Outsourcing Is Good for America A Balanced View
Outsourcing is good for America, but it’s not a simple yes or no. This exploration delves into the complex economic, social, and ethical implications of outsourcing, examining its effects on American jobs, wages, and industries. We’ll analyze the potential benefits and drawbacks, and ultimately, attempt to provide a balanced perspective on the role of outsourcing in the American economy’s future.
The article will consider the impact on job markets, focusing on both job losses and the creation of new, potentially higher-skilled roles. We’ll look at how outsourcing affects wages and salaries across different sectors and analyze the cost savings of outsourcing compared to domestic production. This analysis will also consider the social consequences, potential for income inequality, and the psychological impact of job displacement on workers.
The long-term economic effects, including the role of outsourcing in maintaining global competitiveness, will be discussed, along with potential government policies to mitigate any negative impacts.
Economic Impacts of Outsourcing
Outsourcing, the practice of contracting out tasks to external providers, has profoundly impacted the American economy. While proponents highlight cost savings and increased efficiency, critics point to job losses and potential long-term economic consequences. This exploration delves into the multifaceted effects of outsourcing on American job markets, wages, and the overall economic landscape.The impact of outsourcing on the American job market is complex, exhibiting both job losses and job creation.
Companies often outsource tasks to reduce labor costs, potentially leading to job displacement in specific sectors. Conversely, outsourcing can create new jobs in areas focused on managing and coordinating outsourced tasks. The net effect depends on various factors, including the specific industries involved, the nature of the outsourced work, and the overall economic climate.
Job Market Impacts
Outsourcing frequently affects employment in manufacturing, customer service, and information technology. Companies seeking to reduce operational costs may move production or customer support functions to countries with lower labor costs. This shift can lead to significant job losses in the affected sectors within the US. However, outsourcing also stimulates growth in other sectors, such as technology and management, that provide services or support for these outsourced functions.
The ability of the American workforce to adapt and acquire new skills plays a crucial role in mitigating the negative impacts and capitalizing on the opportunities created by outsourcing.
Outsourcing, while sometimes demonized, can actually be a boon for America. It frees up domestic resources for innovation and allows companies to focus on core competencies. However, the potential for malicious use of these global connections, as highlighted by the MyDoom worm incident – a prime example of the the MyDoom effect crossing the line into terrorism – underscores the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Ultimately, careful management of global partnerships, along with a proactive approach to digital security, is crucial for a healthy, productive outsourcing model.
Wage and Salary Effects
Outsourcing can exert downward pressure on wages in certain industries. When companies outsource tasks, they may reduce the need for highly-skilled labor or employees in specific areas. This competitive pressure can result in lower wages for American workers in these sectors. Conversely, the demand for specialized workers in fields related to managing, coordinating, and overseeing outsourced operations might increase, leading to higher wages in those roles.
The overall impact on wages depends on the industry, the specific skills involved, and the ability of workers to acquire relevant new skills.
Short-Term and Long-Term Impacts
In the short term, outsourcing can lead to significant job losses and potentially lower wages in certain sectors. This can result in economic hardship for workers and communities directly affected. However, in the long term, outsourcing can stimulate economic growth through increased efficiency and cost savings. This can potentially lead to lower prices for consumers and increased investment in other areas.
The long-term impact hinges on the ability of the American economy to adapt, retrain workers, and create new jobs that complement outsourced functions.
Cost Savings Comparison
| Industry | Cost Savings (Outsourcing vs. Domestic Production) |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing (e.g., apparel) | Potentially significant due to lower labor costs in countries like Bangladesh or Vietnam. |
| Customer Service | Substantial savings through lower labor costs in countries like India or the Philippines. |
| Information Technology (e.g., software development) | Potentially substantial due to lower salaries for skilled workers in countries like India or Eastern Europe. |
| Call Centers | Significant cost reductions due to lower labor costs in countries with lower minimum wages. |
| Data Entry | Considerable cost savings, often associated with outsourcing to regions with lower operational costs. |
Note: Cost savings are highly dependent on specific factors such as labor laws, infrastructure, and transportation costs. Furthermore, factors such as quality control, communication, and logistical considerations can influence the final cost of outsourcing.
Social Implications of Outsourcing
Outsourcing, while potentially boosting a nation’s economy, often carries significant social repercussions. The shifting of jobs overseas can have profound effects on American workers, families, and communities, leading to a complex web of challenges that extend far beyond the immediate economic impact. These consequences require careful consideration and potential mitigation strategies.The social implications of outsourcing are multifaceted, impacting not only individual workers but also the fabric of communities and the overall social structure.
This section delves into the negative consequences of this practice, examining the ripple effects on workers, families, and local economies.
Consequences for American Workers and Their Families
The loss of jobs due to outsourcing can create significant hardship for American workers. Layoffs and reduced employment opportunities can lead to financial instability, impacting families’ ability to meet basic needs. Workers often face unemployment, requiring them to adapt to new career paths with potentially lower wages or less desirable working conditions. This economic uncertainty can lead to stress, anxiety, and other mental health concerns.
The displacement of skilled workers in specific industries can create a skills gap, potentially hindering future economic growth and societal progress. Family dynamics can be disrupted as individuals struggle to maintain their standard of living and cope with the emotional toll of job loss.
Impact on Communities and Local Economies
The loss of jobs in specific industries often disproportionately affects communities dependent on those industries. This can lead to a decline in local tax revenue, hindering the ability of communities to fund essential services like schools, hospitals, and public safety. Businesses and local economies can suffer as consumer spending decreases due to job losses and income reduction. Reduced business activity can trigger a vicious cycle, impacting the community’s overall well-being.
Potential Rise in Income Inequality
Outsourcing often concentrates profits in the hands of companies that benefit from lower labor costs overseas, while American workers experience stagnant wages or reduced earnings. This gap in compensation can exacerbate existing income inequality, leading to a greater divide between the wealthy and the working class. The concentrated wealth can further destabilize communities and affect social mobility.
Outsourcing, while sometimes portrayed negatively, can actually boost America’s economy. It allows companies to focus on core competencies and often results in lower consumer prices. However, a recent Symantec report, symantec report puts corporations consumers in crosshairs , highlights the increasing cybersecurity risks associated with outsourcing. This emphasizes the need for robust security measures and responsible practices in global supply chains to mitigate those risks, ensuring that the benefits of outsourcing continue to outweigh the vulnerabilities.
Psychological Effects of Job Displacement
The loss of a job, especially due to outsourcing, can have profound psychological effects on affected workers. Job displacement can lead to feelings of helplessness, frustration, and hopelessness. Workers may experience anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues as they grapple with the uncertainty of their future and the perceived loss of their identity. The disruption can also impact their self-esteem and confidence.
Potential Solutions for Mitigating Negative Social Impacts
Addressing the social implications of outsourcing requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simple economic considerations. A proactive and comprehensive approach is essential to support workers and communities impacted by job displacement.
| Potential Solution | Description |
|---|---|
| Government Support Programs | Expanding and improving unemployment benefits, retraining programs, and job placement services to help displaced workers transition to new careers. |
| Investment in Education and Training | Providing access to quality education and training programs to equip workers with the skills needed for emerging industries and occupations. |
| Community Development Initiatives | Supporting local businesses and economic development initiatives to create new job opportunities and bolster local economies. |
| Wage and Benefit Standards | Promoting fair wages and benefits, and strengthening labor protections to safeguard workers’ rights and ensure fair compensation. |
| International Cooperation | Collaborating with foreign governments to ensure ethical labor practices in countries where outsourcing occurs. |
Outsourcing and National Competitiveness
Outsourcing, the practice of contracting out tasks to external providers, has become a significant aspect of the global economy. For the United States, understanding its role in maintaining competitiveness is crucial. While often viewed with apprehension, outsourcing can be a powerful tool when implemented strategically. This analysis delves into the intricacies of outsourcing’s impact on American global competitiveness, examining the driving factors behind outsourcing decisions, and evaluating the trade-offs between cost-effectiveness and innovation.Outsourcing decisions are complex, driven by a multitude of factors.
These factors range from the search for lower labor costs to access to specialized skills or technologies unavailable domestically. American companies frequently outsource to countries with a lower cost of labor, a key consideration for businesses seeking to optimize their production costs. However, other factors like proximity to markets, political stability, and infrastructure quality also play a significant role in shaping outsourcing choices.
Ultimately, the decision to outsource hinges on a meticulous evaluation of various economic and logistical factors.
Factors Influencing Outsourcing Decisions
Companies consider several factors when deciding to outsource. Cost reduction is often paramount, as it directly impacts profitability. However, access to specialized expertise, particularly in emerging fields like software development or engineering, is another powerful incentive. Additionally, a company might outsource to leverage a partner’s superior infrastructure or access to a larger talent pool. Ultimately, the decision is a careful balancing act between various potential benefits and drawbacks.
- Cost reduction: Lower labor costs in countries like India or the Philippines are a major driver for outsourcing. This allows companies to maintain competitive pricing in the global market. For instance, a US-based call center might find it significantly cheaper to operate from India, while still serving American clients.
- Access to specialized skills: Some countries excel in specific industries. For example, many tech companies in the US outsource software development to countries with a large pool of skilled programmers. This can provide quicker turnaround times and cost-effective solutions to complex projects.
- Infrastructure and technology: Countries with advanced infrastructure, including reliable internet access and efficient transportation networks, are more attractive for outsourcing. These elements support efficient communication and delivery of services, which can positively impact a company’s operations.
Cost-Effectiveness and Innovation in Outsourcing
Outsourcing can significantly reduce operational costs for American companies. By leveraging lower labor costs in other countries, businesses can enhance their profitability and competitiveness. However, the relationship between outsourcing and innovation is more nuanced. While outsourcing can free up resources for innovation by focusing on core competencies, it can also potentially stifle creativity if not managed carefully.
- Cost-effectiveness: A key advantage of outsourcing is the potential for substantial cost savings. Lower labor costs, reduced overhead, and access to specialized expertise can contribute to a more profitable business model.
- Innovation: Outsourcing can facilitate innovation by freeing up internal resources to focus on research and development. However, a complete reliance on external providers might limit a company’s ability to adapt to evolving market demands.
Successful Outsourcing Strategies by American Companies
Numerous American companies have successfully implemented outsourcing strategies. A prime example is Apple, which leverages manufacturing partnerships in countries like China for cost-effective production. Similarly, many large American companies utilize outsourcing to handle customer service, data processing, or other non-core business functions. These examples highlight the potential for outsourcing to enhance operational efficiency and global reach.
- Apple: Apple’s reliance on Foxconn in China for manufacturing exemplifies a successful outsourcing strategy. It allows Apple to produce high-volume products at a competitive cost, keeping prices low for consumers while maximizing profit margins.
- Accenture: A global consulting and technology company, Accenture employs extensive outsourcing strategies. They leverage the expertise of a global network of employees to deliver complex solutions to clients.
Relative Labor Costs in Outsourcing Destinations
The cost of labor varies significantly across countries. This difference is a primary driver for outsourcing decisions. The table below provides a comparative overview of labor costs in selected countries. It’s important to note that these are averages and specific costs can fluctuate based on industry, experience level, and other factors.
| Country | Estimated Hourly Wage (USD) |
|---|---|
| United States | 30-50 |
| India | 5-15 |
| China | 5-15 |
| Philippines | 5-10 |
| Mexico | 10-20 |
Outsourcing and the Future of American Industries: Outsourcing Is Good For America
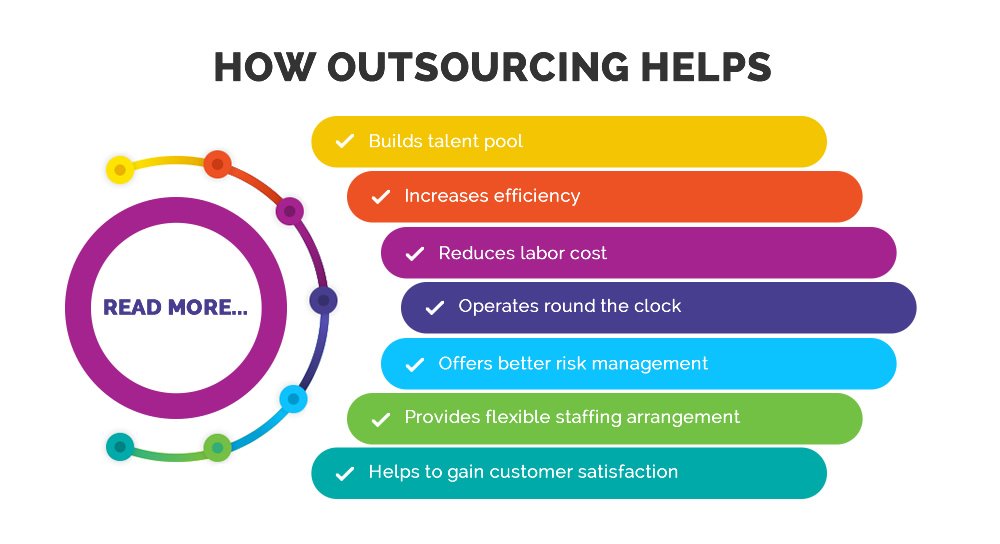
Outsourcing, once a controversial topic, is now a fundamental aspect of the global economy. Its impact on American industries is multifaceted, presenting both challenges and opportunities. Understanding how to leverage outsourcing effectively is crucial for American businesses to thrive in the future. This exploration delves into the potential for emerging industries to leverage outsourcing, identifying sectors where it can be beneficial, and detailing how American companies can adapt to this evolving landscape.The changing global landscape demands adaptability and innovation.
Outsourcing is no longer a threat, but a tool. By strategically employing outsourcing, American companies can enhance their competitiveness, streamline operations, and focus on core competencies. This approach can stimulate innovation and efficiency, potentially leading to increased productivity and economic growth.
Emerging Industries and Outsourcing
Emerging industries, characterized by rapid technological advancement and high growth potential, can significantly benefit from outsourcing. By offloading non-core functions, these industries can allocate resources to research and development, product innovation, and market expansion. This allows them to gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Sectors Benefiting from Outsourcing
American businesses in various sectors can leverage outsourcing to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Specific sectors that stand to gain from outsourcing include software development, customer service, and data processing. Outsourcing these functions can allow companies to access specialized talent at a lower cost, improving productivity and quality.
Outsourcing for Innovation and Efficiency
Outsourcing can be a catalyst for innovation and efficiency in various industries. For instance, by outsourcing research and development tasks, companies can access a wider pool of expertise and accelerate the pace of innovation. This can lead to the development of new products, processes, and services that enhance the company’s competitiveness.
Adapting to a Changing Global Landscape
American companies need to adapt to the global landscape where outsourcing is a prevalent practice. This involves identifying core competencies, streamlining operations, and building strong partnerships with outsourcing providers. By focusing on core strengths, American businesses can leverage outsourcing to enhance their global competitiveness.
Outsourcing can be a real boon for America, fostering economic growth and innovation. Recent developments like the Microsoft appeal denied trial with Lindows set ( microsoft appeal denied trial with lindows set ) highlight how global competition shapes our technological landscape. Ultimately, a flexible approach to outsourcing, especially in sectors like tech, can keep American businesses competitive and resilient in the global market.
Evolving Technology and Outsourcing Decisions
Evolving technology significantly impacts outsourcing decisions and processes. Automation and artificial intelligence are changing the nature of work, impacting the types of tasks that can be outsourced. Companies need to stay abreast of these technological advancements to make informed outsourcing decisions. Outsourcing strategies must be continuously evaluated to ensure they remain aligned with the latest technological developments.
Evolution of Outsourcing Trends (Last Two Decades)
| Decade | Key Trends | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 2000s | Growth of offshore outsourcing, particularly to India and China. | Increased call center operations in India, software development in India. |
| 2010s | Rise of cloud computing and the gig economy, increasing automation. | Growth of remote work, use of cloud-based platforms for outsourcing. |
| 2020s | Increased focus on cybersecurity, ethical considerations in outsourcing. | Rise of nearshoring, emphasis on data privacy, AI-driven outsourcing solutions. |
Ethical Considerations of Outsourcing
Outsourcing, while often presented as a cost-effective strategy, raises significant ethical concerns. The decision to outsource jobs frequently involves a complex interplay of economic pressures, labor standards, and societal values. This section delves into the ethical implications of transferring work to countries with potentially lower labor standards, examining the potential risks and the role ethical considerations play in shaping outsourcing decisions.
Ethical Implications of Lower Labor Standards
Outsourcing to countries with lower labor standards can lead to exploitation of workers. This often manifests in reduced wages, unsafe working conditions, and limited worker protections. The difference in labor laws and enforcement mechanisms between countries can create a gap, making it difficult for companies to ensure ethical treatment of workers in outsourced facilities. A company prioritizing cost savings over worker well-being risks contributing to a system where human rights are compromised.
Potential Risks Associated with Outsourcing to Countries with Poor Labor Practices
Outsourcing to countries with poor labor practices presents several risks. These include reputational damage, legal repercussions, and a potential negative impact on the company’s brand image. Negative publicity surrounding labor abuses can severely impact a company’s public perception and financial performance. Further, in some jurisdictions, companies can face legal action for violating labor standards, even if the violations occur in a foreign country.
A company’s ethical responsibility extends beyond its immediate operations and encompasses the entire supply chain.
Examples of Companies Facing Criticism for Outsourcing Practices
Several companies have faced criticism for their outsourcing practices. Examples include companies that have been accused of using sweatshops or paying workers significantly less than prevailing local wages. The negative publicity generated by these accusations can lead to boycotts, investor divestment, and decreased consumer trust. The resulting damage to reputation can be extensive and long-lasting. These cases highlight the importance of companies considering the ethical implications of their outsourcing decisions.
Role of Ethical Considerations in Shaping Outsourcing Decisions
Ethical considerations should play a crucial role in shaping outsourcing decisions. Companies should conduct thorough due diligence to assess the labor standards and working conditions in the countries where they plan to outsource. This includes evaluating the legal framework, investigating working conditions, and ensuring fair compensation for workers. Ethical outsourcing goes beyond mere compliance; it involves actively promoting fair labor practices throughout the supply chain.
Companies should prioritize worker well-being and human rights alongside economic efficiency.
Ethical Frameworks for Evaluating Outsourcing Decisions
Different ethical frameworks can be used to evaluate outsourcing decisions. These frameworks provide a structured approach to considering the moral implications of outsourcing practices. Understanding the potential consequences of different choices, from a utilitarian perspective to a rights-based perspective, can lead to more informed and ethical outsourcing strategies.
| Ethical Framework | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Utilitarianism | Maximizing overall well-being, considering the benefits and harms to all stakeholders (workers, companies, consumers, communities). |
| Deontology | Focusing on duties and moral obligations, ensuring that outsourcing decisions respect the rights and dignity of all involved. |
| Virtue Ethics | Considering the character and motivations of the company and its decision-makers, striving for honesty, fairness, and integrity in outsourcing practices. |
| Justice Ethics | Ensuring fairness and equity in the distribution of benefits and burdens associated with outsourcing, addressing potential disparities and inequalities. |
Government Policies and Outsourcing
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of outsourcing. These policies can either encourage or hinder the practice, impacting not only businesses’ decisions but also the economic well-being of nations. Understanding these influences is essential for evaluating the long-term implications of outsourcing on national competitiveness and economic growth.Government policies are a powerful tool to influence outsourcing decisions.
They can affect the cost of labor, tax incentives, and regulations, all of which play a significant role in a company’s decision-making process. Favorable tax policies, for example, can make outsourcing more attractive, while stringent environmental regulations might make some outsourcing options less desirable. The presence or absence of regulations addressing worker safety and labor standards also affects the outsourcing equation.
Government Policies Supporting Outsourcing
Government policies can actively support outsourcing by offering tax breaks, subsidies, or streamlined processes for companies seeking to offshore their operations. Countries often implement these incentives to attract foreign investment and boost their economies. For example, tax holidays or deductions for overseas investments are common strategies used to encourage businesses to outsource. These incentives are frequently targeted at specific industries or regions, aiming to revitalize specific sectors or address regional economic disparities.
Government Policies Discouraging Outsourcing
Conversely, governments can implement policies to discourage or limit outsourcing. These measures may include tariffs on imported goods produced by outsourced labor or restrictions on the repatriation of profits earned from overseas operations. Such policies are often motivated by concerns about job losses or national security implications. For example, some nations impose tariffs on products they fear are being produced at lower costs through outsourcing, thus protecting domestic industries.
Government Regulations Addressing Labor Standards
Regulations on labor standards and working conditions in countries where outsourcing is common are essential. These regulations aim to protect workers’ rights, ensure fair wages, and maintain safe working environments. International organizations like the International Labour Organization (ILO) establish minimum standards, and many countries have implemented domestic legislation to enforce these standards. However, the effectiveness of these regulations can vary significantly based on the enforcement mechanisms and the resources available to inspect and monitor working conditions.
Comparison of Outsourcing Policies Across Countries
Different countries adopt various approaches to outsourcing. Some countries, like those in Southeast Asia, have policies that actively promote outsourcing by offering tax incentives and relaxed labor laws. In contrast, some developed nations, like Germany, may prioritize policies that aim to maintain a strong domestic manufacturing sector by imposing regulations that make outsourcing less attractive. This comparison highlights the diverse motivations and priorities driving government policies regarding outsourcing.
Potential Economic Impacts of Different Government Policies, Outsourcing is good for america
| Government Policy | Potential Economic Impacts |
|---|---|
| Tax incentives for outsourcing | Increased foreign investment, potential job creation in the receiving country, but also potential job losses in the home country. |
| Tariffs on outsourced goods | Protection of domestic industries, potential for higher prices for consumers, potential for trade disputes. |
| Stricter labor regulations in outsourcing destinations | Improved working conditions and wages in the outsourcing country, potential for higher production costs and decreased competitiveness of the outsourced company. |
| Investment restrictions on specific industries | Potential to support domestic production and employment, potential to limit economic growth and innovation in specific sectors. |
Outcome Summary

In conclusion, outsourcing presents a multifaceted challenge for America. While it can offer significant economic advantages, such as cost savings and increased global competitiveness, its social and ethical implications cannot be ignored. A balanced approach is crucial, one that acknowledges the potential benefits while actively addressing the potential negative consequences. Ultimately, the future of outsourcing in America hinges on a thoughtful and comprehensive strategy that balances economic gains with social responsibility.
Careful consideration of government policies, ethical frameworks, and worker adaptation strategies is vital to ensuring a positive and sustainable future for American industries in a globalized economy.



