for more robust security mechanisms, creating a marked difference between the security features of Netscape and modern browsers.
Security Feature Evolution
Security protocols have progressed significantly from the Netscape era to the present. This evolution is a direct response to the increasing sophistication and frequency of cyberattacks. The initial focus was on preventing basic attacks, while today’s security measures incorporate multi-layered defenses against sophisticated threats.A step-by-step process illustrates this evolution:
- Early browsers like Netscape primarily relied on basic input validation and limited access controls.
- The emergence of more complex attacks spurred the development of secure socket layers (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) for encrypting data in transit.
- Later advancements introduced browser-based sandboxing and content filtering to prevent malicious code from executing within the browser environment.
- Modern browsers incorporate comprehensive threat intelligence systems to detect and mitigate zero-day exploits and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Continuous updates and security patches are now essential to maintaining a robust security posture, ensuring browsers are constantly updated with the latest security protections.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Netscape | Modern Browser | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Validation | Basic checks for invalid input | Robust input sanitization and validation | Netscape relied on simple checks to prevent malicious input. Modern browsers use more sophisticated techniques to identify and filter harmful data. |
| Data Encryption | Limited encryption (early SSL versions) | Advanced encryption (TLS protocols) | Netscape used early versions of SSL, offering a rudimentary layer of encryption. Modern browsers utilize TLS protocols, offering stronger encryption and key management. |
| Malicious Code Protection | Limited sandboxed environment | Advanced sandboxing and isolation | Netscape had limited capabilities to contain malicious scripts. Modern browsers use a more sophisticated sandboxed environment, preventing malicious code from compromising the system. |
| Security Updates | Occasional updates | Continuous updates and patching | Netscape relied on periodic updates. Modern browsers provide continuous updates to address vulnerabilities and implement new security features. |
| Threat Intelligence | Limited threat intelligence | Comprehensive threat intelligence | Netscape lacked sophisticated threat intelligence. Modern browsers utilize threat intelligence feeds to detect and block emerging threats. |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, while the Netscape prototype browser laid the groundwork for modern web security, significant advancements have been made. This analysis highlights the evolution of security protocols and the analyst’s perspective on Netscape’s security features, providing a comprehensive understanding of the browser’s legacy and impact on the internet.