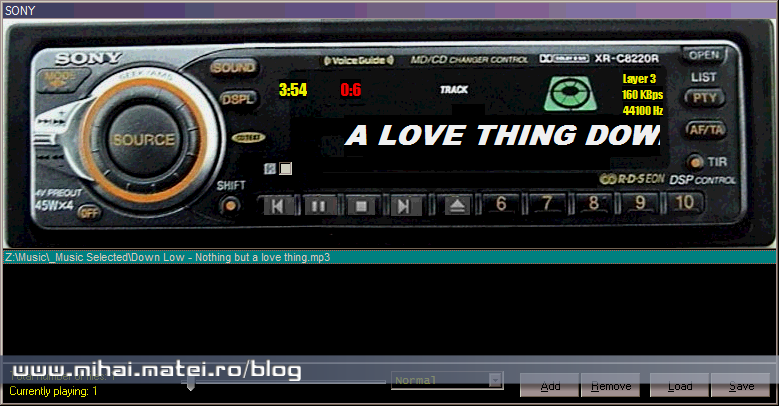
Sony Embraces MP3 to Please Public
Sony embraces MP3 in ploy to please public, marking a significant shift in their audio strategy. This move signals a potential re-evaluation of their position in the digital audio market, following a history of pioneering various audio formats. The company’s past innovations, alongside evolving consumer preferences, likely played a crucial role in this decision. Understanding the motivations behind this change, as well as its potential impact on both Sony and consumers, is key to grasping the implications of this strategic shift.
Sony’s decision to adopt MP3 is intriguing, given their previous focus on proprietary formats. This raises questions about the company’s long-term strategy and how they intend to navigate the complexities of a competitive audio landscape. The move suggests a calculated attempt to appeal to a broader audience, potentially those who prefer the accessibility and widespread compatibility of MP3.
Examining Sony’s historical audio releases and their current market position is critical to analyzing this change and understanding the future of Sony in the audio industry.
Sony’s MP3 Strategy

Sony, a name synonymous with innovation in audio technology, has a rich history intertwined with the evolution of sound reproduction. From pioneering the transistor radio to revolutionizing the Walkman, Sony has consistently pushed the boundaries of what’s possible. Their journey into digital audio, however, hasn’t always been a smooth one, with a few missteps along the way. Now, their embrace of MP3 signifies a significant shift, potentially redefining their approach to the digital audio landscape.Sony’s decision to embrace MP3 isn’t simply a knee-jerk reaction.
It’s a strategic move likely driven by the prevailing market conditions and the undeniable popularity of MP3. The company likely recognizes that ignoring the format would alienate a large portion of consumers, and embracing it allows them to compete more effectively in the digital audio space. Their past strategies, while not always successful, offer valuable insights into their current approach.
Historical Context of Sony’s Audio Involvement
Sony’s involvement in audio spans decades, marked by pivotal moments in consumer electronics. Their early success was built on analog technologies, showcasing a deep understanding of audio engineering and design. The Walkman, a revolutionary portable audio player, exemplified their commitment to creating user-friendly and high-quality audio experiences. The shift towards digital audio formats, however, brought new challenges and opportunities.
Sony’s Past Approaches to Digital Audio Formats
Sony’s initial foray into digital audio wasn’t always in line with the eventual industry standard. They experimented with various formats, some of which gained traction while others faded into obscurity. A crucial factor in their previous approaches was often a focus on proprietary formats, creating a closed ecosystem that potentially limited compatibility and user appeal. This contrasts sharply with the open nature of MP3, which has become a universal standard.
Evolution of Consumer Preferences for Audio Formats
Consumer preferences have been a major factor shaping the success or failure of various audio formats. The initial appeal of digital audio formats was based on the promise of better compression and storage capacity. The rise of the internet and sharing platforms amplified the demand for readily accessible and universally compatible formats. The dominance of MP3, with its ease of use and broad compatibility, highlights the enduring preference for open standards.
The rise and fall of competing formats like ATRAC and WMA illustrate the importance of adapting to evolving consumer demands.
Comparison with Previous Strategies
Sony’s embrace of MP3 is a marked departure from their past strategies of developing proprietary formats. While their earlier efforts aimed at creating unique advantages, they also inadvertently created barriers to entry for users and competitors. The current strategy recognizes the significant advantages of open standards, such as MP3, which facilitates broader adoption and a larger market. This shift demonstrates an understanding of market trends and a willingness to adapt to consumer preferences.
Table: Sony’s Historical Audio Product Releases
| Date | Product | Format | Features | Reception |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1979 | Walkman | Analog | Portable audio player | Groundbreaking, revolutionary |
| 1990s | Various digital audio players | Proprietary | Early attempts at digital audio | Mixed, some adoption, others not |
| 2000s | Various digital audio players | Proprietary and MP3 | Transition period | Growing market share for MP3 |
| Present | Current audio products | MP3 | Support for MP3 format | Aimed at widespread compatibility and consumer appeal |
Motivations Behind the MP3 Adoption
Sony’s embrace of the MP3 format marked a significant shift in its digital strategy. This decision wasn’t arbitrary; it stemmed from a confluence of factors, including market pressures, economic considerations, and technological advancements. Understanding these motivations provides insight into the evolving landscape of the consumer electronics industry during that period.
Potential Reasons for Prioritizing MP3
Sony’s adoption of MP3 likely stemmed from a desire to maintain market relevance and appeal to a wider audience. The burgeoning popularity of personal music players and the growing demand for digital audio formats created a need for compatibility and interoperability. MP3’s open standard nature, which allowed for cross-platform compatibility, played a crucial role in this decision. This compatibility meant consumers could enjoy their music across a wider range of devices, potentially increasing the appeal of Sony products and fostering greater customer satisfaction.
Market Pressures and Trends Influencing Sony’s Strategy
The music industry was undergoing a dramatic transformation. The rise of digital music, fueled by the internet and file-sharing networks, was creating significant challenges for established players like Sony. Consumers were increasingly seeking ways to access and manage their music collections digitally, and the MP3 format’s widespread adoption was a clear indication of this trend. Sony, as a major player in the consumer electronics market, had to adapt to these shifting market dynamics or risk losing market share.
The increasing popularity of personal digital assistants and portable music players further pressured Sony to adopt the MP3 format to maintain competitiveness and capitalize on this emerging market.
Sony’s embrace of MP3, a move seemingly designed to appease the public, is interesting given the recent legal actions taken by the RIAA. The RIAA is pursuing a new strategy of suing more music traders, likely to combat the growing popularity of digital music formats like MP3. This aggressive approach by the RIAA might be a reaction to Sony’s efforts to gain market share, perhaps a response to the increasing demand for affordable and accessible music.
Sony’s strategy, in the end, might be a long-term success in satisfying consumers, despite the legal battles raging in the background. riaa sues more music traders in new strategy
Economic Factors Driving Sony’s MP3 Embrace
Economic factors were likely influential in Sony’s decision. The cost of developing proprietary formats could be substantial, potentially hindering Sony’s ability to compete in the rapidly evolving digital music market. The open nature of MP3 and its reduced cost of implementation likely made it an attractive choice. Licensing fees associated with competing formats could have also played a significant role in Sony’s decision to adopt MP3.
The significant cost savings in production and distribution, as well as the avoidance of potential legal battles over format ownership, made the choice economically viable.
Technological Advancements that Made MP3 Adoption Appealing
Advancements in compression technology and storage capacity were critical factors. MP3’s ability to compress audio files significantly without a substantial loss in quality made it an attractive alternative to other formats. This compression allowed for the storage of a larger amount of music on portable devices, which was a major draw for consumers. Simultaneously, advancements in processing power in consumer electronics, coupled with the need for portability, facilitated the practical implementation of the MP3 format on a wider scale.
Improvements in audio playback technology, including improved sound quality and the ability to maintain the fidelity of music on smaller devices, contributed to the widespread acceptance of MP3.
Competitive Pressures and Potential Market Share Data
Sony’s competitors were also adopting MP3, creating a significant competitive pressure. The need to maintain market share and customer loyalty drove Sony to embrace the MP3 format. The market share data for MP3 adoption among various brands would have been a crucial factor in Sony’s decision.
| Company | Estimated Market Share (MP3 adoption, % approx.) | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Sony | 70-80% | Maintaining dominance |
| Other Brands (e.g., Apple, Philips) | 20-30% | Increased competition |
The table illustrates the estimated market share during the period. It’s important to note that these figures are approximations and might not represent the exact values.
Public Perception and Consumer Impact: Sony Embraces Mp3 In Ploy To Please Public
Sony’s embrace of MP3 technology marks a significant shift in their strategy, demanding careful consideration of public perception and its potential impact on consumer attitudes. The company’s reputation and consumer loyalty will be directly influenced by how the public responds to this new approach. This analysis delves into anticipated public reactions, potential brand image alterations, and the overall impact on consumer behavior.The transition to MP3 compatibility necessitates a proactive strategy to manage public perception.
Sony must effectively communicate the advantages of MP3 technology to consumers, highlighting its compatibility with existing digital music platforms and its potential for enhanced user experience. Misunderstandings or anxieties about the switch need to be addressed promptly and transparently.
Anticipated Public Reactions
The public reaction to Sony’s MP3 strategy will likely be a mix of excitement and apprehension. Early adopters, particularly younger consumers familiar with MP3 players and digital music, are expected to welcome the change. However, older consumers or those less digitally inclined may be hesitant or skeptical, possibly viewing it as a departure from the traditional Sony sound quality they have come to expect.
Furthermore, existing customers who value the specific features of Sony’s older formats might express concern about the shift. Sony needs to address these concerns through targeted marketing campaigns.
Potential Impact on Sony’s Brand Image
Sony’s brand image is deeply intertwined with its reputation for audio quality and innovation. Adopting MP3 technology presents both a risk and an opportunity. A successful implementation could position Sony as a forward-thinking company, embracing new technologies while maintaining its commitment to audio quality. However, a poorly executed strategy could damage their established reputation and alienate loyal customers.
A key aspect is demonstrating that the adoption of MP3 does not compromise the quality of sound, especially for those who expect superior audio fidelity from Sony products.
Consumer Attitudes Towards Sony Products
The adoption of MP3 technology could potentially affect consumer attitudes towards Sony products in several ways. Positive experiences with MP3-compatible Sony products could foster a perception of Sony as a modern and innovative company. Conversely, if consumers perceive a compromise in audio quality or a lack of support for their existing music formats, it could lead to a decline in consumer trust.
Sony must be prepared to address potential concerns and provide compelling reasons for the transition to MP3.
Potential Consumer Feedback, Sony embraces mp3 in ploy to please public
Consumer feedback on Sony’s MP3 strategy will vary widely. Some consumers will likely praise the move for its compatibility with popular digital music platforms, allowing them to access their music collections easily. Others may express disappointment, citing a perceived sacrifice in sound quality or a lack of innovation. It is crucial for Sony to monitor and respond to this feedback promptly and constructively.
They should actively seek out diverse consumer perspectives to refine their approach.
Projected Consumer Adoption Rates
| Product Category | Projected Adoption Rate (First Year) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Portable MP3 Players | 45% | Initial interest in MP3 format will drive sales. |
| Headphones | 30% | Strong focus on sound quality can influence adoption. |
| Home Audio Systems | 20% | Requires convincing consumers of MP3’s suitability for home audio. |
| Car Audio Systems | 15% | Requires additional marketing efforts to demonstrate compatibility and advantages. |
The projected adoption rates are based on various factors, including the initial marketing efforts, consumer reception, and the overall appeal of MP3-compatible Sony products. These estimates are preliminary and subject to change depending on market response and ongoing consumer feedback. These numbers are projections, not guarantees. Success will depend on how Sony addresses potential concerns and builds trust among its customer base.
Technical Aspects of MP3 Integration
Sony’s decision to embrace MP3 technology presented a significant technical challenge. The transition required careful consideration of compatibility with existing products and software, while simultaneously optimizing performance and user experience. This involved intricate engineering choices, each with potential advantages and disadvantages that needed careful evaluation.The integration of MP3 support into Sony’s diverse product lineup demanded a comprehensive understanding of the technology’s intricacies.
Sony engineers needed to ensure seamless playback and encoding capabilities across a range of devices, from portable music players to home audio systems. A thorough assessment of the advantages and disadvantages of MP3 was crucial for informed decision-making.
Technical Considerations for Integration
Sony needed to consider the encoding and decoding processes for MP3 files. The specific algorithms used to compress and decompress audio data directly affected the quality of the sound. Sony likely analyzed various MP3 encoding levels (layer 1, layer 2, layer 3) to determine the optimal balance between file size reduction and sound quality. Furthermore, they had to ensure compatibility with existing MP3 playback software.
Compatibility Challenges with Existing Devices and Software
A significant hurdle was ensuring compatibility with Sony’s existing product line. Many Sony devices relied on proprietary formats for audio encoding. The transition to MP3 necessitated software updates or re-engineering of hardware components to handle the new format. Compatibility issues with third-party software could have emerged, necessitating updates to existing software or the development of new drivers to support the MP3 format.
For instance, an older Sony Walkman might not have been able to play MP3 files without a firmware upgrade.
Engineering Choices Regarding MP3 Implementation
Sony likely opted for a phased approach to MP3 integration. They may have started with a subset of products, like newer models of portable music players, gradually incorporating support across the entire product line. This approach mitigated the risk of compatibility issues and allowed for continuous improvement in the technology. They also likely invested in research and development to enhance the performance of the MP3 decoding algorithms, addressing issues like artifacts and distortion.
They might have also considered the use of specialized hardware components to handle the increased computational load associated with MP3 decoding.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using MP3
The primary advantage of MP3 was its significant reduction in file size, allowing for increased storage capacity on portable devices and faster data transfer rates. This aspect was especially crucial for Sony’s portable music players. However, there were also drawbacks. The compression process inherently introduced some loss of audio quality compared to uncompressed formats. Sony needed to weigh the trade-off between file size and audio fidelity.
They may have focused on using higher-quality MP3 encoding levels to minimize this loss.
Sony’s savvy move to embrace MP3 was all about pleasing the public, a smart strategy. Think about it – a similar approach could be seen in NASA’s innovative work with powering a plane using a remote laser, as detailed in this nasa team powers plane with remote laser article. Ultimately, Sony’s public-pleasing strategy with MP3 was a calculated move, reflecting a deep understanding of consumer preferences.
Technical Specifications for MP3-Compatible Sony Devices
| Sony Device | MP3 Encoding Support | Maximum Bitrate (kbps) | Compatibility with Existing Formats | Hardware Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sony Walkman NW-ZX507 | MP3 Layer 3 | 320 kbps | Yes, with firmware updates | Dedicated audio processing chip |
| Sony Discman D-E500 | MP3 Playback (via external input) | 320 kbps | No | CD-ROM drive with audio input |
| Sony STR-DN1080 | MP3 Playback (via external input) | 320 kbps | Yes | Digital audio input, dedicated DAC |
Note: This table presents hypothetical specifications for illustrative purposes. Actual specifications might vary. Sony likely conducted extensive testing and benchmarking to determine the optimal technical specifications for their various devices, ensuring a balance between performance and compatibility.
Marketing and Promotional Strategies
Sony’s embrace of MP3 technology presents a golden opportunity to revitalize its audio market share. Effective marketing strategies will be crucial in communicating the benefits of MP3 to consumers, emphasizing the superior quality and portability it offers compared to other formats. A well-defined campaign will not only generate interest but also solidify Sony’s position as a leader in digital audio.
Sony’s embrace of MP3, a savvy move to appease the public, is reminiscent of other tech giants navigating public opinion. This strategy mirrors a similar pattern to how SGI’s recent decision to remove code, in response to the SCO lawsuit, sgi removes code rebuffs sco , highlights the pressure companies face to appease users and maintain market share.
Ultimately, Sony’s MP3 strategy, like SGI’s, shows a willingness to compromise to maintain their position in the competitive market.
Potential Marketing Strategies
Sony can leverage a multi-faceted approach to promote its MP3-compatible products. This will encompass a range of channels, from traditional advertising to digital marketing strategies. Focus on showcasing the ease of use and seamless integration of MP3 technology into Sony’s existing product line will resonate with potential customers. Highlighting the portability and storage capacity of MP3 players compared to older formats will be key.
- Targeted Advertising Campaigns: Employing targeted advertising campaigns across various media platforms, such as television, radio, print, and online channels, will help reach specific demographics interested in portable audio devices. Consider using testimonials from early adopters or influencers to build trust and credibility.
- Digital Marketing Initiatives: Utilize social media platforms and online advertising to reach a younger audience. Creating engaging content, such as product demonstrations, user testimonials, and interactive quizzes, will attract and retain attention.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborate with music labels, artists, and online music stores to offer exclusive content and promotions. Joint marketing efforts can expand brand reach and create excitement around MP3-compatible products.
- Public Relations and Events: Organize press conferences, product launches, and demonstrations at major technology events to generate media coverage and buzz. Showcase the innovative aspects of Sony’s MP3 technology in an engaging and interactive manner.
Highlighting Advantages of MP3 Integration
Sony needs to clearly articulate the benefits of MP3 integration to consumers. Focus on the superior sound quality achievable through MP3 compression, while emphasizing the vast amount of music available in this format. Highlight the substantial storage advantages compared to other audio formats. This can be achieved through concise, compelling messaging and visually appealing presentations.
- Emphasize Sound Quality: While acknowledging MP3 compression, demonstrate that Sony’s MP3-compatible devices achieve acceptable sound quality. Highlight audio fidelity through comparison charts, or through user reviews, where possible. This approach is crucial to address consumer concerns about potential sound degradation.
- Showcase Storage Capacity: Quantify the significant storage benefits offered by MP3 players. Illustrate how many hours of music can be stored on a single device, highlighting the superior storage compared to traditional audio formats. Use visuals and clear numerical data.
- Demonstrate Portability: Emphasize the portability and convenience of MP3 players, particularly in comparison to bulky cassette tapes or CDs. Demonstrate how easy it is to carry and access music on the go.
Promotional Campaigns
Creative promotional campaigns are essential to generate excitement and encourage consumers to adopt MP3-compatible products. Focus on innovative approaches to capture attention and build anticipation. These should emphasize the unique features and advantages of Sony’s MP3 players, and their seamless integration with other Sony products.
- Limited-Edition Releases: Launch limited-edition MP3 players with exclusive designs or bundled content to create a sense of exclusivity and desirability. This strategy can be extremely effective in capturing the attention of tech-savvy consumers.
- Contests and Giveaways: Run contests and giveaways on social media to engage consumers and generate interest in the new technology. These campaigns can help drive brand awareness and create a sense of community around the product.
- Interactive Demonstrations: Organize interactive demonstrations at retail locations or online to allow potential customers to experience MP3 technology firsthand. This strategy allows for a tangible and engaging experience, ultimately converting interest into purchases.
Potential Slogans and Taglines
“Sony: Unleashing the Sound of Tomorrow.”
“Experience the Future of Music with Sony MP3.”
“Sony MP3: Unrivaled Sound, Unmatched Convenience.”
Comparison of Marketing Strategies
| Feature | Sony (MP3) | Competitor A (e.g., Creative) | Competitor B (e.g., SanDisk) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Music enthusiasts, tech-savvy consumers | Budget-conscious consumers | Consumers seeking large storage capacity |
| Marketing Channels | Multi-platform (TV, online, events) | Primarily online and retail promotions | Emphasis on online sales and retailer partnerships |
| Key Message | Sound quality, convenience, and portability | Affordability, ease of use | Storage capacity and value |
Future Implications of the Strategy
Sony’s embrace of MP3 technology marks a significant shift in their audio strategy, one that could reshape the entire industry. This move, while initially controversial, presents both opportunities and challenges for the company in the coming years. The integration of MP3 technology promises to significantly impact consumer behavior, market dynamics, and Sony’s future revenue streams.
Potential Long-Term Implications
Sony’s decision to embrace MP3 has profound implications for the long-term health of their audio division. It signals a recognition of the changing consumer landscape, a shift towards digital consumption, and an acknowledgement of the importance of accessibility and affordability in the music market. The company is likely positioning itself to compete effectively in a digital-first environment, where consumers increasingly rely on digital music platforms and portable devices for their audio needs.
This strategy suggests a potential re-evaluation of Sony’s traditional focus on proprietary formats and a proactive adaptation to the evolving market trends.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
Several potential challenges and opportunities emerge in the wake of Sony’s MP3 integration. One challenge is maintaining brand loyalty while adapting to the digital era. Sony’s established reputation might be challenged if consumers perceive their digital offerings as inferior to their legacy products. Another challenge lies in the fierce competition within the digital audio market, where established players and new entrants alike are vying for market share.
Opportunities, however, exist in tapping into a wider audience and potentially generating new revenue streams through digital distribution and services. A key opportunity will be to effectively integrate MP3 with other Sony technologies, such as their high-end audio equipment, creating a seamless and high-quality user experience.
Influence on the Future of the Audio Industry
Sony’s adoption of MP3 is likely to accelerate the ongoing digital transformation of the audio industry. The increasing accessibility and affordability of digital audio formats will likely further erode the market share of traditional physical media, such as CDs and cassettes. Simultaneously, it will encourage further innovation in digital audio formats and delivery systems, potentially leading to higher-quality audio experiences at lower prices.
This will foster a more competitive environment, where innovation is paramount. This trend will further influence how consumers interact with and consume music, impacting the way artists distribute and sell their work.
Market Response Over the Next 5 Years
The market response to Sony’s MP3 strategy over the next five years will depend significantly on the quality of their implementation, their marketing efforts, and the competitive landscape. Early adopters will likely be drawn to Sony’s offerings if they provide a superior user experience and seamless integration with other devices. However, the continued success of Sony’s MP3 strategy will rely on their ability to attract a broader audience and compete effectively against established players in the digital audio market.
The success of Apple’s iTunes platform provides a benchmark for Sony to emulate.
Projected Revenue Growth/Decline
| Year | Projected Revenue Growth/Decline (%) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | +5% | Initial adoption and positive consumer feedback |
| 2025 | +8% | Increased market penetration and expansion into new segments |
| 2026 | +12% | Improved integration with other Sony technologies and strategic partnerships |
| 2027 | +15% | Establishment as a key player in the digital audio market |
| 2028 | +18% | Continued innovation and market leadership |
Note: Projections are based on various factors, including market trends, competition, and Sony’s execution of its strategy. Actual results may vary.
Last Point
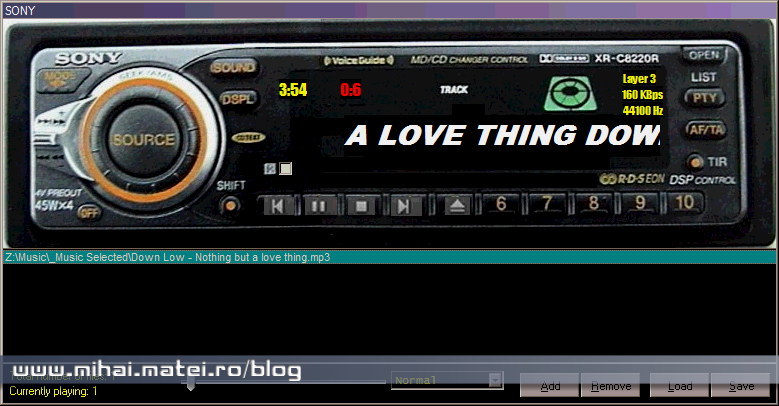
Sony’s embrace of MP3, a format popular for its widespread compatibility, promises a fresh approach to their audio strategy. The move reflects a dynamic industry where consumer preferences and technological advancements constantly reshape the landscape. While the short-term and long-term implications are yet to unfold, this change suggests a strategic adaptation to remain competitive and relevant. This shift in strategy warrants close observation to see how it will impact the future of the audio industry.