Solutions to Spyware Plague Enterprise Users
Solutions to spyware plague come to enterprise users, offering a crucial defense against the ever-evolving threat landscape. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of spyware targeting businesses, from the subtle to the sophisticated, and examines the significant financial, reputational, and legal consequences of a breach. We’ll explore practical solutions and mitigation strategies, emphasizing proactive security measures, employee training, and the latest technological advancements.
Understanding the different types of spyware, including keyloggers, remote access trojans, and data theft tools, is critical to developing effective defense strategies. This article further investigates the methods used to deploy and conceal spyware, from social engineering tactics to sophisticated zero-day exploits. Real-world examples of successful mitigation strategies will be analyzed to provide actionable insights.
Introduction to the Spyware Plague in Enterprises
Enterprise spyware is malicious software designed to secretly monitor and collect sensitive information from corporate networks and systems. This insidious threat can compromise confidential data, intellectual property, and operational efficiency, potentially leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage. The sophistication and stealth of modern spyware make detection and removal challenging, requiring proactive security measures.
Defining Enterprise Spyware
Enterprise spyware encompasses a wide range of malicious software specifically targeting corporate environments. It’s designed to infiltrate networks, gather sensitive data, and potentially disrupt operations without the knowledge or consent of authorized personnel. This clandestine activity often goes unnoticed for extended periods, allowing attackers to gather substantial amounts of information before detection.
Types of Enterprise Spyware
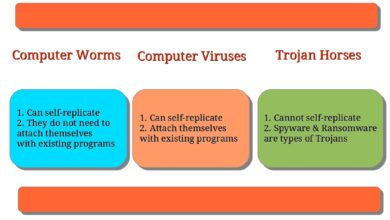
Various types of spyware target different aspects of enterprise operations. Keyloggers record keystrokes, capturing passwords and sensitive information. Spyware Trojans mask their malicious intent by appearing as legitimate applications, enabling covert data exfiltration. Remote access trojans (RATs) grant attackers complete control over infected systems, enabling them to manipulate data, steal credentials, and even install additional malware.
Methods of Deployment and Concealment
Spyware can be deployed through phishing emails, malicious websites, infected software downloads, or compromised networks. Attackers often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated systems or software to gain unauthorized access. Sophisticated techniques like social engineering and spear phishing are used to trick employees into downloading or executing infected files. The concealment of spyware often involves embedding it within seemingly harmless files or hiding its functionality within legitimate programs, making detection extremely difficult.
Real-World Incidents
Numerous incidents highlight the destructive potential of enterprise spyware. For example, a major financial institution suffered significant losses after attackers used spyware to steal customer account details. Similarly, a prominent technology company experienced disruption to its supply chain after spyware was used to compromise its internal communication channels. These incidents underscore the urgent need for robust security measures in the corporate sector.
Spyware Attack Analysis, Solutions to spyware plague come to enterprise users
| Spyware Type | Attack Vector | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Keylogger | Phishing emails, infected software downloads | Stolen passwords, financial losses, compromised intellectual property |
| Spyware Trojan | Malicious websites, infected attachments | Data breaches, reputational damage, loss of customer trust |
| Remote Access Trojan (RAT) | Exploiting vulnerabilities in systems, social engineering | Unauthorized access to sensitive data, system manipulation, data exfiltration |
Impact Assessment and Consequences: Solutions To Spyware Plague Come To Enterprise Users
The insidious nature of spyware extends far beyond simple data theft. A successful spyware breach in an enterprise can trigger a cascade of negative consequences, impacting finances, reputation, legal standing, and even the very core of the organization’s operations. Understanding the full scope of these repercussions is crucial for developing effective preventative measures.
Recent solutions to the enterprise spyware plague are finally hitting the market, offering robust protection against insidious threats. Meanwhile, the recent Microsoft appeal denial regarding the trial with Lindows, detailed in this article , highlights the ongoing complexities in software security. Despite these legal battles, the innovative solutions for combating spyware in enterprise settings show a promising future for secure digital environments.
Financial Implications
Spyware attacks can inflict significant financial damage. Direct costs include the expenses of detection, remediation, and legal proceedings. Indirect costs, often harder to quantify, include lost productivity, disruption of business operations, and potential penalties. For instance, a company experiencing a prolonged system outage due to a spyware infection may incur substantial losses in revenue and contracts. Furthermore, the cost of restoring compromised systems and implementing enhanced security measures can be substantial.
Consider the cost of data recovery, system rebuilding, and the potential for lost future business due to damaged customer trust.
Reputational Damage
A spyware incident can irreparably damage a company’s reputation. Public disclosure of a security breach, especially one involving sensitive customer data, can erode public trust and negatively impact brand perception. Customers may lose confidence in the organization’s ability to protect their information, leading to decreased sales and lost market share. Negative publicity can damage a company’s image and brand, creating long-term challenges to regaining public trust.
Examples abound of companies that suffered severe reputational damage after security breaches, leading to significant market value losses.
Legal and Regulatory Ramifications
Spyware breaches often have severe legal and regulatory implications. Violations of privacy laws, such as GDPR or CCPA, can lead to hefty fines and legal action. Companies must comply with strict data protection regulations and ensure they have robust security protocols in place. Failure to do so can expose them to significant legal penalties. Consider the potential for class-action lawsuits and the associated financial and reputational risks.
Data Loss and Intellectual Property Theft
Spyware poses a direct threat to sensitive data and intellectual property. Compromised systems can lead to the loss of confidential customer information, internal documents, and trade secrets. The theft of intellectual property can have long-term consequences, jeopardizing the company’s competitive advantage. This data loss can be particularly damaging to companies reliant on proprietary algorithms, designs, or research.
Potential Damage Assessment
| Damage Category | Impact Level (Low – High) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | Low | Minor disruption, limited financial loss |
| Financial | Medium | Significant disruption, substantial financial loss, potential loss of contracts |
| Financial | High | Severe disruption, catastrophic financial loss, reputational damage, potential legal action |
| Reputational | Low | Minor damage to reputation, limited impact on public perception |
| Reputational | Medium | Significant damage to reputation, erosion of customer trust, potential loss of market share |
| Reputational | High | Catastrophic damage to reputation, severe loss of public trust, substantial impact on market value |
| Legal | Low | Minor regulatory non-compliance, limited legal consequences |
| Legal | Medium | Significant regulatory non-compliance, potential for legal action, fines |
| Legal | High | Severe regulatory non-compliance, high fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage |
Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
The spyware plague in enterprises necessitates a multi-faceted approach that combines proactive security measures, technological solutions, and robust security protocols. Ignoring these crucial elements leaves organizations vulnerable to significant data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. A proactive strategy is not just about reacting to attacks but preventing them altogether.Proactive security measures are fundamental to mitigating the risk of spyware infiltration.
Enterprise users are finally getting some much-needed relief from the spyware plague. New solutions are emerging, but sometimes, legacy systems need a bit of a refresh, like saving legacy systems with automated software transformation. These modernized approaches can help shore up vulnerabilities and ultimately make the new spyware solutions more effective in protecting sensitive data.
The fight against insidious spyware is ongoing, but the future looks brighter for enterprise security.
This involves understanding potential threats, anticipating vulnerabilities, and implementing preventative controls. By taking these measures, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of a successful attack and minimize the damage if one does occur.
Importance of Proactive Security Measures
Proactive security measures are crucial for thwarting spyware attacks. They involve a holistic approach that encompasses employee training, system hardening, and regular security assessments. These measures are not simply reactive; they are designed to anticipate and prevent threats before they materialize. A proactive approach reduces the attack surface and strengthens the overall security posture of the organization.
Technological Solutions for Spyware Prevention
Various technological solutions are available to prevent spyware infections. These include robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and antivirus software. These tools form the first line of defense against malicious software, including spyware. Employing these technologies can dramatically decrease the chances of a successful spyware attack.
Endpoint Security Tools and Effectiveness
Endpoint security tools are essential for protecting individual devices from spyware. These tools typically include antivirus, anti-malware, and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). The effectiveness of endpoint security tools varies significantly depending on the specific tool, the sophistication of the spyware, and the diligence of the user. Regular updates and proactive scanning are crucial to maintaining effectiveness. Choosing tools that are regularly updated and offer real-time protection is critical.
Security Protocols for Detecting and Removing Spyware
Effective security protocols are vital for detecting and removing spyware once it has infiltrated the system. These protocols include regular system scans, monitoring user activity, and establishing clear incident response procedures. Comprehensive logging of system events and user actions helps in identifying suspicious activity and potential spyware infections. This information allows for quick identification and removal of spyware.
Preventive Measures and Incident Response Plans
Preventive measures and incident response plans are critical for preventing and mitigating spyware attacks. Security awareness training for employees is paramount in educating them about the dangers of spyware and phishing attempts. Incident response plans should be clearly defined and practiced regularly to ensure a swift and effective response to any security incident.
Security Awareness Training
Security awareness training empowers employees to recognize and avoid spyware threats. This includes training on phishing emails, suspicious websites, and social engineering tactics. This knowledge empowers employees to become a crucial part of the defense against spyware.
Incident Response Plans
Incident response plans detail the procedures for handling spyware incidents. This includes steps for isolating infected systems, containing the spread of malware, and restoring systems to a healthy state. Having a well-defined incident response plan is critical for minimizing the impact of a spyware attack.
Comparison of Anti-Spyware Software Solutions
| Software | Cost | Features | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sophos Endpoint Protection | Variable, based on licensing | Real-time protection, threat intelligence, remediation tools | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| Bitdefender GravityZone | Variable, based on licensing | Multi-layered security, cloud-based protection, advanced threat analysis | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| McAfee Endpoint Security | Variable, based on licensing | Endpoint detection and response (EDR), threat prevention, data loss prevention (DLP) | Windows, macOS, Linux |
Note: Pricing and features can vary based on the specific license or subscription plan. Compatibility is also subject to the specific version and operating system.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs

Employee training is not just a box to check; it’s a critical line of defense against the spyware plague. Effective training empowers employees to recognize and avoid threats, significantly reducing the risk of successful attacks. By understanding the tactics employed by malicious actors, employees can become proactive safeguards against the insidious nature of spyware.A robust security awareness program is more than just a lecture; it’s an ongoing, interactive process that fosters a culture of security consciousness within the enterprise.
It’s about equipping employees with the knowledge and skills to identify potential threats and react appropriately. This approach goes beyond simply memorizing policies; it encourages critical thinking and responsible behavior in the digital realm.
Enterprise users are finally getting some much-needed relief from the spyware plague, with new solutions emerging. This progress is closely tied to advancements in artificial intelligence, especially in areas like artificial caregivers. These AI-powered assistants are proving surprisingly adept at tasks previously only performed by human caregivers, demonstrating the potential of AI to improve on the real thing.
artificial caregivers improve on the real thing. These advancements, in turn, are freeing up resources and attention for IT teams to focus on patching and preventing future spyware attacks. Ultimately, this helps to strengthen enterprise security overall.
Components of an Effective Security Awareness Program
A comprehensive security awareness program incorporates various elements to build a strong defense against spyware. These elements work together to reinforce learning and foster a security-conscious culture. Key components include:
- Regular Training Sessions: Scheduled training sessions, delivered in engaging formats, are essential to keep security awareness top of mind. These sessions can cover a wide range of topics, from identifying phishing emails to understanding the risks of social engineering tactics.
- Interactive Exercises and Simulations: Hands-on exercises and realistic simulations provide a practical understanding of how spyware attacks manifest. For example, simulated phishing emails can help employees recognize subtle indicators of fraudulent communication. These interactive elements make learning more engaging and memorable, allowing employees to apply their knowledge in a risk-free environment.
- Personalized Learning Paths: Tailoring training to specific roles and responsibilities ensures employees receive the most relevant information. For instance, customer service representatives might benefit from specialized training on recognizing suspicious customer requests.
- Continuous Reinforcement: Security awareness isn’t a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process. Regular reminders, updates, and new training modules maintain a high level of vigilance. This could include short videos or email reminders highlighting common threats.
Phishing Awareness Training
Phishing is a prevalent method used by spyware perpetrators to gain access to sensitive information. Training programs must emphasize the importance of scrutinizing emails, links, and attachments. Employees should be equipped with the ability to identify red flags and report suspicious activity promptly.
- Recognizing Phishing Tactics: Training should highlight common phishing techniques, such as spoofed email addresses, urgent requests, and fraudulent links. This includes examples of different types of phishing attempts, such as “CEO fraud,” “whaling,” and “spear phishing.”
- Safe Email Practices: Employees need clear guidelines on how to safely handle emails, including verifying sender information, checking for grammatical errors, and avoiding clicking on suspicious links. They should be aware of the importance of not revealing personal information or passwords in unsolicited emails.
- Reporting Procedures: Establishing clear reporting procedures for suspected phishing attempts is crucial. Employees should know how to report suspicious emails and websites without hesitation. This includes the process of forwarding emails to designated IT security teams or using designated reporting portals.
Training Module Design
Effective training modules combine theoretical knowledge with practical application. Modules should include interactive elements, such as quizzes, scenarios, and simulations.
| Module | Target Audience | Key Learning Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| Recognizing Phishing Attempts | All employees | Identify common phishing tactics, recognize suspicious emails and links, and know how to report suspicious activity. |
| Understanding Spyware Threats | IT staff, security personnel, and all employees | Understand different types of spyware, recognize common indicators of infection, and understand the impact of spyware on company data. |
| Safe Internet Browsing Practices | All employees | Identify potentially harmful websites, recognize suspicious downloads, and understand safe browsing practices. |
| Social Engineering Awareness | All employees | Recognize social engineering tactics, understand how attackers manipulate individuals, and learn to resist pressure and manipulation. |
Technological Advancements and Future Trends
The spyware landscape is constantly evolving, requiring a proactive and adaptable security posture. Emerging technologies are crucial in detecting and preventing these threats, and understanding future trends in cybersecurity is paramount for enterprise protection. This section explores the innovative approaches to spyware prevention, emphasizing the importance of continuous adaptation to evolving techniques.The fight against enterprise spyware necessitates a dynamic approach that keeps pace with the constant evolution of malicious actors.
New detection methods and preventative measures must be continually developed to address emerging threats. This requires a commitment to proactive security, encompassing a layered defense system that combines technical solutions with human factors.
Emerging Technologies for Enhanced Detection and Prevention
Advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence are significantly impacting spyware detection and prevention. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify subtle anomalies indicative of malicious activity, often outpacing traditional signature-based detection methods. This allows for quicker identification and response to threats, reducing the potential damage from a successful attack.
Future Trends in Enterprise Cybersecurity
Several trends are shaping the future of cybersecurity, impacting enterprise spyware. These include the increasing sophistication of attacks, the expanding attack surface due to the proliferation of connected devices, and the rise of cloud-based infrastructure. Proactive measures are essential to anticipate and address these trends, focusing on threat intelligence gathering, vulnerability management, and incident response.
Importance of a Proactive Security Posture
A proactive security posture is crucial for mitigating the risks associated with enterprise spyware. This involves anticipating potential threats, implementing robust preventive measures, and developing incident response plans. Organizations must view cybersecurity as an ongoing process, not a one-time event.
Innovative Approaches to Spyware Prevention
AI-powered threat detection is a prime example of an innovative approach. These systems can analyze user behavior, network traffic patterns, and system logs to identify suspicious activities that might indicate spyware infection. Furthermore, advanced encryption techniques and secure coding practices are crucial for preventing the exploitation of vulnerabilities that could be leveraged by spyware.
Evolution of Spyware Techniques and Continuous Adaptation
Spyware techniques are continuously evolving, adapting to new security measures. Traditional methods like keyloggers are being replaced by more sophisticated techniques, leveraging social engineering and zero-day exploits. Therefore, organizations need to stay updated on the latest threats and adapt their security strategies accordingly.
Timeline of Spyware Evolution and Countermeasures
| Year | Spyware Technique | Countermeasure |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | Simple keyloggers, data stealers | Basic anti-virus software, firewalls |
| 2000s | More sophisticated keyloggers, trojans, dialers | Intrusion detection systems, anti-spyware tools |
| 2010s | Advanced rootkits, malware-as-a-service, social engineering | Behavioral analysis, machine learning-based detection, multi-layered security |
| 2020s | AI-powered attacks, targeted attacks, supply chain attacks | AI-powered threat intelligence, Zero Trust security, advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) |
Case Studies of Successful Spyware Mitigation
The relentless proliferation of spyware poses a significant threat to modern enterprises. Understanding how other organizations have successfully countered these attacks offers invaluable insights and practical strategies for proactive defense. These case studies illuminate the critical steps involved in preventing, detecting, and responding to spyware incidents.Successful mitigation of spyware attacks hinges on a multifaceted approach. This involves not only technological solutions but also robust security awareness training and a well-defined incident response plan.
Learning from past successes empowers organizations to adapt and strengthen their defenses against evolving threats.
Real-World Examples of Successful Mitigation
Numerous enterprises have implemented effective strategies to combat spyware, demonstrating the feasibility of robust protection. These cases highlight the importance of a proactive approach encompassing various security layers.
- Company A, a large financial institution, experienced a targeted spyware attack aimed at stealing sensitive customer data. Their multi-layered security approach, including advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, network segmentation, and robust user authentication protocols, prevented the attackers from gaining complete access to their systems. They quickly identified the compromised systems and contained the breach, minimizing the impact on operations and customer data.
They also conducted a thorough review of their security policies and implemented enhanced user training on recognizing phishing attempts, thus reducing the risk of future attacks.
- Company B, a healthcare provider, faced a situation where spyware was used to exfiltrate patient records. Their response involved a rapid incident response team that immediately isolated the affected systems, initiated forensic analysis, and notified affected patients. A critical element in their mitigation strategy was the implementation of regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities before they were exploited.
Furthermore, they strengthened their data encryption protocols and implemented strict access controls to prevent future data breaches.
Stages of Incident Response for Spyware Attacks
A well-defined incident response plan is crucial in mitigating the damage caused by spyware. A standardized process allows for swift and coordinated action.
- Detection: Early detection is paramount. Implementing intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools helps identify suspicious activities indicative of spyware infections. This stage involves monitoring network traffic, system logs, and user behavior for anomalies.
- Containment: Once spyware is detected, immediate containment is necessary. This involves isolating infected systems from the network to prevent further data exfiltration or damage. The goal is to limit the extent of the compromise.
- Eradication: This stage focuses on removing the spyware from affected systems. This may involve using specialized software or manual removal techniques. Carefully documented procedures are essential to avoid unintended consequences.
- Recovery: This involves restoring systems to their pre-infection state. Data backups play a crucial role in recovering lost or compromised data. System hardening and patching are essential to prevent reinfection.
- Post-Incident Analysis: After the incident is resolved, conducting a thorough post-incident analysis is vital. This involves identifying the root cause of the attack and implementing preventative measures to avoid similar incidents in the future. The lessons learned should be integrated into security policies and procedures.
Summary of Case Studies
| Organization | Type of Spyware | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | Keylogger, data exfiltration | EDR tools, network segmentation, enhanced user training, security audits |
| Company B | Data theft (patient records) | Rapid incident response, forensic analysis, data encryption, access controls, security audits |
Final Review

In conclusion, safeguarding enterprise environments from spyware requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing proactive security measures, robust employee training, and continuous adaptation to emerging threats. The solutions presented in this article equip businesses with the knowledge and tools necessary to combat the spyware plague, protect sensitive data, and maintain a strong security posture. By combining technological advancements with employee awareness, organizations can build resilient defenses against future attacks and ensure the long-term success of their operations.