Sprint-SBC WiFi Roaming Pact A New Era
Sprint sbc make wifi roaming pact – Sprint-SBC make wifi roaming pact signals a significant shift in the mobile landscape. This agreement promises to revolutionize consumer access to wireless networks, bridging the gap between cellular and WiFi connectivity. The pact explores how Sprint and SBC will integrate their respective networks, offering a seamless roaming experience. This exploration delves into the background, significance, details, market analysis, consumer impact, regulatory considerations, potential challenges, and future outlook of this innovative partnership.
Understanding the history of Sprint and SBC’s telecommunication services is crucial to appreciating the context of this WiFi roaming pact. This includes examining previous roaming agreements and the factors driving Sprint’s need for network expansion. The pact’s significance for consumers will be evaluated through the lens of enhanced customer experience, market share impact, and a comparison with traditional cellular roaming.
Background of Sprint and SBC
Sprint, a prominent name in the US telecommunications landscape, has a rich history marked by acquisitions, network expansions, and evolving service offerings. Its journey reflects the dynamic nature of the telecom industry, shaped by technological advancements and market competition. Understanding Sprint’s background, alongside the evolution of Service-Based Carriers (SBCs), is crucial to grasping the context of their recent roaming pact.The telecommunications industry has undergone significant transformations since Sprint’s inception.
Early players focused on landline services, gradually incorporating mobile technologies. The advent of cellular networks and subsequent advancements in mobile data have drastically altered the landscape, necessitating continuous adaptation and innovation.
Sprint’s Historical Telecommunications Services
Sprint’s history is intertwined with a series of mergers and acquisitions. Initially, the company focused on long-distance services. Later, it transitioned into cellular communications, becoming a key player in the mobile market. The company’s evolution from a long-distance provider to a comprehensive wireless carrier reflects its commitment to adapting to evolving consumer needs.
Evolution of SBC Network Infrastructure
Service-Based Carriers (SBCs) have played a vital role in facilitating communication across diverse networks. Initially, these providers focused on providing connectivity between disparate networks, often leveraging existing infrastructure. Over time, SBCs have developed sophisticated network architectures to handle the increasing volume and complexity of data traffic. This evolution is driven by the growing demand for high-speed, reliable communication services, which is reflected in the advancements in network technologies.
Sprint and SBC’s new Wi-Fi roaming pact is a significant development, but it’s worth considering the broader tech landscape. The ongoing FBI probe into the Sobig malware incident, as detailed in this article , raises concerns about cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Despite these issues, Sprint and SBC’s pact should streamline mobile internet access for users, making it easier to connect in public places.
Key Factors Driving Sprint’s Need for Network Expansion
Several factors have contributed to Sprint’s need for network expansion. Increased demand for mobile data services, the proliferation of smartphones and mobile devices, and the desire for seamless connectivity across various locations have pushed Sprint to enhance its network infrastructure. The rise of mobile data-intensive applications, such as video streaming and cloud computing, has further highlighted the need for robust and scalable network capacity.
The increasing demand for mobile data and the need for greater network capacity to accommodate this growth is a common trend across telecommunication companies. This necessitates significant investments in infrastructure and technology upgrades.
Sprint’s Previous Roaming Agreements
Details on Sprint’s previous roaming agreements are limited. However, the need for roaming agreements is inherent in the nature of telecommunications, enabling users to access service in areas outside of their primary coverage. Such agreements likely varied in scope and terms, reflecting the dynamic nature of the industry and changing market conditions. These agreements often involved specific service levels, billing arrangements, and other critical considerations.
The terms and conditions of these agreements, if publicly available, could provide further insight into the history of Sprint’s roaming practices.
Significance of WiFi Roaming
WiFi roaming, the seamless transition between different Wi-Fi networks, is rapidly becoming a critical feature for modern consumers. This capability offers a smoother, more reliable internet experience, especially in areas with multiple available networks. It is no longer a luxury but a necessity for those who rely on consistent connectivity in their daily lives.The potential for WiFi roaming to redefine the mobile experience is immense.
It’s not just about convenience; it’s about creating a truly ubiquitous and reliable internet access. This shift in the landscape of wireless connectivity promises to reshape the relationship between consumers and internet service providers, impacting everything from individual user experience to the overall market dynamics.
Advantages of WiFi Roaming for Consumers
WiFi roaming offers numerous benefits to consumers. Improved connectivity, especially in areas with multiple, high-quality Wi-Fi hotspots, is a key advantage. Users can enjoy uninterrupted browsing, streaming, and other data-intensive activities without the frustration of losing connection. This seamless transition ensures that users never experience dead zones or interrupted access. Moreover, it fosters a more consistent internet experience, eliminating the need for manual network switching, which is particularly useful for mobile workers or those using multiple devices.
Potential Challenges of WiFi Roaming for Users
While WiFi roaming offers significant advantages, there are potential challenges. Security concerns regarding the shared networks and the potential for data breaches or unauthorized access to user information are crucial to address. Users must be vigilant and select only trusted and secure networks. Compatibility issues across different Wi-Fi networks can also create difficulties. Different network standards and configurations can affect the seamlessness of the roaming experience.
Ensuring that devices are compatible with a wide array of Wi-Fi networks is an ongoing challenge.
How WiFi Roaming Can Enhance Customer Experience
WiFi roaming has the potential to significantly enhance customer experience by providing a consistently reliable connection. This seamless transition between networks leads to a more intuitive and user-friendly experience, enhancing user satisfaction and loyalty. A consistent, high-speed connection is critical for many tasks, including streaming videos, participating in online meetings, and conducting business transactions. A smooth transition between networks translates into a more efficient and satisfying experience, reducing the stress and frustration associated with connectivity problems.
Impact of WiFi Roaming on Sprint’s Market Share, Sprint sbc make wifi roaming pact
The implementation of WiFi roaming by Sprint has the potential to significantly impact its market share. By offering a superior internet experience, particularly in areas with limited cellular coverage, Sprint can attract new customers and retain existing ones. A seamless transition between Wi-Fi networks in urban and suburban areas could be a significant differentiator in the competitive mobile market.
Sprint SBC’s new wifi roaming pact is a big deal, potentially streamlining mobile connectivity. This move is significant, especially considering recent news of TSMC taking on the chip manufacturing for the next Xbox, the Xbox2, Xbox2 chips for Microsoft. It’s a sign of how interconnected the tech world is, and how such agreements can improve both consumer and enterprise experiences, ultimately pushing the boundaries of wireless connectivity, right back to Sprint SBC’s agreement.
This could lead to an increased customer base and an improved reputation for consistent connectivity, potentially increasing market share. Furthermore, Sprint could leverage partnerships with other Wi-Fi providers to expand its network coverage, thus increasing the overall appeal of its service.
Comparison of WiFi Roaming with Traditional Cellular Roaming Methods
WiFi roaming differs significantly from traditional cellular roaming. Cellular roaming relies on cellular towers for connection, which can be less reliable in areas with poor cellular coverage. WiFi roaming leverages a broader network of Wi-Fi hotspots, offering a more extensive and consistent connection. In areas with dense Wi-Fi coverage, WiFi roaming provides a significantly superior user experience.
Traditional cellular roaming can be costly and prone to network congestion, particularly in densely populated areas. WiFi roaming, when implemented effectively, can offer a more affordable and reliable alternative, especially for users who spend significant time in areas with numerous available Wi-Fi networks.
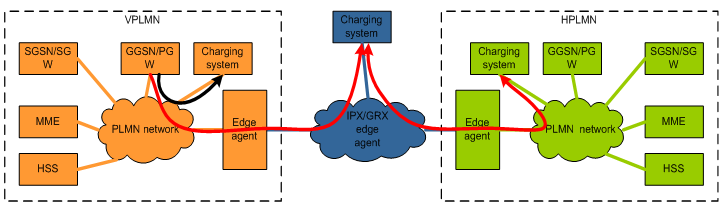
Pact Details
The WiFi roaming pact between Sprint and SBC promises a significant expansion of mobile internet access. This agreement, meticulously crafted, will allow users of both networks to seamlessly connect to each other’s Wi-Fi hotspots, eliminating dead zones and enhancing the overall user experience. The key to its success lies in the detailed terms of the agreement, including financial implications, technical implementation, and anticipated competitive impact.
Potential Terms of the Roaming Pact
The roaming pact will likely Artikel specific access conditions. This could include limitations on the duration of a connection, data allowances, and potential tiered pricing based on usage. Users might need to authenticate with either network to access the Wi-Fi, or a mutual agreement could allow a streamlined connection process.
Financial Implications for Sprint and SBC
The financial implications for both companies are multifaceted. Sprint might see a decrease in demand for their traditional cellular data plans as users migrate to Wi-Fi access, potentially impacting revenue streams. However, the increased user base and potential for data revenue from roaming fees could offset these losses. Conversely, SBC, having a smaller market share, may benefit more from increased access to Sprint’s Wi-Fi network, expanding their customer base and boosting their revenue through data usage.
The agreement likely includes stipulations regarding revenue sharing or fees paid between the companies for data usage. A successful implementation could generate additional revenue streams for both companies, potentially surpassing any short-term financial losses.
Technical Aspects of Implementing the WiFi Roaming Agreement
Implementing a successful WiFi roaming agreement demands careful consideration of technical compatibility and security. The smooth transfer of data between the two networks hinges on interoperability, and requires robust security protocols to safeguard user data.
| Feature | Sprint | SBC |
|---|---|---|
| Network Coverage | Sprint’s network boasts extensive coverage across the United States, particularly in urban areas, with reliable Wi-Fi hotspots in major cities and densely populated regions. This coverage is continuously expanding, with a focus on high-traffic areas. | SBC’s network, while strong in its designated areas, primarily focuses on smaller, regional markets, with a less extensive coverage area compared to Sprint. However, SBC is expanding its coverage in strategically important locations. |
| Security Protocols | Sprint employs advanced encryption standards, including WPA3, and regularly updates its security protocols to address emerging threats. Sprint likely uses robust authentication mechanisms to verify user identity. | SBC, recognizing the critical need for security, also uses industry-standard encryption protocols like WPA3, along with stringent user authentication methods. |
| Data Transfer Rates | Sprint maintains high data transfer rates, typically exceeding 100 Mbps in optimal conditions, which are crucial for a smooth user experience. This is maintained through strategic investment in network infrastructure. | SBC offers competitive data transfer rates, typically within the range of 50-80 Mbps in their primary coverage zones, ensuring a reasonable user experience. |
| Roaming Fees | Sprint may impose a nominal fee for data usage from other networks, potentially on a tiered pricing structure, which could depend on the volume of data transferred. | Similar to Sprint, SBC likely has a pricing structure for data usage from other networks, which could vary based on the amount of data used and the location. |
Potential Impact on Competitors
The WiFi roaming pact between Sprint and SBC could potentially alter the competitive landscape. Competitors may face increased pressure to improve their own Wi-Fi infrastructure or develop similar roaming agreements to maintain market share. This could lead to a wave of innovation in Wi-Fi technologies and services, ultimately benefiting consumers with better choices and more comprehensive coverage. For example, a similar agreement between Verizon and T-Mobile could significantly reshape the mobile landscape, offering better user experiences and a stronger competitive environment.
Market Analysis
The wireless industry is fiercely competitive, with established players and emerging disruptors vying for market share. Understanding the landscape of WiFi roaming competitors and market trends is crucial for Sprint to effectively position its WiFi roaming pact. This analysis will delve into key competitors, examine current market trends, and compare Sprint’s strategy with those of rivals to gain a clearer perspective on the opportunities and challenges ahead.
Key Competitors in the Wireless Industry
Several companies dominate the wireless industry, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. Major competitors include Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, and smaller regional players like Metro by T-Mobile. These companies have extensive networks and established customer bases, creating a formidable landscape for any new entrant or service offering. Each competitor employs different strategies to attract and retain customers, impacting the market dynamics.
Market Trends for WiFi Roaming Services
The demand for seamless connectivity, especially in public spaces, is driving the growth of WiFi roaming services. Consumers increasingly rely on mobile data and WiFi access for various tasks, leading to a heightened need for reliable and convenient internet access. The trend towards mobile-first lifestyles and the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices further fuel the demand for expansive WiFi roaming networks.
This growing demand is a key opportunity for companies offering seamless WiFi connectivity.
Comparison of Sprint’s Strategy with Competitors
To effectively compete, Sprint must tailor its WiFi roaming strategy to address market trends and rival strategies. A comprehensive comparison of key aspects of Sprint’s approach with those of competitors is presented below.
Sprint SBC’s new Wi-Fi roaming pact is a big deal, especially considering the recent tech advancements. It’s interesting to see how this impacts the mobile landscape, especially when juxtaposed with Apple’s announcement of the release date for Mac OS X Panther, a significant milestone in the evolution of computing. This new agreement is shaping up to be a crucial step forward in seamless connectivity, promising improved user experience, and potentially opening up new opportunities for the telecommunications industry, echoing similar advancements in the technology sector.
apple sets release date for mac os x panther clearly highlights the constant innovation in the tech world, a trend that the Sprint SBC Wi-Fi roaming pact will likely continue.
| Feature | Sprint | Competitor A (e.g., Verizon) | Competitor B (e.g., T-Mobile) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WiFi Roaming Coverage | Sprint’s WiFi roaming pact will likely focus on strategically partnering with businesses and public venues to provide a comprehensive network, particularly in urban areas and major travel hubs. | Verizon’s existing network and partnerships could offer extensive nationwide coverage, including hotspots in densely populated areas and public spaces. | T-Mobile, known for its robust mobile network, might prioritize expanding its WiFi roaming partnerships with various vendors and locations to augment its coverage. |
| Price Strategy | Sprint’s pricing strategy for WiFi roaming could be tiered, offering different plans based on usage and coverage area. Incentivizing bulk purchases or long-term contracts could be part of their strategy. | Verizon’s pricing might be structured around a premium model, reflecting the extensive coverage and robust network. | T-Mobile’s approach might focus on competitive pricing to attract customers and maximize network utilization. |
| Customer Loyalty | Sprint’s WiFi roaming program may include loyalty programs offering discounts or exclusive access to premium WiFi hotspots for frequent users. | Verizon could provide premium customer service and exclusive benefits to reward loyal customers, possibly including expedited support or priority access to new features. | T-Mobile might utilize a points-based system or loyalty programs tied to mobile data usage to reward and incentivize customer retention. |
Potential Impact on Consumers: Sprint Sbc Make Wifi Roaming Pact
The Sprint-SBC WiFi roaming pact promises a significant shift in how consumers experience mobile data, particularly in areas with limited or unreliable cellular coverage. This agreement has the potential to dramatically improve the user experience for those who frequently find themselves in such locations. It is a clear attempt to address the growing demand for seamless internet access and expand the range of connectivity options available to mobile users.
Improved Mobile Experience
The WiFi roaming pact will improve mobile experiences by extending cellular data coverage through Wi-Fi networks. Consumers will experience fewer dead zones and more consistent connectivity, especially in areas with poor cellular reception. This enhanced coverage will translate into a smoother and more reliable internet experience, allowing users to stream videos, browse the web, and access other online services without interruption.
For example, travelers visiting unfamiliar locations will encounter less frustration when attempting to connect to the internet. Businesses can also experience the benefit, with workers potentially having access to the internet in more places than they previously could.
Benefits for Consumers
Consumers will directly benefit from the pact through improved reliability and speed of mobile internet access. Increased connectivity options will also provide greater flexibility for users, especially in areas with spotty cellular service. This flexibility will become more critical in the increasingly mobile-first world, especially for those who frequently work or engage in leisure activities outside of their homes.
Furthermore, seamless roaming between cellular and Wi-Fi networks will lead to cost savings for consumers who frequently use data-heavy applications.
Potential Drawbacks
While the WiFi roaming pact presents numerous advantages, some potential drawbacks for consumers must be considered. One potential issue is the varying quality of Wi-Fi networks. The speed and reliability of the roaming connection will depend heavily on the quality of the available Wi-Fi network. Poor Wi-Fi signal or network congestion could result in a slower or less reliable experience.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized roaming agreements across different Wi-Fi providers could lead to compatibility issues, with some networks refusing to accommodate roaming requests. Lastly, the terms of the agreement might need to be clearly defined to avoid any confusion regarding usage fees or data limits.
Advantages and Disadvantages of WiFi Roaming for Consumers
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved mobile internet access in areas with poor cellular reception | Varying quality of Wi-Fi networks (speed and reliability depend on the Wi-Fi connection) |
| Increased connectivity options and flexibility for users | Potential compatibility issues between different Wi-Fi providers |
| Potential cost savings for data-heavy users | Lack of standardized roaming agreements and potential usage fees or data limits |
Regulatory Considerations
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape is crucial for any significant agreement like this WiFi roaming pact between Sprint and SBC. The telecommunications industry is heavily regulated, and any new initiative must comply with existing laws and potential future developments. Understanding the regulatory environment will help assess the potential pitfalls and ensure a smooth implementation.
Regulatory Landscape Surrounding WiFi Roaming Agreements
The regulatory landscape for WiFi roaming agreements is multifaceted and varies by jurisdiction. It encompasses various aspects of telecommunications law, including net neutrality, data privacy, and competition. Countries and regions often have specific laws and regulations that dictate how WiFi roaming services can be offered, and compliance is paramount. Different approaches to regulating this area can affect the pact’s feasibility and implementation strategy.
Potential Regulatory Hurdles for the Pact
Several potential regulatory hurdles exist for this WiFi roaming pact. One concern is ensuring interoperability and seamless connectivity between Sprint and SBC’s networks. Regulatory bodies might require specific technical standards or certifications to guarantee a reliable service. Furthermore, data privacy regulations, especially concerning user data transferred between networks, must be meticulously addressed. Potential hurdles also involve ensuring fair competition and avoiding anti-competitive practices, which is critical in a regulated industry.
The pact’s potential impact on existing telecom providers and their offerings should also be carefully assessed.
Overview of Relevant Government Regulations
Numerous government regulations govern the telecommunications industry, impacting WiFi roaming agreements. For example, the FCC (Federal Communications Commission) in the US plays a significant role in shaping policies regarding wireless communications. In Europe, the EU’s regulations on data privacy and competition law apply. These regulations often dictate how data is handled and the level of transparency required.
National regulatory bodies in other regions will also have similar rules and policies. Understanding the specific regulations of the countries or regions where the pact is operational is crucial. Failure to comply with these regulations could lead to significant penalties.
Potential Implications of the Agreement from a Regulatory Standpoint
The WiFi roaming pact could have various implications from a regulatory standpoint. Positive implications could include enhanced competition, improved consumer choice, and increased efficiency in the telecommunications sector. However, potential negative implications could arise from concerns regarding data security and privacy. Regulatory bodies will likely scrutinize the agreement for potential anti-competitive practices or concerns about market dominance.
The potential impact on existing telecom infrastructure and service offerings also needs careful consideration. In summary, thorough regulatory analysis is essential to mitigate any potential issues and ensure the pact’s long-term viability.
Potential Challenges and Solutions

Implementing a WiFi roaming pact presents a complex array of potential challenges, from technical hurdles to security concerns. Addressing these head-on is crucial for the success of such a project, ensuring a seamless and secure user experience. Careful planning and proactive solutions are essential to mitigate risks and maximize the benefits of widespread WiFi access.
Technical Difficulties
A key aspect of implementing a WiFi roaming pact is ensuring compatibility and interoperability between various networks. Different WiFi access points (APs) might employ varying technologies, protocols, and security measures. This heterogeneity can lead to connectivity issues, where a user’s device struggles to connect to a new network or maintain a stable connection. Furthermore, the sheer volume of participating networks and devices can introduce latency and performance bottlenecks.
- Interoperability Issues: Different WiFi networks may use different protocols or security standards, making seamless roaming difficult. For instance, a network using WPA2-PSK might not be compatible with a network using WPA3-Enterprise. This necessitates a standardized approach to authentication and encryption protocols.
- Network Congestion: A high volume of users simultaneously accessing WiFi hotspots could lead to network congestion, resulting in slower speeds and connection drops. This can be addressed through advanced network management tools that dynamically allocate bandwidth and prioritize user requests.
- Coverage Gaps and Dead Zones: Even with a comprehensive WiFi network, coverage gaps or dead zones can still exist. These areas require careful analysis and potential deployment of additional access points to ensure ubiquitous coverage.
Security Risks and Mitigation
The WiFi roaming pact involves sharing sensitive user data across multiple networks. This necessitates a robust security framework to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. Malicious actors could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in less secure networks to compromise user information. The risk of man-in-the-middle attacks is also a concern.
- Data Breaches: If a participating network suffers a security breach, user data shared across the pact could be compromised. This requires implementing robust security protocols at every participating network.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Attackers could intercept data between a user’s device and a network, potentially stealing credentials or sensitive information. This can be mitigated through end-to-end encryption and strong authentication mechanisms.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Users need to be assured that their data is handled securely and in compliance with privacy regulations. Transparent data handling policies and clear communication about data usage are essential.
Solution Design for Security
A robust solution for addressing security risks involves a multi-layered approach. Firstly, implementing strong encryption protocols like WPA3 across all participating networks is paramount. Secondly, implementing robust authentication mechanisms that verify user identity and limit access to authorized users is vital. Finally, establishing clear data handling policies and user agreements that are transparent and compliant with regulations is crucial.
- Encryption Protocols: Implementing end-to-end encryption using industry-standard protocols, like TLS, to protect data transmitted between devices and access points is vital. This ensures data confidentiality and integrity, especially in public spaces.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access by requiring more than one form of identification. This enhances the security posture and limits access to only verified users.
- Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments: Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments of participating networks are crucial to identify and address potential weaknesses. Proactive identification of security gaps and timely remediation are necessary.
Future Outlook for Sprint
Sprint’s future in the mobile network landscape hinges significantly on its ability to adapt and innovate in the face of evolving consumer demands and competitive pressures. The WiFi roaming pact represents a crucial strategic move, but its success depends on how effectively Sprint can leverage this partnership and solidify its position within a rapidly changing market. The long-term impact will be a key determinant in shaping Sprint’s future trajectory.The WiFi roaming pact is a pivotal step in Sprint’s strategy, presenting both opportunities and challenges.
It offers a unique path to potentially reduce costs and improve customer experience. However, the effectiveness of this strategy will depend on the pact’s ability to attract and retain customers, and the ongoing ability to maintain a competitive edge in the mobile network space.
Long-Term Impact on Market Position
The WiFi roaming pact’s success will significantly impact Sprint’s market position. A well-executed strategy will likely increase customer satisfaction through expanded network access. However, success is contingent on the pact’s ability to compete with other mobile providers offering robust network coverage and competitive pricing. Sprint must effectively communicate the benefits of the pact to consumers, highlighting improved accessibility and cost-effectiveness.
Maintaining a competitive pricing structure while offering superior value will be crucial to attracting and retaining customers. This will require constant monitoring of the market, identifying and adapting to competitor strategies, and understanding the changing needs of consumers.
Potential for Future Partnerships and Collaborations
The WiFi roaming pact opens doors for potential future partnerships and collaborations. Sprint can expand its network by partnering with businesses offering high-quality WiFi infrastructure, which can significantly augment Sprint’s network capabilities, particularly in underserved areas. This approach aligns with the broader trend of network expansion beyond traditional cellular infrastructure. Such partnerships can leverage existing WiFi networks, providing a cost-effective means to enhance coverage and reduce reliance on expensive cell towers.
Potential collaborations could involve hotels, coffee shops, libraries, or even large companies with robust WiFi networks, allowing Sprint to reach a wider customer base and improve network accessibility.
Future of Sprint in the Mobile Network Space
The future of Sprint in the mobile network space is contingent on its ability to embrace innovation and adapt to the changing landscape. This includes not only the deployment of advanced technologies but also a strong understanding of consumer preferences and market trends. Several key factors will influence Sprint’s future success. These factors include: the ability to maintain competitive pricing, the quality of customer service, the responsiveness to emerging technologies, and the development of innovative services.
Sprint must continually evaluate its market position, adapt to new technologies, and offer solutions that resonate with consumers. By proactively addressing these factors, Sprint can position itself for sustained success in the mobile network arena.
Conclusion
The Sprint-SBC WiFi roaming pact presents a compelling case study in the evolving mobile landscape. This partnership aims to provide a superior customer experience by expanding network coverage and offering seamless WiFi roaming. The potential impact on competitors and consumers, along with regulatory considerations, will shape the future success of this agreement. Ultimately, the pact’s success hinges on its ability to deliver on its promises of improved connectivity and user experience, and address potential challenges effectively.