Patch Holes Quickly Microsoft Urges
Patch holes quickly Microsoft urges, highlighting the critical need for timely software updates. This urgency stems from the ever-evolving threat landscape, where vulnerabilities in outdated software can be exploited by malicious actors. Delays in patching can expose systems to significant risks, potentially leading to costly data breaches and operational disruptions. The article explores the rationale behind Microsoft’s push for rapid patching, its impact on businesses and individuals, technical aspects, security considerations, future trends, user experience, and the challenges involved.
Microsoft’s commitment to rapid patching reflects a proactive approach to cybersecurity. The company recognizes the potential for significant harm caused by delayed updates, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage. This proactive stance contrasts with other software companies, and the article will delve into the rationale behind Microsoft’s choices. The article will examine the potential consequences of delayed patching, the technical procedures for quick deployments, and the measures to maintain software integrity during this process.
Microsoft’s Urgency for Quick Patching: Patch Holes Quickly Microsoft Urges

Microsoft’s consistent emphasis on rapid patching reflects a crucial understanding of the ever-evolving threat landscape. The digital world is constantly bombarded with new vulnerabilities, and the window of opportunity for malicious actors to exploit these weaknesses is often narrow. Swift action is paramount in mitigating these threats.The potential risks associated with delayed patching are substantial. Unpatched systems leave organizations and individuals exposed to a wide range of cyberattacks, ranging from data breaches and financial losses to complete system compromise.
Time is a critical factor in these situations, as attackers are constantly refining their techniques and exploiting vulnerabilities before they are addressed.
Potential Risks of Delayed Patching
Delayed patching opens doors for various security threats. Unpatched systems become vulnerable targets for malware, ransomware, and other malicious software. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, disrupt operations, or cause significant financial harm. Critically, delayed patching can also lead to reputational damage and loss of customer trust.
High-Profile Security Breaches
Numerous high-profile security breaches have underscored the importance of timely patching. The WannaCry ransomware attack, for example, exploited a vulnerability in outdated Microsoft Windows systems, causing widespread disruption and significant financial losses. Similarly, the SolarWinds supply chain attack highlighted the critical nature of securing software updates across the entire ecosystem. These examples demonstrate the potential devastation caused by failing to address vulnerabilities promptly.
Microsoft’s urgent call to patch holes quickly is understandable, given the ever-evolving threat landscape. This need for swift action is further emphasized by recent developments, like Microsoft letting developers peek at a glimpse of the future with microsoft lets developers see a little longhorn. While this preview gives us a taste of what’s to come, the immediate priority remains on patching those existing vulnerabilities, a task that remains crucial for security.
Impact on Software Development Cycles
Rapid patching demands a delicate balance within software development cycles. Microsoft needs to strike a balance between providing immediate security fixes and maintaining the stability and functionality of its products. This involves prioritizing security patches and incorporating them into release cycles without compromising the overall quality and user experience. The challenge lies in efficiently identifying and addressing vulnerabilities while maintaining development schedules.
Comparison with Other Software Companies
Microsoft’s approach to patching differs slightly from other software companies, particularly in the frequency of releases. While other companies may prioritize stability over speed, Microsoft often leans towards quicker release cycles to quickly address identified vulnerabilities. This is driven by the sheer volume of users relying on Microsoft’s products and the critical nature of maintaining their security. Some companies might prioritize stability, resulting in less frequent but more comprehensive updates.
Patching Frequency Comparison
| Software Category | Patching Speed | Patching Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Systems (e.g., Windows, macOS) | Generally rapid, often weekly or bi-weekly releases | High |
| Productivity Suites (e.g., Office) | Moderate, typically monthly or quarterly releases | Medium |
| Gaming Software | Variable, depending on game update cycles | Low to Moderate |
| Embedded Systems | Relatively slow, potentially monthly or quarterly releases | Low |
This table provides a general comparison, and specific releases may vary based on the severity and prevalence of vulnerabilities. The frequency and speed of patching are often driven by the criticality of the software and its user base.
Impact on Businesses and Individuals
Rapid patching is crucial for maintaining operational stability and security in today’s digital landscape. Ignoring timely updates leaves systems vulnerable to exploitation, potentially disrupting business operations and exposing sensitive data. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of swift patching on businesses and individuals, exploring the consequences of delayed updates and strategies for ensuring timely software updates.
Impact on Business Operational Efficiency
Proactive patching is paramount for maintaining smooth business operations. Delayed patching can lead to significant disruptions, including system failures, service outages, and decreased productivity. Businesses heavily reliant on software applications, such as financial institutions or e-commerce platforms, face heightened risks if their systems are not regularly updated. These disruptions can result in substantial financial losses and damage to the company’s reputation.
Microsoft’s urgent call for quickly patching holes is certainly timely. While Sony’s continued commitment to the Blu-ray DVD standard, as detailed in sony moves forward with blu ray dvd standard , is commendable, it doesn’t change the immediate need for robust software updates. Ultimately, fast and effective patching remains crucial for maintaining a secure digital landscape.
For instance, a critical vulnerability in a financial software system could expose sensitive customer data, leading to a major security breach with severe financial consequences.
Consequences for Individuals Using Vulnerable Software
Individuals using outdated software expose themselves to a range of risks. Malicious actors can exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain unauthorized access to personal information, including financial data, passwords, and sensitive documents. Such breaches can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and emotional distress. For example, a user with an unpatched web browser might fall victim to a phishing attack, unwittingly handing over their login credentials to cybercriminals.
Challenges Faced by Users in Keeping Systems Updated
Users face numerous challenges in maintaining updated software. These include the complexity of update processes, the potential for conflicts with existing software, and the time required to complete updates. Furthermore, a lack of awareness or technical expertise can hinder the adoption of update procedures. In addition, users might be hesitant to install updates due to concerns about compatibility issues with existing applications or fear of data loss.
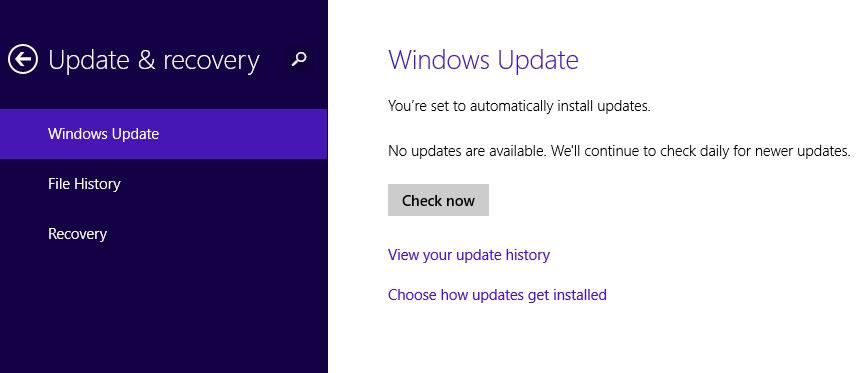
Methods to Ensure Timely Software Updates
Several methods can help users ensure timely software updates. Firstly, enabling automatic updates whenever possible is highly recommended. Secondly, users should regularly check for updates and install them promptly. Thirdly, developing a robust software update schedule can streamline the process. Moreover, staying informed about security advisories and patches is crucial.
Finally, seeking assistance from IT professionals or online communities can address any technical hurdles encountered during the update process.
Examples of How Outdated Software Can Lead to Data Breaches
Outdated software provides fertile ground for malicious actors. Exploiting vulnerabilities in unpatched systems allows attackers to infiltrate networks and steal sensitive information. For instance, an unpatched operating system could be exploited to gain access to internal files, databases, and confidential data. Similarly, a compromised web server with outdated software could lead to a data breach, exposing customer records and financial information.
Vulnerabilities Related to Delayed Patching, Patch holes quickly microsoft urges
The table below Artikels different categories of users and their respective vulnerabilities related to delayed patching.
| User Category | Potential Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|
| Home Users | Identity theft, financial loss, malware infections, compromised personal data |
| Small Businesses | Data breaches, disruption of operations, financial losses, damage to reputation |
| Large Enterprises | Massive data breaches, significant financial losses, operational disruptions, legal repercussions, damage to brand reputation |
| Government Agencies | Compromised sensitive information, potential national security risks, disruption of public services, legal ramifications |
Technical Aspects of Rapid Patching
Staying ahead of evolving cyber threats demands swift and effective patching procedures. Organizations and individuals must adapt to the increasingly rapid pace of software vulnerability discoveries and exploits. This necessitates a deep understanding of the technical intricacies involved in creating, testing, and deploying patches efficiently without compromising software integrity.Rapid patching isn’t simply about speed; it’s about striking a balance between security and stability.
Effective strategies for rapid patching must consider the potential risks and limitations inherent in deploying updates quickly, prioritizing critical vulnerabilities and addressing them effectively.
Patch Creation and Deployment Procedures
The process of creating patches involves meticulous analysis of the affected software components. Programmers identify the specific code segments vulnerable to exploitation and develop corrective measures. These corrections are then integrated into the software’s source code, undergoing rigorous testing to ensure they resolve the vulnerability without introducing new problems. Once validated, the patches are packaged for distribution.
Deployment methodologies range from automated systems that push updates to end-user devices to manual processes for targeted groups or environments. This variation allows for tailored deployments that optimize patch application based on the specific needs of the target system or user group.
Maintaining Software Integrity During Rapid Patching
Ensuring software integrity during rapid patching is a crucial aspect of minimizing disruptions and potential harm. Developers must meticulously test the patches to ensure they don’t introduce new vulnerabilities or negatively impact existing functionalities. This testing often involves a variety of methods, from automated regression tests to manual code reviews and security audits. Rigorous testing protocols and a strong emphasis on code quality are paramount in maintaining software integrity.
Patch Testing Strategies
Thorough testing is vital to ensure the patch addresses the vulnerability without causing unforeseen issues. Different strategies can be employed, including unit tests that isolate specific components, integration tests to verify interactions between different modules, and system-level tests to evaluate the patch’s impact on the entire software environment. Furthermore, penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify any new vulnerabilities introduced by the patch.
The specific testing strategy often depends on the type of software, the nature of the vulnerability, and the resources available. A comprehensive approach incorporating various testing methods ensures that the patch is reliable and secure before deployment.
Patching Methodologies Comparison
Different patching methodologies cater to various needs and environments. Traditional patching methods typically involve downloading and installing updates manually. Modern approaches utilize automated systems to deploy patches across large networks, minimizing the administrative burden. Another approach is targeted patching, focusing on specific user groups or systems, which allows for selective deployment based on the risk level and impact of the vulnerability.
The optimal patching methodology depends on the organization’s infrastructure, security policies, and the specific vulnerabilities being addressed.
Steps Involved in the Patching Process
A clear and concise patching process streamlines the deployment of updates and minimizes disruptions. The process typically starts with vulnerability assessment, identifying the specific vulnerabilities that require patching. Followed by patch creation and testing, ensuring the patch addresses the vulnerability without introducing new problems. Finally, comes the deployment phase, using appropriate methodologies to implement the patch across the affected systems.
This systematic approach minimizes risks associated with patching and ensures timely resolution of security issues.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities is crucial. This stage involves analyzing systems and applications for potential weaknesses. A detailed inventory of software versions and configurations is essential for accurate assessment.
- Patch Creation: This stage focuses on developing the necessary code modifications to address the identified vulnerabilities. The quality of the patch code directly impacts its effectiveness and security.
- Patch Testing: Comprehensive testing is critical to validate the patch’s efficacy and stability. This involves running unit tests, integration tests, and system-level tests to confirm the patch functions correctly and doesn’t introduce new vulnerabilities.
- Deployment: This phase involves deploying the patch to the targeted systems. Deployment methods vary, from automated processes for large-scale deployments to manual interventions for specific systems.
Vulnerability Types Addressed by Recent Patches
Recent patches have addressed a variety of vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities encompass different aspects of software security, including buffer overflows, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting.
| Vulnerability Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Buffer Overflow | A vulnerability that occurs when a program attempts to write data beyond the allocated buffer space. | A program that doesn’t validate the size of input data, leading to the overflow of a buffer. |
| SQL Injection | A technique that manipulates SQL queries to gain unauthorized access to databases. | Inserting malicious SQL code into input fields, altering database queries. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | A vulnerability that allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. | Injecting JavaScript code into a website to steal user data or redirect them to malicious sites. |
Security Considerations
Rapid patching, while crucial for maintaining system security, introduces specific security considerations that must be carefully evaluated. Balancing the need for swift vulnerability remediation with the potential for unintended consequences is paramount. A thorough understanding of the potential risks associated with rapid patching is vital for both businesses and individual users.
Security Implications of Rapid Patching
The rush to apply patches can lead to unforeseen security vulnerabilities if the patching process itself is not thoroughly vetted. Developers may introduce new vulnerabilities during the intense pressure of rapid patching, potentially creating new avenues for malicious actors to exploit. Furthermore, inadequate testing and quality assurance can compromise the integrity of the patch, rendering the system more vulnerable than before.
The goal is to achieve a balance between speed and thoroughness.
Potential for Introducing New Vulnerabilities During Patching
The accelerated pace of patching can sometimes lead to rushed development and testing. Developers may introduce new vulnerabilities in the process of fixing existing ones, creating a complex and potentially dangerous situation. This risk is amplified when there is limited time for comprehensive testing. Thorough code reviews, rigorous testing procedures, and independent audits are essential for mitigating this risk.
Potential Issues Related to Rollback of Patches
Rollback procedures are crucial for maintaining system stability. If a patch introduces critical issues, a robust rollback mechanism is essential. Failure to have a reliable rollback strategy can leave systems in a vulnerable state, potentially exposing them to attacks. Comprehensive testing of rollback procedures is equally vital as the patch itself.
Microsoft’s urgent call for quickly patching holes highlights the ever-present need for robust security measures. Considering IBM’s future strategy, like their push towards grid computing everywhere, IBM’s future strategy grid computing everywhere could potentially offer a more distributed and resilient approach to security, ultimately helping to address these vulnerabilities more effectively. So, while Microsoft urges swift patching, the broader context of evolving technologies like grid computing is key to long-term security.
Impact on User Experience
Rapid patching can affect user experience, leading to unexpected downtime, system instability, or application malfunctions. Careful planning and execution of the patching process are vital to minimize disruptions. Consideration should be given to the potential impact on various user groups and how to communicate the process transparently.
Measures to Ensure Patch Security and Reliability
To ensure patch security and reliability, a multi-faceted approach is necessary. Rigorous testing procedures are essential to identify and address potential issues before deploying the patch. Independent security audits can further validate the patch’s integrity. Furthermore, clear communication with users about the patching process and potential impacts is critical for minimizing disruption and maintaining trust.
Security Risks Associated with Different Patching Speeds
| Patching Speed | Security Risks | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Extremely Fast | High risk of introducing new vulnerabilities, insufficient testing, potential for rollback issues, significant disruption to user experience. | Critical system instability, high risk of exploits. |
| Fast | Moderate risk of introducing new vulnerabilities, potential for limited testing, increased possibility of rollback issues. | Moderate system instability, increased chance of exploits. |
| Moderate | Low risk of introducing new vulnerabilities, adequate testing, manageable rollback issues. | Minimal system instability, reduced risk of exploits. |
| Slow | Low risk of introducing new vulnerabilities, comprehensive testing, minimal rollback issues. | Minimal system instability, low risk of exploits. |
Robust patch management strategies are essential to maintain a secure and reliable system, while balancing speed with thoroughness.
Future Trends and Predictions
The pace of software development and deployment continues to accelerate, demanding ever-faster patching strategies. Anticipating future trends in patching is crucial for organizations to maintain security and stability. This section explores emerging technologies and potential challenges in the rapidly evolving landscape of software updates.
Automated Patching Systems
Automated patching systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, capable of identifying, downloading, and applying security updates across diverse environments. These systems leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence to predict vulnerabilities and prioritize patches, streamlining the patching process and reducing manual intervention. This automation significantly reduces the time and resources needed for patching, especially in large-scale deployments. For instance, companies like SolarWinds and others offer automated patching solutions for various operating systems and applications.
Impact of AI on Patching
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the patching process by enabling proactive vulnerability identification and automated remediation. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify potential vulnerabilities in software before they are exploited, allowing for a proactive approach to security. AI can also analyze system logs and user behavior to detect anomalies that could indicate malicious activity, and even predict potential vulnerabilities based on observed patterns.
This predictive capability is especially beneficial in preventing attacks before they occur.
Challenges of Patching Legacy Systems
Patching legacy systems presents unique challenges. These systems often lack the necessary APIs or compatibility with modern update mechanisms. Compatibility issues with older operating systems and applications, combined with the difficulty of obtaining or updating necessary drivers and support documentation, pose significant obstacles. For example, maintaining support for older operating systems like Windows XP or servers running on outdated hardware can be a major hurdle.
Furthermore, the lack of updated documentation and the limited availability of skilled personnel further complicate the process.
Role of Cloud Computing in Accelerating Patching
Cloud computing plays a significant role in accelerating patching. Cloud-based platforms allow for rapid deployment of patches across numerous servers and virtual machines. This scalability and efficiency are essential for organizations with distributed environments. Moreover, cloud environments often have built-in patch management capabilities, reducing the burden on internal IT teams. Cloud providers typically handle infrastructure management, allowing for quicker and more efficient patching.
A good example of this is using cloud-based virtual machines to deploy and test patches before rolling them out to production servers.
Projected Future Patching Speeds and Frequencies
The speed and frequency of software patching are expected to increase significantly in the coming years. This is driven by the accelerating pace of software development and the rising frequency of security vulnerabilities. Automation and AI-driven tools will play a key role in this trend.
| Year | Estimated Patching Speed (minutes/patch) | Estimated Patching Frequency (patches/month) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 5-10 | 10-15 |
| 2025 | 2-5 | 15-20 |
| 2026 | 1-2 | 20-25 |
Note: These are estimations and may vary depending on the complexity of the software and the security posture of the organization.
User Experience and Adoption
Rapid patching, while crucial for security, can present significant hurdles for users. Understanding these challenges and implementing solutions that prioritize user experience is vital for successful adoption and maintenance of a secure environment. This section delves into the practical aspects of user experience during patching and the importance of user education in promoting timely updates.
Challenges in User Adoption
Users often face a range of challenges when adopting rapid patching. Resistance to change, especially when updates require downtime or disrupt workflows, is common. Furthermore, complex update processes and a lack of clear communication regarding the benefits can deter users from actively participating in the patching process. Technical limitations, such as insufficient system resources or compatibility issues, can also hinder the smooth implementation of patches.
In some cases, users may simply not be aware of the importance of timely updates and the potential consequences of neglecting them.
Improving User Experience During Patching
Microsoft can significantly improve the user experience by implementing several key strategies. Prioritizing a seamless and unobtrusive patching process, with minimal disruption to users’ work, is essential. Offering clear, concise, and readily accessible information about the benefits and necessity of updates is crucial. Providing options for scheduled updates or allowing users to choose update times that minimize disruption is a valuable approach.
Thorough testing of patches in various environments before deployment can minimize unforeseen issues. Moreover, a robust support system, providing readily available help and guidance, is critical in resolving any problems that may arise.
Importance of User Education
User education plays a critical role in fostering a culture of proactive security updates. Educating users about the importance of timely updates and the potential risks associated with outdated software is essential. Clear and engaging communication, utilizing various channels such as email, in-app notifications, and company-wide training sessions, is vital in effectively conveying this message. Examples of good communication strategies include explaining the security vulnerabilities addressed by patches and demonstrating how updates enhance system performance.
Ultimately, informed users are more likely to embrace and support rapid patching.
User-Friendly Patching Interfaces
The design of patching interfaces significantly impacts user experience. Intuitive interfaces with clear instructions, progress indicators, and feedback mechanisms are key to a smooth process. Minimizing the number of steps involved and providing visual cues regarding the status of the updates are crucial. For instance, visually displaying the affected components, outlining the necessary steps, and providing an estimated time for completion will enhance the user experience.
Offering options for different update schedules or allowing users to opt out of updates for specific applications can further enhance control.
Comparison of Patch Notification Methods
| Notification Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | User Impact ||—|—|—|—|| In-app notifications | Immediate alerts, direct action, integrated with existing workflow | Potential for distraction, overload, may not be seen by all users | High user awareness, immediate action || Email notifications | Accessible across devices, detailed information, record keeping | Can be ignored, less immediate, potential for spam | Moderate user awareness, delayed action || System tray notifications | Subtle, unobtrusive, alerts on the desktop | May be missed, less information | Moderate user awareness, delayed action || Scheduled updates | Reduced disruption, planned downtime | Potential for missed urgent updates | High user satisfaction, less disruption || Automated updates | Least user interaction, efficiency | No user control, potential for unforeseen issues | High efficiency, but user needs to be informed about the process|This table highlights the strengths and weaknesses of various notification methods.
Careful consideration of user preferences and the specific needs of the environment is critical in selecting the most appropriate approach.
Closure
In conclusion, Microsoft’s emphasis on rapid patching is a critical aspect of modern cybersecurity. While the urgency necessitates efficient technical procedures and careful consideration of security implications, it also presents challenges in user experience and legacy system compatibility. The future of software patching likely involves a greater degree of automation and AI integration, along with continued efforts to improve user adoption.
Ultimately, this approach balances the need for robust security with the demands of a dynamic threat landscape and evolving user needs.