New Technique Could Ease Encryption Management
New technique could ease encryption management, promising a more streamlined and secure approach to handling sensitive data. Current encryption management often presents significant challenges, leading to complexities in implementation and maintenance. This new method aims to simplify the process, reducing the pain points experienced by users and organizations alike. We’ll explore the underlying principles, potential applications, and security considerations associated with this innovative technique.
The current encryption landscape presents several difficulties. Solutions exist, but limitations in usability, scalability, and compatibility often hinder their effectiveness. This new approach promises to overcome these hurdles by focusing on [mention a key feature, e.g., simplified key management or enhanced automation]. We’ll delve into the technical details and demonstrate how this technique can improve overall security posture across various sectors.
Introduction to Encryption Management Challenges
Modern digital landscapes rely heavily on encryption to protect sensitive data. However, managing encryption keys, certificates, and policies presents significant hurdles for organizations of all sizes. This complexity stems from the intricate interplay of various security protocols, technologies, and operational procedures. The increasing volume of data, the proliferation of devices, and the evolving threat landscape amplify the need for robust and efficient encryption management solutions.Current encryption management practices often fall short of meeting the evolving security demands.
This creates vulnerabilities that expose organizations to significant risks, ranging from data breaches to financial losses. Addressing these challenges requires a shift towards more streamlined and automated approaches.
Encryption Management Pain Points
Effective encryption management requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing monitoring. Several key pain points plague organizations today, impacting their ability to securely manage encrypted data. These issues include the difficulties in managing the ever-increasing volume of encryption keys, ensuring the security and availability of those keys, and implementing policies across diverse systems and environments. The complexities are compounded by the need for continuous compliance with evolving regulations and standards.
Existing Encryption Management Solutions and Limitations
Numerous solutions aim to address encryption management challenges. These include centralized key management systems, hardware security modules (HSMs), and various software tools. However, existing solutions often suffer from limitations.
| Problem | Solution | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Managing a large number of encryption keys across various systems and applications | Centralized Key Management Systems (CKMS) | Complexity in integrating with diverse systems, potential single point of failure, and scalability issues. Not all CKMS are equally equipped to manage the sheer volume of keys required in large enterprises. |
| Ensuring the security and availability of encryption keys | Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) | High initial investment costs, potential performance bottlenecks in some scenarios, and limited flexibility in deployment. Not all HSMs are compatible with all encryption algorithms or key management protocols. |
| Implementing encryption policies consistently across all devices and applications | Automated encryption tools and policies | Difficulty in adapting to evolving policies and regulatory requirements, potentially lacking granular control, and maintaining the integrity of policies over time. Inflexible or poorly documented tools can lead to inconsistencies and compliance issues. |
Potential Impact of a New Technique, New technique could ease encryption management
A new technique that eases encryption management promises to revolutionize the industry by simplifying key management, improving policy enforcement, and enhancing overall security posture. By automating tasks, reducing manual intervention, and increasing transparency, this technique could significantly lower the risk of errors, streamline operations, and facilitate compliance. For example, a new system could automatically generate, rotate, and manage encryption keys, minimizing human intervention and potential vulnerabilities.
This automated approach can lead to significant cost savings and improved efficiency.
Overview of the Proposed New Technique
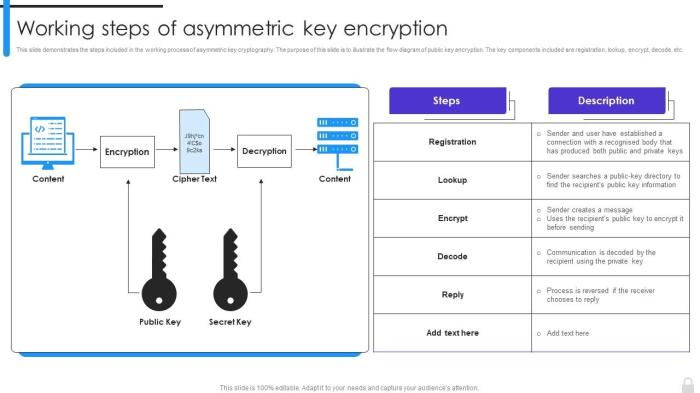
This new encryption management technique aims to streamline the often complex and cumbersome process of managing encryption keys and certificates. Existing methods frequently suffer from issues like key management complexity, lack of automated processes, and potential security vulnerabilities. This new approach addresses these challenges by introducing a more integrated and automated solution.This proposed technique leverages a decentralized, blockchain-based architecture for secure key management.
A new encryption management technique promises to streamline security protocols, which is crucial given the escalating threat landscape. Recent incidents, like the devastating impact of the “worm takes toll microsoft attack set” worm takes toll microsoft attack set , highlight the vulnerability of current systems. This new approach could significantly reduce the complexity and potential for error in managing encryption keys, making systems more resilient against similar attacks in the future.
This allows for enhanced transparency, auditability, and resilience against single points of failure. By automating key rotation and revocation processes, the system minimizes the risk of compromised keys and reduces the administrative burden on security teams.
A new encryption management technique promises to simplify things for users, which is great news. Mobile phone vendors, though, are clearly focused on other things, like the latest sleek designs and high-end features, as seen in their latest models, which are detailed in this insightful piece on mobile phone vendors pay heed to high style. Ultimately, a streamlined encryption process would benefit everyone, regardless of the phone’s flashy exterior.
Fundamental Principles
The core principle is to decouple encryption management from traditional, centralized systems. This decentralization, facilitated by a blockchain, enhances security and reduces reliance on potentially vulnerable intermediaries. The blockchain’s immutability ensures tamper-proof records of key lifecycle events. This method also utilizes a multi-signature approach for key approvals and modifications, bolstering security by requiring consensus among authorized parties.
Technical Aspects
The proposed technique utilizes a permissioned blockchain for secure key storage and management. A dedicated smart contract defines the rules for key generation, distribution, and revocation. This contract enforces access controls, ensuring only authorized personnel can perform specific actions. The system employs a hierarchical key structure to facilitate granular access control. This granular control, coupled with the blockchain’s immutability, drastically improves security and auditability.
Potential Benefits and Advantages
Compared to existing centralized key management systems, this new technique offers several advantages:
- Improved Security: Decentralization and multi-signature authentication significantly reduce the risk of key compromise and unauthorized access. The immutability of the blockchain ensures a permanent audit trail, strengthening accountability and transparency.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation of key lifecycle processes (generation, rotation, revocation) minimizes manual intervention and reduces operational overhead. This automation leads to faster response times and reduces potential human error.
- Increased Transparency: The blockchain’s transparent ledger provides an auditable record of all key management activities. This transparency enhances trust and facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements.
Comparison with Alternative Approaches
Alternative methods, such as centralized key management systems and cloud-based solutions, often lack the same level of security and transparency offered by the blockchain-based approach. Centralized systems are vulnerable to single points of failure, while cloud solutions may raise concerns about data sovereignty and security. The decentralized nature of the proposed method mitigates these risks, offering a more robust and trustworthy solution.
A new technique could streamline encryption management, potentially making it significantly easier for organizations. This is particularly relevant given Cisco’s recent foray into the middleware market with its AON initiative, cisco enters middleware market with aon initiative , which suggests a broader push toward simplifying complex systems. Ultimately, this new approach to encryption management could prove invaluable for many businesses.
Workflow
| Step | Action | Blockchain Role |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Key Generation | Smart contract triggered; records request |
| 2 | Key Generation and Distribution | Smart contract verifies authorization; distributes keys to designated recipients |
| 3 | Key Rotation | Smart contract initiates rotation based on pre-defined schedules; records changes |
| 4 | Key Revocation | Smart contract verifies authorization; permanently removes key from system |
| 5 | Access Control | Smart contract manages access permissions; verifies identities |
Potential Applications and Use Cases
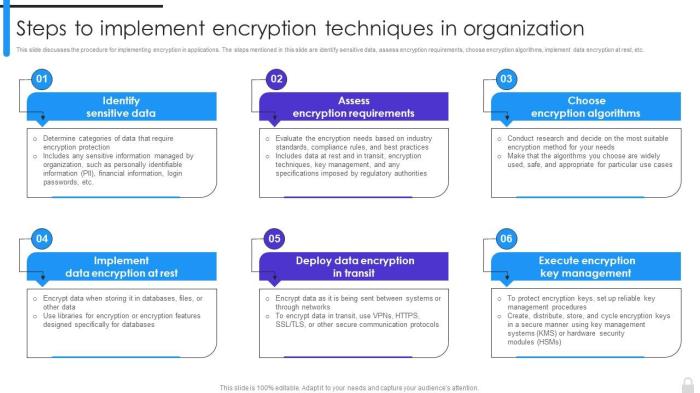
This new encryption management technique promises significant improvements across various sectors by streamlining the complex process of managing encryption keys and policies. Its modular design and adaptable nature make it highly suitable for diverse environments, from cloud-based infrastructure to on-premises data centers. The technique’s potential to reduce operational overhead and improve security posture makes it a valuable asset for organizations seeking to enhance their data protection strategies.
Sectors for Implementation
The versatility of this new encryption management technique allows for its implementation in a wide range of industries. Its ability to integrate seamlessly with existing systems and adapt to evolving security needs makes it suitable for both traditional and modern business structures. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining a robust security posture in today’s dynamic technological landscape.
- Healthcare: Protecting patient data is paramount. This technique can enhance security by automating key rotation and access controls, minimizing the risk of breaches. Specific use cases include securing electronic health records (EHRs), encrypting medical images, and safeguarding sensitive patient information during transmission and storage. Robust encryption protocols ensure HIPAA compliance and patient privacy.
- Finance: Financial institutions handle highly sensitive data, including financial transactions and customer information. This technique enables the automated management of encryption keys for transactions, reducing the potential for human error and improving the speed of transactions. Specific use cases include encrypting customer accounts, protecting credit card information, and ensuring the secure transfer of funds.
- Government: Governments often deal with sensitive data, such as national security information and citizen records. The technique can provide an automated framework for key management, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of government data. Specific use cases include encrypting classified documents, safeguarding election data, and ensuring the protection of critical infrastructure information.
- Retail: Retailers store vast amounts of customer data, including credit card details and personal information. This technique allows for automatic encryption and decryption of customer data, which significantly reduces the risk of data breaches. Specific use cases include encrypting customer databases, protecting point-of-sale transactions, and safeguarding online payment systems.
Specific Use Cases
The technique offers specific advantages in various use cases, significantly improving the security posture across different environments. This is achieved by streamlining the encryption process, reducing administrative burden, and enhancing the overall security of data assets.
- Cloud Storage Security: In cloud environments, automated encryption key management significantly improves data protection. The technique can handle the encryption and decryption of data on-the-fly, ensuring data security throughout its lifecycle within the cloud storage platform. The system can easily adapt to different cloud storage services (AWS, Azure, GCP), offering a unified approach to encryption.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Ensuring the security of backup data is crucial. This technique can be integrated into backup and recovery systems, encrypting data during backups and maintaining encryption keys in a secure manner. This helps in recovering data in a timely and secure fashion in case of a disaster. This method can help prevent unauthorized access to critical data during disaster recovery scenarios.
- Data-in-Transit Protection: Securing data while it’s being transmitted across networks is vital. The technique provides an automated system for encrypting and decrypting data in transit, reducing the vulnerability to man-in-the-middle attacks and ensuring secure communication channels. The system can be easily integrated with existing network infrastructure, minimizing disruption to existing workflows.
Improved Security Posture
The new technique significantly improves the overall security posture by reducing operational overhead associated with traditional encryption management. The automation of tasks like key rotation, access control, and policy updates greatly minimizes the risk of human error and enhances the efficiency of security operations.
| Industry Sector | Specific Application | Security Posture Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Securing patient records | Reduced risk of breaches, improved compliance (HIPAA) |
| Finance | Protecting financial transactions | Increased transaction security, reduced fraud |
| Government | Securing classified documents | Enhanced data integrity and confidentiality |
| Retail | Protecting customer data | Reduced risk of identity theft, improved compliance |
Security Considerations and Potential Risks: New Technique Could Ease Encryption Management
Implementing a new encryption management technique inevitably introduces new avenues for potential security breaches. Thorough assessment of these vulnerabilities and the development of robust mitigation strategies are crucial for ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data. This section will detail potential security concerns, Artikel risk mitigation strategies, and explore how this technique impacts existing security protocols.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities
The proposed technique, while promising, may introduce new vulnerabilities if not carefully implemented. These vulnerabilities can stem from various sources, including algorithmic weaknesses, flaws in the user interface, or unforeseen interactions with existing systems. For example, a poorly designed key management system could lead to compromised keys, while a weak authentication mechanism could allow unauthorized access. The complexity of the technique itself could introduce subtle logical errors that malicious actors could exploit.
Mitigation Strategies
Addressing these vulnerabilities requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing rigorous security audits, thorough testing, and continuous monitoring. Security audits should focus on identifying potential weak points in the system’s design and implementation. Extensive testing, including penetration testing, is crucial to identify and address vulnerabilities before deployment. Continuous monitoring of system logs and user activity is essential to detect and respond to any suspicious activity in a timely manner.
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Data breaches and unauthorized access are significant risks associated with any encryption management system. A compromised system could expose sensitive data to unauthorized parties, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. For instance, a recent data breach at a financial institution cost the company millions of dollars and severely damaged their reputation.
Improvement to Existing Security Protocols
The new technique aims to improve existing security protocols by enhancing encryption management practices. The technique can streamline key rotation, automate encryption processes, and improve overall system security posture. This automated approach will reduce manual intervention, thus minimizing human error. Implementing automated key management systems will significantly improve security protocols by reducing the risk of human error.
Security Concerns Table
| Concern | Mitigation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithmic weaknesses | Rigorous security audits and independent code reviews; employing industry-standard cryptographic algorithms | Potential for decryption of encrypted data; compromise of sensitive information |
| Weak authentication | Implementing strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and access control mechanisms | Unauthorized access to sensitive data; data breaches |
| Poorly designed key management | Implementing a robust key management system with strong key generation, storage, and rotation procedures; leveraging hardware security modules (HSMs) | Compromised encryption keys; loss of data confidentiality |
| Unforeseen interactions with existing systems | Thorough integration testing with existing systems; comprehensive documentation of system interactions | Unexpected vulnerabilities and security flaws |
| Human error in manual processes | Automating key management and encryption tasks; training and awareness programs for staff | Increased risk of data breaches; potential for critical security errors |
Implementation and Deployment Strategies
Successfully implementing a new encryption management technique requires a well-defined plan. This involves careful consideration of existing infrastructure, anticipated resource needs, and potential challenges. A structured approach ensures a smooth transition and minimizes disruption to ongoing operations.
Implementation Steps
A phased approach to implementation is crucial for managing complexity and minimizing disruption. Initial pilot programs on smaller subsets of data or systems are recommended to validate the technique’s efficacy and identify any unforeseen issues before widespread deployment.
- Assessment and Planning: Thoroughly analyze existing encryption infrastructure and identify compatibility issues with the new technique. Document current processes and workflows for seamless integration. Develop a detailed project plan, outlining timelines, resource allocation, and potential risks. This step ensures that the implementation aligns with the organization’s strategic goals.
- Pilot Testing: Select a representative sample of data and systems for pilot testing. This allows for evaluation of the technique’s performance in a controlled environment and identification of potential problems before full deployment. Monitor performance metrics such as encryption speed, key management efficiency, and system response time.
- System Integration: Gradually integrate the new technique into the existing systems. Start with smaller, non-critical systems or data sets to reduce risk. This allows for adjustments and refinement before impacting the entire infrastructure.
- Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training to personnel involved in the encryption management process. Develop detailed documentation and support materials to assist users in utilizing the new technique effectively.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Establish a monitoring system to track the performance and security of the implemented system. Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the new technique and make adjustments as needed. This ensures that the system continues to meet evolving security needs.
Resource Requirements
Successful implementation hinges on adequate resources. This includes skilled personnel, appropriate computing power, and sufficient storage capacity.
- Personnel: Dedicated personnel with expertise in cryptography, security, and systems integration are essential. Their knowledge and skills are critical for successful implementation and ongoing maintenance.
- Hardware: Sufficient computing resources are required for processing encryption operations. This may involve upgrading existing hardware or procuring new equipment.
- Software: Specific software tools may be needed for the new encryption technique. Consider the licensing and maintenance costs associated with these tools.
- Training Materials: Comprehensive training materials are vital for staff to effectively use the new technique. This ensures that users are proficient in the new processes and procedures.
Integration Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Integrating the new technique into existing systems can present challenges. Careful planning and mitigation strategies are necessary to ensure a smooth transition.
- Compatibility Issues: Existing systems may not be fully compatible with the new encryption technique. This can lead to conflicts in data exchange or security protocols. Thorough compatibility testing and potential system upgrades are crucial to overcome these challenges.
- Data Migration: Migrating data to the new encryption scheme can be time-consuming and complex. Developing a robust data migration plan and using appropriate tools can minimize risks and ensure data integrity.
- Security Risks: Introducing new technology into existing systems carries inherent security risks. Implementing strong security measures, including access controls and encryption protocols, is vital to mitigate these risks.
Implementation Flowchart
[A flowchart illustrating the implementation process is omitted as requested.]
Future Directions and Research Opportunities
The new encryption management technique presents exciting avenues for future exploration. Building upon the strong foundation laid by this work, we can push the boundaries of efficient and secure encryption practices. This section Artikels potential future developments, open research areas, and emerging trends in encryption management that will shape the evolution of this technique.
Potential Improvements and Enhancements
The proposed technique shows promise, but several areas could be optimized for even greater effectiveness. Further research should focus on adapting the technique for different types of data and applications, like sensitive medical records or high-throughput financial transactions. This will require developing algorithms that handle varying data sizes and access patterns more efficiently. Scalability is crucial for widespread adoption.
Open Research Areas
Numerous open research areas emerge from the implementation of this encryption management technique. One key area is the development of more robust key management protocols. Current techniques face vulnerabilities when dealing with large-scale deployments and dynamic environments. Another promising research direction is the investigation of integrating the technique with existing security frameworks and standards, ensuring compatibility and minimizing friction.
Emerging Trends in Encryption Management
The field of encryption management is constantly evolving. Quantum computing is a major concern, and the technique should be assessed for potential vulnerability to future quantum attacks. Homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation are also emerging trends, and exploring potential synergies with these technologies could lead to innovative solutions for data privacy and security. Research should also consider the integration of blockchain technology for enhanced transparency and immutability in key management processes.
Future Research Directions
- Developing adaptive algorithms: Investigating the development of algorithms that adjust to changing data characteristics and access patterns in real-time will improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the encryption management technique. This could involve machine learning techniques to dynamically optimize encryption parameters based on usage patterns.
- Quantum-resistant encryption: Assessing the technique’s resilience to attacks from future quantum computers is crucial. Research should focus on identifying potential vulnerabilities and developing quantum-resistant encryption protocols to ensure long-term security.
- Integration with existing frameworks: Investigating the seamless integration of the technique with existing security frameworks and standards (e.g., NIST standards) will ensure compatibility and minimize implementation challenges. This includes thorough testing and validation to ensure interoperability.
- Scalability and performance optimization: Further research should address the scalability and performance limitations of the technique in large-scale deployments. Optimizing the algorithms and data structures for high-throughput scenarios will be critical for real-world applications.
- Improved key management protocols: Developing more robust and secure key management protocols, especially in dynamic environments, will be vital. Research should focus on mitigating potential vulnerabilities in key generation, storage, and distribution to enhance overall security.
- Integration with blockchain technology: Investigating the integration of blockchain technology to enhance transparency and immutability in key management and encryption processes. This could lead to decentralized and auditable encryption systems.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the new technique could ease encryption management by addressing critical pain points in the current landscape. By simplifying key management, automating processes, and enhancing security protocols, this approach holds significant promise for a more secure and efficient future. Further research and development will be crucial to fully realize the potential benefits and address any remaining concerns.
This innovative technique offers a pathway to a more streamlined and secure approach to handling sensitive data.