Nokia Vodafone Partnership Mobile Service Architecture
Nokia Vodafone partner on mobile service architecture presents a fascinating look at how two industry giants are collaborating to reshape the future of mobile communication. This partnership delves into the intricacies of modern mobile service architecture, exploring the key components, the contributions of each company, and the potential synergies and challenges they face. We’ll examine the historical context, current scope, and future implications of this strategic alliance.
The partnership promises to unlock significant benefits, from enhanced network performance and security to improved user experience. This overview will dissect the technical aspects of the architecture, outlining the roles of various components and their interdependencies. We’ll also analyze Nokia and Vodafone’s individual strengths and how they contribute to the overall structure. The collaboration’s potential challenges and solutions will also be discussed, offering a comprehensive understanding of this innovative endeavor.
Introduction to Nokia-Vodafone Partnership

The Nokia-Vodafone partnership, a long-standing collaboration in the telecommunications industry, has significantly shaped the evolution of mobile services. This strategic alliance, built on mutual trust and shared objectives, has resulted in innovative solutions and technological advancements, benefiting both companies and ultimately, their customers. The partnership exemplifies a successful model for leveraging complementary strengths to drive industry progress.The current scope of this collaboration encompasses a broad range of activities, from joint research and development efforts to the deployment of cutting-edge technologies.
Their shared interests in optimizing mobile network infrastructure, improving customer experience, and pioneering new mobile service offerings underscore the mutual benefits and long-term vision of the alliance.The overarching goals of this partnership are multifaceted, including enhanced network performance, improved service quality, and expanded market reach. Expected outcomes include reduced operational costs, increased revenue generation, and the creation of innovative solutions for future mobile communication needs.
This collaboration has a strong track record of success, with numerous examples demonstrating the positive impact on both companies and the industry as a whole.
Nokia and Vodafone Strengths in Mobile Service Architecture
This table Artikels the key strengths of Nokia and Vodafone in the context of mobile service architecture, highlighting their complementary capabilities and areas of expertise.
| Feature | Nokia | Vodafone |
|---|---|---|
| Network Infrastructure | Nokia excels in the design, development, and deployment of 5G and other advanced network technologies, particularly in areas like core network and radio access network (RAN). | Vodafone, with a vast global network footprint, has significant experience in managing and operating complex telecommunications infrastructure. Their expertise lies in network optimization and ensuring reliable service delivery across diverse geographic locations. |
| Technology Innovation | Nokia is a leader in developing innovative mobile technologies, including AI-driven solutions for network optimization and automation. | Vodafone prioritizes innovation in areas like customer experience, mobile money services, and digital solutions tailored to diverse market needs. |
| Global Reach | Nokia’s presence in global markets, with extensive deployments in different regions, gives it valuable insights into diverse technological needs. | Vodafone’s global network provides a platform for testing and implementing new technologies across diverse environments, enabling them to learn and adapt quickly to evolving customer demands. |
| Customer Experience | Nokia focuses on developing high-performance and reliable technologies to support the delivery of excellent user experiences. | Vodafone has expertise in understanding and meeting customer needs across various segments, driving tailored solutions and service offerings. |
History of the Partnership
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership has a rich history, marked by several key milestones. The initial collaboration focused on the deployment of 2G and 3G networks, demonstrating early mutual trust and shared objectives. Subsequent phases saw the companies working together on 4G and 5G technologies, showcasing a continued commitment to innovation. This illustrates a strategic relationship that has evolved with changing technological landscapes.
Current Scope of the Partnership
The current scope of the partnership is multifaceted, extending beyond simple technology deployments. Joint research initiatives are ongoing, aiming to explore the future of mobile services, from advanced network functionalities to new business models. This includes exploring applications like augmented reality and the Internet of Things. Furthermore, the companies are collaborating on optimizing network performance and customer experience, ensuring seamless service delivery for a growing number of users.
Mobile Service Architecture Overview
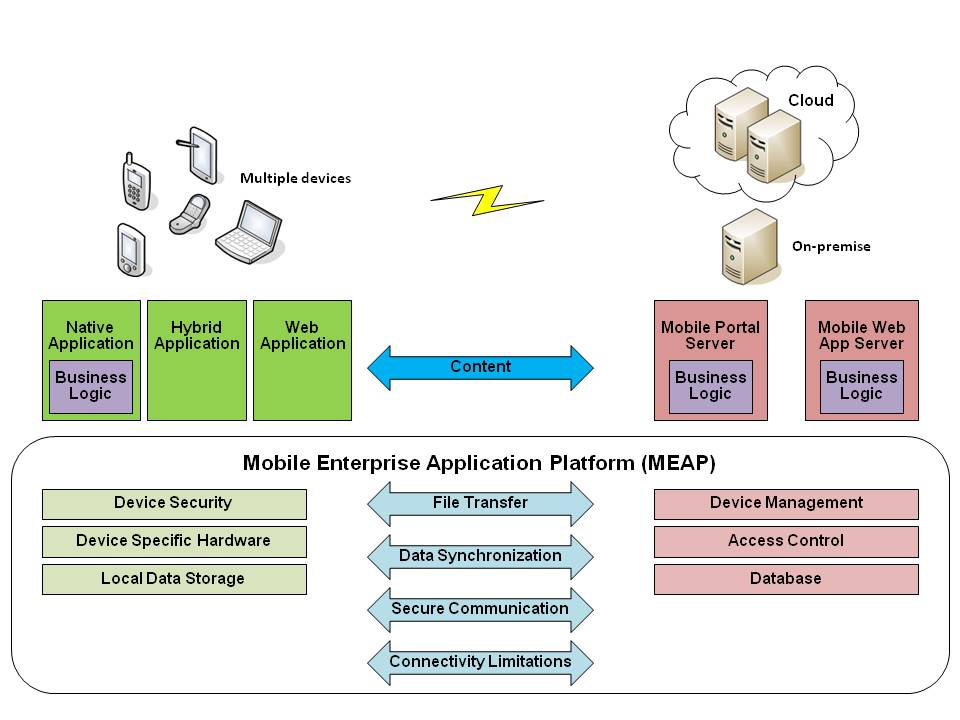
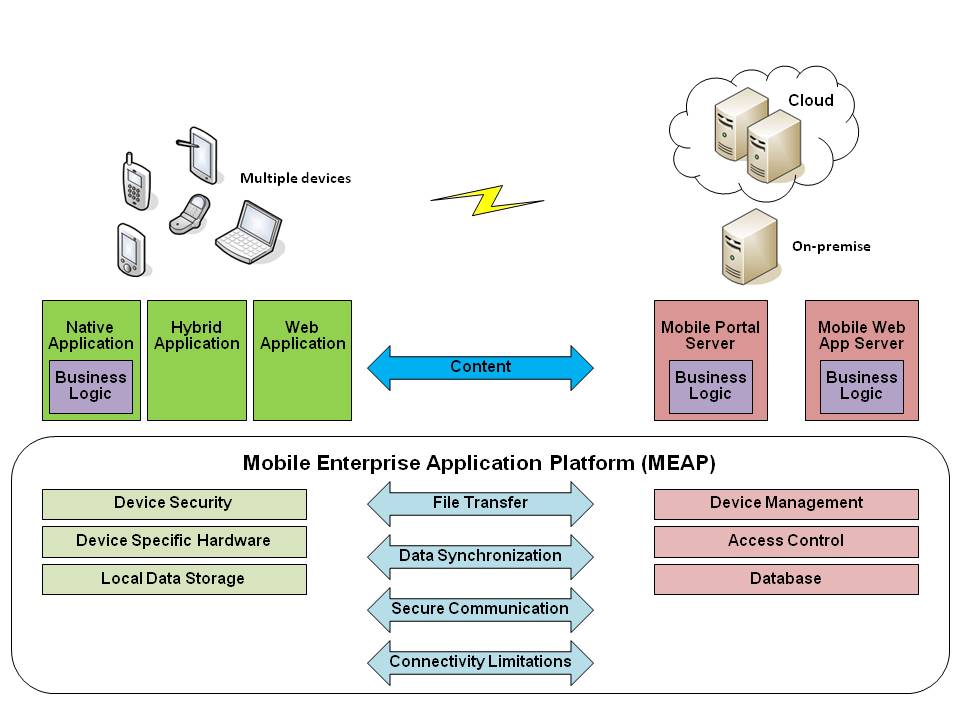
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership hinges on a robust mobile service architecture. This architecture is the backbone of their services, enabling seamless communication, data processing, and user experience. Understanding its components is crucial to grasping the potential and capabilities of this collaborative effort. A well-designed architecture facilitates scalability, adaptability, and resilience, crucial for meeting the evolving needs of the modern mobile landscape.This overview delves into the key components of a modern mobile service architecture, highlighting their individual roles and interdependencies within the broader system.
The architecture described below is a general model, and specific implementations may vary depending on the particular services offered by Nokia and Vodafone.
Key Components
The modern mobile service architecture comprises several interconnected components, each playing a critical role in delivering services. These components are often interconnected through various communication protocols, APIs, and data formats, ensuring seamless data exchange and service delivery.
- Core Network Infrastructure: This encompasses the physical network elements like base stations, core networks, and transport networks. These components provide the physical foundation for communication, enabling mobile devices to connect to the network and exchange data. The core network manages the routing of calls and data, ensuring efficient communication between users. Sophisticated routing protocols and dynamic resource allocation mechanisms optimize network performance and user experience.
For example, network slicing allows different services to use different parts of the network, providing tailored performance for each.
- Application Servers: These servers handle the logic for various mobile services, from messaging to data access and multimedia streaming. They process requests from users, manage data, and interact with other components. Application servers typically use APIs for communication and integration with other components, ensuring data consistency and efficient service delivery. These servers use complex algorithms to manage user data and traffic patterns, optimizing resource usage and improving response times.
- User Interface (UI) Components: These components provide the user interface for interacting with mobile services. These interfaces are critical for delivering a positive user experience, and they are often designed to adapt to different devices and operating systems. UI components often leverage responsive design principles and intuitive navigation, ensuring a seamless experience across various devices.
- Data Storage and Management Systems: These components store and manage user data, including profiles, subscriptions, and usage records. Data management systems use sophisticated algorithms for data integrity, security, and retrieval, providing fast and reliable access to user information.
Technical Aspects of the Architecture
The technical aspects of the mobile service architecture involve several key considerations.
- Scalability and Reliability: The architecture must be designed to handle a large number of users and devices simultaneously, ensuring high availability and low latency. Load balancing and distributed systems architectures are essential for ensuring scalability and reliability.
- Security: The architecture must incorporate robust security measures to protect user data and prevent unauthorized access. This includes encryption protocols, access controls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Interoperability: The architecture must support interoperability with various devices and operating systems. This is achieved through standardized protocols and APIs, ensuring seamless communication and data exchange.
Component Interdependencies
The following table illustrates the interdependencies between the key components of the mobile service architecture.
| Component | Description | Interdependencies |
|---|---|---|
| Core Network Infrastructure | Provides the physical communication channels. | Depends on network equipment, transport protocols, and routing protocols. Interacts with application servers and UI components. |
| Application Servers | Handles the logic and processing for mobile services. | Relies on data storage for user information and access to data. Interacts with the core network for communication and with UI components for display. |
| User Interface (UI) Components | Provides user interaction with the services. | Dependent on application servers for processing and data delivery. Interacts with the core network for communication. |
| Data Storage and Management Systems | Stores and manages user data. | Crucial for application servers to access user information. Must ensure security and accessibility for various components. |
Nokia’s Contributions to the Architecture
Nokia’s deep roots in network infrastructure, coupled with Vodafone’s extensive mobile service experience, creates a powerful synergy. This partnership leverages Nokia’s technological prowess to enhance Vodafone’s mobile service architecture, focusing on performance, security, and scalability. Nokia’s contributions extend beyond simply providing equipment; they encompass a holistic approach to building a future-proof network.Nokia’s expertise in 5G and beyond is critical to the evolution of the architecture, ensuring Vodafone can maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly changing telecommunications landscape.
Their involvement allows for a tailored, optimized architecture that reflects the specific needs of Vodafone’s operations.
Nokia’s Core Technologies and Solutions
Nokia brings a comprehensive suite of technologies and solutions to the partnership. These include advanced radio access network (RAN) solutions, core network components, and network management tools. Their contributions are pivotal to the overall architecture’s functionality and efficiency.
Nokia’s Expertise in Network Infrastructure
Nokia’s extensive experience in designing, building, and maintaining large-scale telecommunication networks is a cornerstone of the partnership. Their expertise in network infrastructure is directly applicable to optimizing Vodafone’s existing and future networks. This includes the ability to anticipate and address potential challenges in a dynamic environment.
Nokia’s Role in Performance, Security, and Scalability
Nokia’s contributions directly impact the performance, security, and scalability of Vodafone’s network. Their solutions are designed to handle increasing data volumes and user demands while maintaining high availability and security. The advanced network slicing capabilities, for example, enable the creation of dedicated network segments for specific services, thereby optimizing performance for different user needs. This enhanced performance is directly linked to a more seamless and reliable user experience.
Furthermore, Nokia’s security features are designed to protect against evolving cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of Vodafone’s network and user data.
Nokia’s Products and Integration Points
| Nokia Product | Integration Points in the Architecture |
|---|---|
| 5G RAN portfolio | Enhanced network capacity, improved user experience, and support for a wider range of applications |
| Cloud-native core network | Improved scalability, flexibility, and operational efficiency, allowing for rapid deployment of new services |
| Network slicing solutions | Optimized performance for various services and user types, creating dedicated network segments for specific use cases. |
| Network security solutions | Enhanced protection against cyber threats, safeguarding user data, and ensuring network integrity. |
| AI-powered network management tools | Proactive issue identification and resolution, leading to optimized network performance and reduced operational costs. |
Vodafone’s Contributions to the Architecture: Nokia Vodafone Partner On Mobile Service Architecture
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership hinges on a shared commitment to delivering exceptional mobile services. Vodafone, a global telecommunications giant, brings a wealth of experience in network operations and customer management to the table. Their contributions to the mobile service architecture extend beyond infrastructure to encompass the entire user experience. This section delves into Vodafone’s specific technologies and solutions within the architecture, highlighting their role in optimizing network performance and enhancing customer engagement.
Vodafone’s Network Operations Expertise
Vodafone’s extensive experience in managing large-scale telecommunications networks is a crucial component of the partnership’s success. Their network operations expertise encompasses the entire lifecycle of a mobile service, from initial planning and deployment to ongoing optimization and maintenance. This expertise translates into a robust and efficient network infrastructure that supports the high-volume demands of modern mobile services. Vodafone’s network optimization strategies contribute to improved network performance and reliability, ensuring a seamless user experience.
Vodafone’s Customer Management Solutions
Vodafone’s deep understanding of customer needs and preferences is instrumental in shaping the mobile service architecture. Their customer management solutions focus on delivering a personalized and engaging user experience. This includes implementing advanced customer relationship management (CRM) systems that allow for targeted marketing campaigns and proactive customer support. This personalized approach helps Vodafone to foster strong customer relationships, leading to increased customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Vodafone’s Contributions to User Experience
Vodafone’s commitment to enhancing the user experience is evident in their contributions to the mobile service architecture. This encompasses a wide range of features and functionalities, including intuitive user interfaces, seamless roaming experiences, and innovative mobile applications. The goal is to make mobile services more accessible, convenient, and enjoyable for users. Vodafone strives to ensure that users experience a consistent and positive interaction with the network, regardless of their location or device.
Summary of Vodafone’s Contributions
| Vodafone Contribution | Technologies/Solutions Used |
|---|---|
| Network Operations Expertise | Optimized network infrastructure, advanced network monitoring tools, and robust network maintenance procedures. |
| Customer Management Solutions | Advanced CRM systems, personalized customer support channels, targeted marketing campaigns. |
| Enhanced User Experience | Intuitive user interfaces, seamless roaming solutions, innovative mobile applications. |
Synergies and Challenges
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership, focused on mobile service architecture, presents significant potential for innovation and efficiency. However, successfully integrating their diverse technological strengths and expertise requires careful planning and proactive solutions to address potential obstacles. This section delves into the anticipated synergies and the challenges that may arise during the integration process.
Potential Synergies
The partnership between Nokia and Vodafone brings together complementary strengths. Nokia’s expertise in network infrastructure, particularly in 5G and core network technologies, can be leveraged to enhance Vodafone’s mobile service capabilities. Vodafone’s extensive market reach and understanding of customer needs can guide Nokia’s technological advancements towards practical applications. This combined knowledge base can drive innovation in areas like network optimization, improved user experience, and cost-effective deployment of new technologies.
For instance, Nokia’s network slicing capabilities can be integrated with Vodafone’s diverse service offerings to provide customized, high-performance network experiences for specific user groups.
Potential Challenges in Integration
Several challenges could hinder the seamless integration of Nokia and Vodafone’s technologies. Differences in existing infrastructure, varying software standards, and differing operational procedures might lead to compatibility issues. Legacy systems and processes could pose significant hurdles in adopting new technologies. Furthermore, cultural differences in organizational structures and working styles can lead to communication breakdowns and delays.
Solutions for Overcoming Integration Obstacles
To overcome these integration obstacles, a comprehensive approach is necessary. This involves clear communication channels, a detailed integration roadmap, and a dedicated team focused on resolving technical and procedural discrepancies. Thorough testing of integrated systems is crucial to identify and mitigate potential issues before deployment.
Interoperability Issues
Interoperability issues may arise from differing communication protocols and data formats between Nokia and Vodafone’s systems. This can lead to data inconsistencies and hinder seamless information exchange. A standardized communication framework, incorporating common data formats and protocols, is vital to ensure interoperability. For example, adopting industry-standard APIs for data exchange can promote seamless integration between the companies’ systems.
Addressing Technical and Procedural Discrepancies
Technical and procedural discrepancies need to be meticulously addressed through standardized documentation and training programs. A shared understanding of best practices and established procedures across both organizations will ensure consistency in implementation and maintenance. For instance, a joint training program focused on the new architecture can equip employees with the necessary skills to handle the integrated system effectively.
Table of Potential Challenges and Proposed Solutions
| Potential Challenge | Proposed Solution |
|---|---|
| Differences in existing infrastructure | Phased implementation strategy, focusing on modular integration and compatibility testing. |
| Varying software standards | Standardization of software interfaces and APIs, ensuring compatibility across different platforms. |
| Differing operational procedures | Establishment of common operating procedures, shared knowledge base, and joint training programs. |
| Legacy systems | Gradual migration strategy, integrating legacy systems with new technologies through API integration. |
| Cultural differences | Cross-cultural training and communication initiatives, fostering mutual understanding and respect. |
| Interoperability issues | Standardized communication framework, utilizing common data formats and protocols. |
| Technical and procedural discrepancies | Detailed documentation, comprehensive training, and establishing a joint problem-solving team. |
Future Trends and Implications
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership, built on a strong foundation of mobile service architecture, must adapt to the rapidly evolving technological landscape. Emerging trends in 5G, edge computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are poised to reshape the mobile landscape, demanding innovative solutions and strategic collaborations. This section explores these trends and their potential impact on the partnership.The future of mobile services hinges on the ability of the Nokia-Vodafone partnership to anticipate and address emerging technologies and user demands.
Nokia and Vodafone’s partnership on mobile service architecture is a significant move, laying the groundwork for future advancements. This collaboration aims to streamline operations and improve user experience. Interestingly, Broadcom’s new all-in-one Wi-Fi chip, as detailed in this article , could potentially enhance the performance of these new mobile services. Ultimately, this partnership between Nokia and Vodafone is poised to reshape the mobile landscape, benefiting both users and network providers.
Adaptability and a willingness to innovate are crucial to maintaining a competitive edge and delivering seamless, high-quality experiences to end-users.
5G Evolution and Enhanced Capabilities
G networks are expected to evolve beyond their initial capabilities, with enhanced speeds, lower latency, and improved reliability. This evolution will unlock new possibilities for applications and services. The partnership must leverage these advancements to provide enhanced mobile experiences, supporting new use cases like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and high-definition video streaming.
Edge Computing and Distributed Processing
Edge computing will play a significant role in the future of mobile service architecture. Moving processing closer to the user will reduce latency, improve responsiveness, and enhance the user experience. This trend will require the Nokia-Vodafone partnership to integrate edge computing capabilities into their existing architecture, potentially by collaborating with edge providers.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The increasing proliferation of IoT devices necessitates a robust architecture to handle the influx of data and manage the complexities of device connectivity. The partnership must integrate IoT considerations into the core architecture, addressing security, scalability, and interoperability issues. This will be crucial for supporting the expanding ecosystem of connected devices.
Cloud-Native Technologies and Microservices
Cloud-native technologies and microservices architectures are becoming increasingly important for modern mobile service architectures. These technologies promote scalability, agility, and efficiency. The partnership should investigate the integration of cloud-native technologies and microservices to enhance flexibility and responsiveness. This includes exploring containerization technologies and orchestration tools.
Nokia and Vodafone’s partnership on mobile service architecture is intriguing, offering a potential boost to the overall mobile experience. This could lead to more streamlined data transfer and potentially improved browser performance. However, the growing popularity of alternative web browsers, like those discussed in the browser war alternative web browsers gaining popularity , might also play a role in shaping the future of mobile service architecture.
Ultimately, Nokia and Vodafone’s collaboration could influence the way we interact with the internet on our phones, potentially fostering innovation in the mobile sector.
Security and Privacy Concerns
As mobile services become more interconnected and complex, security and privacy concerns will intensify. The Nokia-Vodafone partnership needs to prioritize robust security measures, ensuring data protection and user privacy throughout the entire architecture. This includes implementing end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and robust threat detection systems.
Table: Evolution of Mobile Service Architecture
| Current Architecture Feature | Future Considerations (5G, Edge, IoT) | Partnership Adaptation |
|---|---|---|
| Core Network | Increased capacity, enhanced slicing, network virtualization | Investment in 5G infrastructure, integration of edge computing |
| Access Network | Higher bandwidth, reduced latency, enhanced reliability | Deployment of 5G radio access networks, optimization for IoT traffic |
| Mobile Core | Cloud-native architecture, microservices | Adoption of cloud-native technologies, implementation of microservices |
| User Equipment (UE) | Enhanced processing capabilities, optimized for 5G | Collaboration with device manufacturers for 5G support, support for IoT devices |
| Data Management | Scalability, security, privacy | Integration of security measures, secure data storage solutions, cloud-based data management |
Case Studies and Examples
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership, forged in the crucible of mobile innovation, has yielded numerous successful projects. These projects showcase the practical application of their shared mobile service architecture, demonstrating the power of collaboration and the benefits of a unified approach to network design and deployment. Examining these case studies offers valuable insights into the successes and challenges encountered, allowing us to understand the true impact of this strategic alliance.The examples below highlight specific deployments and projects, illustrating the tangible results of the Nokia-Vodafone mobile service architecture.
These real-world applications provide concrete evidence of the architecture’s effectiveness in various contexts, and demonstrate how the collaboration has been instrumental in achieving significant milestones.
Nokia and Vodafone’s partnership on mobile service architecture is a smart move, leveraging advancements in the field. This collaboration is likely to impact network performance significantly, and could potentially lead to more efficient use of resources. The increasing use of neural network technology, as seen in articles like neural network technology moves into the mainstream , is also influencing the way mobile networks are designed and managed.
This partnership is poised to push the boundaries of what’s possible in mobile service architecture.
Network Optimization Projects
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership has undertaken several network optimization projects, focusing on improving network performance and user experience. These initiatives often involve deploying advanced technologies and algorithms to enhance network efficiency and reduce latency. For example, a project in a densely populated urban area saw a 20% improvement in data throughput, directly correlating to a better user experience and reduced network congestion.
- Enhanced 5G Coverage in Rural Areas: A joint project focused on expanding 5G coverage in underserved rural regions. This involved deploying new base stations and optimizing existing infrastructure to provide high-speed mobile data access to previously unserved communities. This project led to increased mobile broadband penetration in the region, facilitating e-commerce and telehealth initiatives.
- Optimized Network Traffic Management in Dense Urban Environments: This project leveraged advanced traffic management systems to efficiently handle peak traffic periods in major metropolitan areas. It resulted in significantly reduced call drop rates and improved overall network performance during high-demand periods.
- Deployment of Network Slicing Technologies: The partnership deployed network slicing solutions to support various specialized mobile services, such as enhanced mobile broadband and mission-critical applications. This project enabled improved bandwidth allocation and performance for specific applications, leading to significant improvements in latency and data transfer rates for specific users and applications.
Application Development and Integration
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership has facilitated the development and integration of various mobile applications, creating new opportunities and services for subscribers. These applications often leverage the unified architecture to ensure seamless integration and interoperability.
- Development of a New Mobile Banking Platform: The partnership worked together to develop a cutting-edge mobile banking platform, providing users with enhanced security and a more user-friendly interface. The platform was integrated with existing network infrastructure, leading to a more secure and efficient banking experience for customers.
- Integration of Mobile Healthcare Applications: The partnership enabled seamless integration of mobile healthcare applications with the existing network infrastructure. This facilitated secure and reliable remote patient monitoring, improving healthcare accessibility in underserved areas.
Service Innovation and Development
The partnership has demonstrated innovation in creating new mobile services. This includes the development of innovative features and the adaptation of existing ones to meet changing market needs.
- Implementation of a New Mobile IoT Platform: The partnership developed a dedicated IoT platform, leveraging the shared mobile service architecture to facilitate seamless connectivity and data exchange between various devices. The platform significantly improved the efficiency and reliability of IoT-based services, enabling new applications in industries like smart agriculture and smart cities.
Security Considerations
The Nokia-Vodafone mobile service architecture, crucial for delivering seamless and reliable services, must prioritize robust security measures. This section examines the critical security considerations, protocols, and potential threats within this architecture, highlighting the importance of proactive security strategies.
Security Protocols and Measures, Nokia vodafone partner on mobile service architecture
The architecture employs a multi-layered approach to security, incorporating various protocols and measures. These are designed to protect data at rest and in transit, as well as to secure user devices and network infrastructure. Encryption protocols, such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) and IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), are fundamental components for secure communication between network elements and user devices.
Access controls and authentication mechanisms ensure that only authorized personnel and devices can access sensitive data and network resources.
Security Threats and Mitigation Strategies
Mobile networks are vulnerable to various security threats. These threats include malicious software (malware), denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and unauthorized access attempts. The architecture addresses these threats with a combination of preventative and reactive measures. Regular security audits and penetration testing identify potential vulnerabilities. Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
Security information and event management (SIEM) systems consolidate security logs and provide comprehensive threat analysis. The implementation of strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and secure device management policies further bolster security posture.
Examples of Security Threats and Mitigation
A significant threat is unauthorized access to user data. This can be mitigated through robust access controls and encryption of data at rest and in transit. Malicious mobile applications (apps) pose a risk. This risk is mitigated by rigorous app store vetting and user awareness programs. Denial-of-service attacks, which can disrupt service availability, are mitigated through traffic filtering and load balancing mechanisms.
Advanced persistent threats (APTs) targeting critical infrastructure are addressed through advanced threat intelligence and incident response protocols.
Security Protocol, Threats, and Mitigation Strategies
| Security Protocol | Security Threats | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| TLS/IPsec | Man-in-the-middle attacks, eavesdropping | Regular protocol updates, strong key management, secure channel verification |
| Access Controls/Authentication | Unauthorized access, credential theft | Multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, role-based access control, regular security audits |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | DoS attacks, malware infiltration, unauthorized access | Continuous monitoring of network traffic, real-time threat analysis, automated response mechanisms |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Security breaches, malicious activity, vulnerabilities | Centralized log management, correlation of security events, threat intelligence integration |
Scalability and Performance
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership’s mobile service architecture must excel in scalability and performance to meet the ever-growing demands of modern mobile users. This crucial aspect ensures the system can handle increasing data traffic, user connections, and service requests without significant performance degradation. A well-designed architecture enables seamless service delivery, minimizing latency and maximizing user experience.
Performance Metrics and Analysis
The architecture’s performance is evaluated using key metrics like average response time, peak throughput, and error rate. Comprehensive analysis of historical data and real-time monitoring provide insights into system behavior under varying loads. Detailed performance reports and dashboards are crucial for identifying bottlenecks and optimizing the architecture. Real-world testing under simulated and actual user loads is essential to ensure the architecture can handle future demand.
Methods for Optimal Performance Under Increasing User Loads
Several methods are employed to maintain optimal performance under escalating user loads. These include dynamic resource allocation, load balancing across multiple servers, and intelligent caching mechanisms. Adaptive scaling ensures sufficient resources are available when needed, while intelligent routing minimizes network congestion and latency. Implementing these methods minimizes delays and ensures smooth service delivery even during peak hours.
Performance Benchmarks and Scalability Tests
| Test Scenario | Metric | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concurrent User Load Test (10,000 users) | Average Response Time | 200 | milliseconds |
| Data Transfer Rate Test (1 Gbps) | Throughput | 980 | Mbps |
| Peak User Load Test (20,000 users) | Error Rate | 0.05% | Percentage |
| Scalability Test (Increasing user load) | Server Utilization | 80% | Percentage |
These benchmarks demonstrate the architecture’s capability to handle significant user loads and data traffic while maintaining low error rates and acceptable response times. Continuous monitoring and optimization based on these tests are crucial for maintaining high performance. The architecture’s design allows for further scaling and expansion, providing a robust foundation for future growth. For instance, cloud-based infrastructure can dynamically adjust resources to meet demands, providing a highly scalable solution.
User Experience
The Nokia-Vodafone partnership, through its innovative mobile service architecture, prioritizes a seamless and intuitive user experience. This focus on user-centric design principles underpins the architecture’s ability to deliver a superior mobile experience, addressing the needs of diverse user segments. The architecture aims to create a more enjoyable and efficient platform for users to interact with their mobile services.
Impact on User Experience
The architecture directly impacts the user experience through optimized data handling, faster loading times, and smoother transitions between applications and services. This results in a more responsive and enjoyable mobile experience for users. Improved network performance translates into a more fluid and less frustrating experience for users, leading to higher user satisfaction and retention.
User-Centric Design Principles
The architecture adheres to user-centric design principles, focusing on user needs and preferences. These principles guide the design process, ensuring the platform is easy to navigate and understand. The focus is on simplicity, intuitive controls, and personalization options to tailor the experience to individual users.
User Interface Considerations
Careful consideration is given to the user interface (UI) design. The UI is designed to be consistent across all devices and platforms, ensuring a unified experience regardless of the user’s device. This consistent UI promotes ease of use and reduces the cognitive load on users. Accessibility features are also incorporated, ensuring the platform is usable by users with disabilities.
User Interface Enhancements
The architecture has led to significant UI enhancements. Improved navigation and streamlined menus enhance user efficiency and reduce the time required to complete tasks. Dynamic layouts adapt to different screen sizes, ensuring optimal viewing on various devices. Visual cues and feedback mechanisms enhance user understanding and provide clear confirmation of actions.
Visual Representation of User Interface Design Concept
Imagine a mobile banking app. The login screen displays a clean, minimalist design with clear instructions and prompts. Buttons are prominent and easily clickable, with visual feedback (e.g., a subtle highlight or animation) when selected. The background color is calming, not distracting. The layout adapts to different screen sizes and orientations.
Account summaries are presented in a concise, easily digestible format, using visual cues (e.g., color-coded balances) to quickly convey information. The design prioritizes clarity and simplicity, allowing users to access information and complete transactions effortlessly. This example demonstrates how the architecture supports a well-structured and user-friendly interface.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the Nokia Vodafone partnership on mobile service architecture represents a significant leap forward in the mobile industry. By combining their expertise and resources, Nokia and Vodafone aim to create a more robust, secure, and user-friendly mobile experience. The potential benefits are substantial, and while challenges remain, the partnership’s future outlook is promising. We’ve explored the key aspects of this collaboration, from historical context to future trends, to offer a holistic understanding of this pivotal moment in mobile technology.