Nokia Unveils Free Map Service A Game Changer?
Nokia unveils free map service, promising a revolutionary new way to navigate the world. This innovative service offers a wealth of features, designed to cater to a wide range of users. From detailed street maps to real-time traffic updates, the service aims to be the ultimate mobile navigation tool. This new offering is set to shake up the competitive landscape, challenging established players and potentially impacting the mobile app development industry.
It’s a game changer, and we’re diving deep to understand the details, the challenges, and the potential impact.
The service boasts a user-friendly interface, designed to be intuitive and accessible to everyone. It seamlessly integrates with various mobile apps, offering unparalleled convenience. The technology behind the maps is robust and scalable, promising accurate and reliable navigation, even for large volumes of users. Nokia has also taken into consideration the needs of developers, making it easy to integrate their services.
This strategic move could redefine how people interact with maps on their mobile devices, and it promises to be a powerful tool for the future.
Introduction to Nokia’s Free Map Service
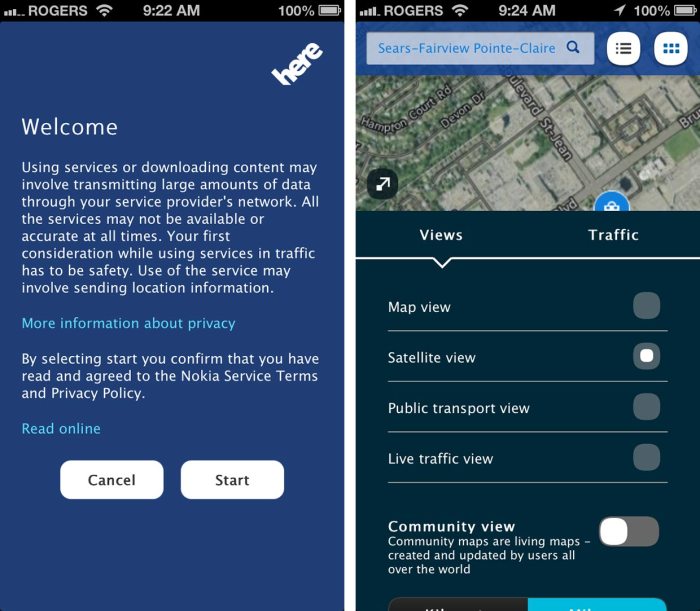
Nokia has unveiled a new, free map service designed to provide comprehensive and accessible geographic information to a wide range of users. This initiative marks a significant step towards democratizing map access, potentially revolutionizing navigation and location-based services for individuals and businesses alike. The service is anticipated to offer substantial improvements over existing solutions, with an emphasis on simplicity, usability, and accessibility.This free map service is a valuable resource for users seeking convenient and reliable map data.
It addresses the need for accurate and up-to-date geographical information, facilitating navigation, location-based services, and various applications. The service’s key features and functionalities are meticulously designed to meet the diverse requirements of its target audience, from casual explorers to professional users.
Key Features and Functionalities
The service encompasses a broad range of functionalities, designed to cater to various user needs. These functionalities include detailed maps, real-time traffic updates, route planning tools, and location-based search capabilities. The user-friendly interface ensures seamless navigation and information retrieval.
- Detailed Maps: The maps offer comprehensive coverage of geographical locations, including roads, buildings, landmarks, and points of interest. High-resolution imagery and detailed street views are integrated, providing users with a clear and accurate representation of the environment.
- Real-time Traffic Updates: The service provides real-time traffic data, allowing users to plan their journeys effectively by adjusting routes in response to current traffic conditions. This feature is particularly beneficial during peak hours or in areas with heavy traffic.
- Route Planning Tools: Users can utilize the service’s route planning tools to find the most efficient and optimal routes based on various criteria, such as time, distance, or preferred modes of transportation. This feature simplifies travel planning and enhances efficiency.
- Location-Based Search Capabilities: Users can easily search for specific locations, businesses, or points of interest using s or coordinates. The service provides relevant search results with detailed information, such as addresses, contact details, and opening hours.
Target Audience
This free map service is designed for a diverse range of users, from casual travelers to professionals. Its accessibility and user-friendly design make it suitable for individuals needing directions, businesses seeking location-based services, and students conducting geographical research.
| Features | Functionalities | Target Users |
|---|---|---|
| Detailed Maps | High-resolution imagery, detailed street views | Casual travelers, tourists, researchers |
| Real-time Traffic Updates | Dynamic route adjustments based on traffic conditions | Commuters, drivers, delivery services |
| Route Planning Tools | Optimized routes based on time, distance, or mode of transport | Drivers, public transport users, event organizers |
| Location-Based Search Capabilities | Finding businesses, points of interest, and specific locations | Businesses, customers, researchers, delivery services |
Competitive Landscape Analysis

Nokia’s foray into the free map service market presents an interesting case study in navigating a crowded and competitive landscape. The availability of free map services has become ubiquitous, with consumers accustomed to seamless navigation and location-based services. This analysis will delve into the strengths and weaknesses of Nokia’s offering compared to established competitors, examining the potential market impact of this new venture.The map service industry is highly competitive, with established players like Google Maps, Apple Maps, and numerous regional competitors vying for market share.
Nokia’s entry necessitates a thorough understanding of the existing ecosystem and how their service can carve a niche for itself. Factors such as user experience, feature set, and pricing strategies will all play crucial roles in determining Nokia’s success.
Nokia’s free map service is a fantastic development, making navigation easier than ever. Imagine the possibilities for quick, accurate directions, especially when combined with advancements like speech recognition, which are a real boon for two finger typists. Speech recognition a boon for two finger typists This could significantly reduce the time spent fumbling with a phone’s touchscreen, freeing up users to focus on the road ahead, rather than the screen.
The new Nokia map service seems like a game-changer for navigation.
Comparison with Major Competitors
Nokia’s free map service will need to contend with established giants. Understanding the competitive landscape is critical for success. This comparison examines three major players: Google Maps, Apple Maps, and a leading regional competitor (e.g., HERE Maps).
| Feature | Nokia Maps | Google Maps | Apple Maps | HERE Maps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Free | Free (with optional premium features) | Free (with optional premium features) | Free (with optional premium features) |
| Key Features | Real-time traffic updates, offline map downloads, 3D building views, augmented reality navigation, and local search (e.g., nearby restaurants). | Extensive search options, street-level imagery, satellite view, real-time traffic, transit directions, and location sharing. | Integration with Apple ecosystem, turn-by-turn navigation, real-time traffic, and local search capabilities. | High-quality map data, detailed street-level information, route optimization for various transportation modes, and strong enterprise integrations. |
| Target Audience | Broad consumer base, with a focus on users seeking affordable and comprehensive navigation solutions. | Global user base, especially users relying on navigation for business and leisure travel. | Apple users, targeting a strong integration with existing ecosystem applications and services. | Businesses, fleet managers, and navigation professionals seeking advanced map data and route optimization. |
| Strengths | Potential to leverage Nokia’s existing network and brand recognition; possible unique integrations with mobile devices. | Extensive data sets, advanced mapping algorithms, and vast user base provide superior coverage and accuracy. | Seamless integration with iOS devices and services. | Strong in data quality and specialized features for enterprise use. |
| Weaknesses | Potential lack of established user base compared to competitors; unknown level of user adoption. | May face challenges with maintaining accuracy in dynamic areas, such as construction sites. | Limited coverage in certain areas or countries, compared to Google Maps. | Potential difficulty in competing with Google Maps for consumer market share due to sheer size. |
Potential Market Share Impact
The potential market share impact of Nokia’s free map service is uncertain. Factors like the service’s unique features, pricing strategy, and marketing efforts will determine its success. A strong focus on niche areas, such as real-time traffic updates or augmented reality navigation, could help Nokia carve out a specific market segment. For example, if Nokia’s service excels in providing accurate offline maps for remote areas, it could attract a loyal user base in those regions.
Direct comparisons to established players such as Google Maps will be crucial in gauging Nokia’s potential market penetration.
Technological Aspects

Nokia’s free map service relies on a sophisticated blend of technologies to deliver accurate, up-to-date, and accessible maps to users globally. This section delves into the core technological underpinnings, future enhancements, and the crucial data sources that maintain the service’s reliability. Understanding these elements is key to appreciating the scale and potential of Nokia’s initiative.
Underlying Map Rendering Technology
The service employs a combination of vector and raster map rendering techniques. Vector data represents geographical features as mathematical objects, allowing for high-resolution zoom capabilities without loss of detail. Raster data, on the other hand, uses images to represent the map’s appearance, which is crucial for displaying intricate details like terrain and imagery. The optimal approach for Nokia likely involves a hybrid system, leveraging the strengths of each technique to achieve a balance between performance and visual quality.
Data Sources for Map Accuracy
Maintaining accurate map data is paramount for a service like this. Nokia likely draws on a variety of data sources. These include satellite imagery for updating elevation data, aerial photography for visual representation, and user-submitted updates to ensure real-world accuracy. The combination of these sources allows for a dynamic and reliable map experience.
Scalability and Handling Large User Volumes
The service’s scalability is critical for ensuring performance under high user demand. Nokia likely employs cloud-based infrastructure to distribute map data and rendering tasks. This distributed architecture allows the system to handle a significant number of concurrent users without performance degradation. Real-world examples of large-scale map services, like Google Maps, demonstrate the feasibility of this approach, showcasing the ability to handle millions of requests simultaneously.
Load balancing techniques and redundant server infrastructure are key elements in this architecture.
Future Updates and Improvements
The map service is not static; it must adapt to changing conditions and user needs. Future improvements might include integrating real-time traffic data, incorporating augmented reality elements for navigation assistance, or supporting more advanced map interaction features. The addition of 3D map visualization and interactive street-level views could further enhance the user experience. The ability to quickly update maps with changes in road layouts, building construction, or other real-world developments is a critical element of future updates.
Map Rendering Technologies Comparison
| Rendering Technology | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Vector | High resolution, smooth zoom, efficient storage, easy updating | May not display complex imagery or terrain as vividly as raster |
| Raster | High-quality imagery, detailed terrain representation | Larger file sizes, less efficient zoom capabilities, updating can be complex |
| Hybrid (Vector & Raster) | Combines strengths of both, allowing for high detail and smooth zoom | Requires more complex processing, potentially higher initial development costs |
The table above illustrates the comparative advantages and disadvantages of different map rendering techniques. A well-designed hybrid approach would likely offer the best balance for Nokia’s free map service.
User Experience and Interface
Nokia’s free map service has the potential to revolutionize mobile navigation, but its success hinges heavily on a user-friendly interface and seamless integration with other applications. A positive user experience fosters engagement and encourages repeated use, ultimately driving adoption and market share. This section delves into the critical aspects of the user interface, highlighting potential usability issues and suggesting improvements to enhance the overall experience.The user interface of a map service should prioritize intuitive navigation and clear visual cues.
Nokia’s free map service is a welcome addition, especially considering the need for reliable navigation. But, while mapping is great, it’s also important to understand the intricacies of file sharing. Exploring the complexities of file sharing, like the different protocols and security considerations involved, is vital. For a deeper dive into the truth about file sharing, check out this excellent resource: dig deep to get the truth about file sharing.
Ultimately, Nokia’s new map service is a useful tool, but understanding the technology behind file sharing provides a broader perspective on the digital landscape.
Effective use of color, iconography, and typography is essential for a visually appealing and easily understandable experience. The user’s ability to quickly locate information and interact with the map is paramount. Poorly designed interfaces can lead to frustration and abandonment, highlighting the need for a meticulous approach to UI/UX design.
User Interface Design Considerations
The overall design should prioritize clarity and simplicity. Users should be able to easily identify key elements like zoom controls, search bars, and route planning tools. A consistent layout across different screen sizes and resolutions is crucial for a seamless experience. Using a clean, minimalist design approach can greatly improve the user experience.
Usability and Navigation, Nokia unveils free map service
Smooth navigation is vital for a successful map service. The responsiveness of the interface to user input, the clarity of directions, and the availability of alternative routes all contribute to a positive navigation experience. For example, users should be able to quickly switch between different map views (satellite, street, hybrid) and easily zoom in and out. The map should be interactive and allow users to easily pinpoint locations, make route adjustments, and access relevant information.
Integration with Other Applications
Seamless integration with other mobile applications is key to maximizing the utility of the map service. Integration with popular navigation apps, ride-sharing services, and social media platforms can provide a richer user experience. For instance, users should be able to share their location with friends, plan routes that incorporate public transport options, or directly access nearby points of interest from social media feeds.
Such integrations will significantly enhance the service’s appeal.
Potential Usability Issues and Improvements
Some potential usability issues include overly complex menus, confusing information displays, and a lack of customization options. To mitigate these, the service should offer a user-friendly interface with clear labels, well-organized menus, and easily accessible settings. Adding options for personalization, such as custom markers or saved locations, would enhance the user experience and encourage long-term engagement.
Interface Design Options and Potential Impact
| Interface Design Option | Potential Impact on User Engagement |
|---|---|
| Clean, minimalist design with intuitive controls | High user engagement due to ease of use and visual appeal. |
| Detailed, information-rich design with advanced features | Potentially higher engagement for users requiring extensive information but could overwhelm less tech-savvy users. |
| Customizable interface allowing users to tailor the map display | High user engagement and satisfaction as users can personalize their experience. |
| Integrated social media sharing options | Increased user engagement and potential for viral spread due to social sharing features. |
Potential Market Impact: Nokia Unveils Free Map Service
Nokia’s free map service has the potential to reshape the mobile landscape, impacting everything from app development to the very structure of navigation businesses. This initiative, if successful, could drastically alter the competitive dynamics within the industry, presenting both opportunities and challenges for existing players. The implications for location-based services are significant, promising both innovation and disruption.This section delves into the potential market impact of Nokia’s free map service, examining its influence on mobile app development, economic benefits for Nokia, the navigation business, and location-based services.
It also analyzes the potential challenges and opportunities for the mobile app industry, offering a comprehensive overview of the expected effects.
Potential Impact on Mobile App Development
The availability of a high-quality, free map service from a reputable company like Nokia will likely stimulate the development of innovative location-based mobile applications. Developers will have access to a robust platform without the need to build their own mapping infrastructure. This will significantly reduce the initial development costs and time required for creating map-centric apps, fostering a more competitive and dynamic ecosystem.
Examples include improved navigation apps, enhanced augmented reality experiences, and new social interaction tools built on location data.
Economic Benefits for Nokia
The free map service can generate substantial economic benefits for Nokia. By offering a free service, Nokia can attract a massive user base, potentially increasing brand recognition and market share. This, in turn, could lead to higher demand for Nokia devices and services, as well as creating a significant platform for future revenue streams. The user base can become a valuable asset for targeted advertising, promoting partnerships, and driving ancillary product sales.
Nokia could potentially leverage this vast user data for personalized location-based services.
Implications for Navigation Businesses
The introduction of a free, comprehensive map service by Nokia will likely challenge existing navigation businesses, particularly those reliant on paid services. Many navigation apps and services have built their business models around the monetization of mapping data and services. The free service could potentially lead to reduced demand for premium features, or necessitate a reevaluation of business models.
Companies will need to adapt and differentiate themselves through superior user experience, specialized functionalities, or additional services beyond basic mapping.
Potential Impact on Location-Based Services
The proliferation of location-based services has been significantly influenced by mapping technology. Nokia’s free map service will further enhance the accessibility and utility of these services, empowering developers to create more innovative and practical applications. Users will gain access to a wider range of location-based services, leading to a more comprehensive and integrated experience.
Analysis of Potential Benefits, Challenges, and Opportunities for the Mobile App Industry
| Potential Benefit | Challenge | Opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced development costs for location-based apps | Increased competition for developers | Innovation in user experience and features |
| Wider access to map data | Potential for decreased revenue for existing map providers | New business models focused on specialized location data |
| Enhanced user experience for location-based apps | Maintaining high data quality and accuracy | Development of location-aware social interactions |
| Stimulation of app development and innovation | Need for a clear monetization strategy for Nokia | Creation of innovative location-based experiences |
Marketing and Promotion Strategies
Nokia’s free map service, poised to disrupt the navigation market, needs a strong marketing push to capture user attention and establish its position. Effective marketing strategies will be crucial in communicating the service’s value proposition and driving adoption. Successful campaigns will not only promote the service itself but also build a positive brand image around Nokia’s technological prowess.A comprehensive marketing plan needs to resonate with target audiences, highlighting the key benefits of the free map service, such as ease of use, accuracy, and comprehensive coverage.
The approach should focus on building trust and demonstrating value to potential users. The marketing strategy should leverage various channels and techniques to achieve widespread reach and engagement.
Potential Marketing Strategies
Nokia can leverage a multi-faceted approach to effectively promote its free map service. This will involve a combination of targeted advertising, strategic partnerships, and engaging content creation. The campaign should emphasize the user-friendly interface and the high quality of the mapping data, differentiating it from existing competitors.
Examples of Successful Marketing Campaigns
Many successful marketing campaigns for map services have utilized compelling visual elements and user testimonials. For example, Google Maps, through its user-centric approach and focus on accuracy, has established itself as a leader in the market. Similarly, Apple Maps, with its integration into the broader Apple ecosystem, has successfully captured a significant market share. These examples highlight the importance of seamless integration and user-friendly design.
Importance of Branding and Visibility
A strong brand identity plays a pivotal role in establishing trust and recognition for the free map service. Consistent branding across all promotional materials is essential for creating a cohesive and memorable image. High visibility through strategic placement of advertisements and partnerships will amplify the message and build awareness. This visibility, coupled with a clear value proposition, will establish the service as a preferred choice among users.
Promotional Channels
- Social Media Marketing: Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram can be utilized to engage with potential users, build communities, and share updates about the service. Running contests, hosting Q&As, and showcasing user experiences through compelling visuals will foster engagement and increase visibility. Leveraging influencer marketing can also expand the reach and credibility of the service.
- Partnerships: Collaborating with mobile carriers, automotive companies, and other technology providers can offer wider exposure and increase user adoption. These partnerships can offer bundled services and integrated functionalities, providing a more holistic user experience. For example, offering the maps service as a standard feature in new mobile devices or car navigation systems will significantly boost the user base.
- Advertising Campaigns: Targeted advertising campaigns on relevant platforms can reach a wider audience and effectively communicate the service’s benefits. These campaigns should highlight the service’s key features, such as real-time traffic updates, detailed street-level views, and offline map capabilities. For instance, advertising during popular travel-related television programs or on websites frequented by potential users can significantly boost brand awareness.
- Public Relations and Media Outreach: Building relationships with journalists and tech bloggers can generate positive media coverage and create a buzz around the service. Press releases, interviews, and product demonstrations can effectively communicate the service’s unique features and benefits. This outreach will position Nokia as a leader in the mapping technology space.
- Community Building: Actively engaging with users through forums, feedback mechanisms, and user groups can foster a sense of community and encourage loyalty. Providing support and addressing user concerns will build trust and confidence in the service. Collecting user feedback and incorporating it into the service will demonstrate responsiveness and improve the overall user experience.
Technical Specifications and Infrastructure
Nokia’s free map service hinges on a robust and scalable technical infrastructure. This ensures reliable performance, rapid response times, and smooth user experience, critical factors for the service’s success and widespread adoption. The architecture must be designed with future growth in mind, as the map service’s popularity increases and user demand grows.The service’s architecture relies on a distributed system, employing various technologies to provide high availability and resilience.
Nokia’s free map service is a welcome addition, especially considering the recent shift in photography. Just like Nokia’s innovative mapping, the industry is rapidly evolving. Nikon’s decision to largely abandon film cameras in favor of digital models, as detailed in this article , highlights this trend. It seems the future of both navigation and photography is undeniably digital, a trend that Nokia’s free maps service perfectly complements.
This approach ensures that even if one part of the system fails, the service can continue to operate without significant disruption. The choice of technologies and the specific implementation details are carefully considered to balance performance, cost, and security.
Server-Side Architecture
The server-side architecture employs a layered approach, optimizing for both speed and reliability. A load balancer sits at the front, distributing incoming requests across multiple application servers. This load balancing approach is critical for handling fluctuations in user traffic, preventing bottlenecks and ensuring that the service remains responsive. Each application server is responsible for processing user requests, interacting with the data storage layer, and returning the appropriate map data.
Data Storage and Retrieval Mechanisms
The data storage mechanism utilizes a highly optimized database system. This system is designed to efficiently store and retrieve the vast amount of geospatial data required for the map service. The system employs spatial indexing techniques to accelerate queries, allowing users to quickly locate desired locations and navigate the map. Data retrieval mechanisms are carefully engineered to balance speed and efficiency.
Techniques such as caching frequently accessed data further improve response times. This caching strategy is crucial for maintaining responsiveness, particularly during peak usage periods.
Technical Specifications and Infrastructure Overview
| Specification | Description | Scalability Considerations | Reliability Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | High-performance servers with redundant components, including multiple network interfaces, power supplies, and disk arrays. | Scalable server clusters can be added to handle increasing traffic. | Redundant hardware and failover mechanisms ensure continuous operation even during hardware failures. |
| Software | A robust and scalable database management system, optimized for spatial data. High-performance web servers and application servers. Load balancing software for distributing user requests. | The software architecture allows for easy scaling to handle increasing data volumes and user traffic. | Software redundancy and failover mechanisms, ensuring uninterrupted service in case of server failures. Regular maintenance and security updates. |
| Data Storage | A distributed database system with sharding and replication to ensure data availability and minimize latency. | Data sharding allows for horizontal scaling, enabling the system to handle increasing data volumes. | Data replication across multiple servers ensures data redundancy and fault tolerance. |
| Networking | High-bandwidth, low-latency network infrastructure to ensure rapid data transmission. | Network infrastructure can be upgraded or expanded as needed to handle increasing traffic. | Redundant network connections and failover mechanisms provide high availability and minimize disruptions. |
Future Trends and Developments
Nokia’s free map service has the potential to become a cornerstone of location-based services. Its future trajectory depends heavily on embracing emerging technologies and adapting to evolving user expectations. This section explores potential developments in augmented reality integration, offline functionality, real-time traffic updates, and new features.
Augmented Reality Integration
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing user interaction with maps. Integrating AR into Nokia’s map service would enable users to visualize directions and landmarks superimposed on their real-time surroundings. Imagine seeing a virtual arrow pointing directly to your destination, or identifying nearby points of interest through an overlaid display on your smartphone screen.
This would enhance wayfinding, especially in unfamiliar locations, and make navigation more intuitive and engaging.
Offline Map Functionality
Providing offline map access is crucial for areas with limited or no internet connectivity. This functionality is vital for travelers, hikers, and anyone venturing into regions with unreliable network coverage. Users can download map data for specific areas, enabling navigation and exploration even when offline. This would create a more robust and accessible service, crucial for global adoption.
Real-Time Traffic Updates
Real-time traffic updates are essential for optimal navigation. The incorporation of real-time traffic data into the map service would dynamically adjust routes based on current conditions, minimizing travel time and improving user experience. This would be particularly useful in congested urban areas or during peak hours. Data sources like GPS tracking, sensor data, and user reporting could contribute to the accuracy of these updates.
Possible Future Features and Improvements
The potential for future features and improvements is extensive. A comprehensive map service should adapt to diverse user needs and preferences. This includes expanding the coverage area, improving the accuracy of location data, and incorporating alternative transportation options.
- Enhanced POI (Point of Interest) data: Expanding and refining the data about Points of Interest (POIs) would enrich the map experience. Adding details like operating hours, ratings, user reviews, and photos would make the service more informative and user-friendly.
- Integration with other services: Linking with other apps, like ride-sharing services or public transportation providers, would allow users to seamlessly plan and execute their journeys.
- 3D map view: Adding a 3D view option would provide a more immersive and engaging map experience, particularly for exploring urban landscapes and mountainous regions.
- Personalized map recommendations: Tailoring map recommendations to individual user preferences based on past journeys, location history, and user interests could enhance the service’s usability and value.
- Integration of safety features: Adding safety features such as emergency contacts, safety alerts, and crime reporting mechanisms would enhance the overall user experience, especially in unfamiliar areas.
Ultimate Conclusion
Nokia’s free map service presents a compelling proposition in the crowded mobile navigation market. The combination of free access, intuitive design, and potential for future integration with other services makes it a strong contender. While challenges remain in terms of competing with established players and capturing market share, Nokia’s strategy suggests a commitment to innovation and user experience.
The service’s potential to impact mobile app development and location-based services is significant. The future looks promising, and we’ll continue to monitor its progress and impact.