Sun Virtualization Plan Services Support
Sun virtualization plan to include services support Artikels a comprehensive strategy for integrating various services into Sun’s virtualization platform. This plan delves into the core concepts, key features, and benefits of Sun’s virtualization technology, while exploring the necessary steps for implementation, management, and future considerations. It examines the different services supported, from storage and networking to security, providing a detailed roadmap for deploying and scaling these services within the Sun environment.
The plan encompasses detailed explanations of Sun’s virtualization technology, including its architecture and comparison with other platforms. It features tables outlining products, supported services, and implementation tools, along with a clear roadmap for managing and maintaining these services.
Defining Sun Virtualization
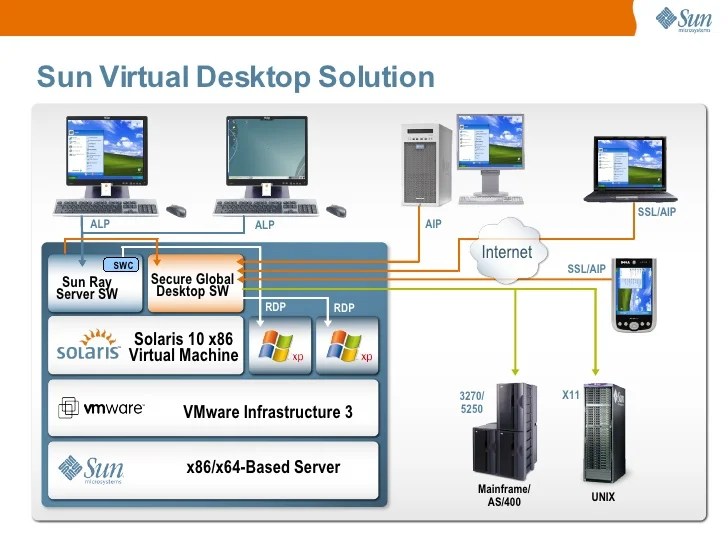
Sun Microsystems, now Oracle, pioneered virtualization technologies that significantly impacted the server landscape. Their approach to virtualization, though not as ubiquitous as some newer platforms, introduced key concepts and solutions that influenced subsequent developments. This exploration delves into Sun’s virtualization techniques, highlighting their core concepts, architecture, features, and comparison to other platforms.Sun’s virtualization solutions, often categorized under the umbrella term “Sun xVM,” offered a way to efficiently utilize hardware resources.
This approach allowed for multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run concurrently on a single physical server, improving resource utilization and reducing costs. This was achieved through various techniques, ultimately aiming to improve efficiency and flexibility in server management.
Core Concepts and Architecture
Sun’s virtualization solutions primarily focused on server virtualization. The core concept revolved around partitioning physical server resources to create multiple virtual environments. Each virtual machine, or VM, appeared to the user as a dedicated physical machine, with its own operating system and applications. The underlying architecture utilized a hypervisor, a layer of software that managed the allocation and access to hardware resources among the VMs.
This hypervisor effectively separated the virtual machines from the physical hardware, allowing for greater flexibility and independence.
Key Features and Benefits
Sun’s virtualization approach provided several key features, including:
- Resource Allocation and Management: The ability to dynamically allocate resources like CPU, memory, and storage to each virtual machine based on its needs. This feature enhanced resource utilization, leading to greater efficiency and improved performance.
- Improved Server Utilization: By running multiple VMs on a single physical server, Sun’s virtualization reduced the need for dedicated servers, saving space and power. This translated to reduced capital expenditures and operational costs.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability: The ability to quickly create and deploy new VMs, adapt to changing workloads, and easily scale resources as needed.
- Increased Availability and Reliability: Virtual machines could be easily migrated between physical servers, leading to greater availability and reduced downtime.
Comparison with Other Virtualization Platforms
While Sun’s virtualization technology played a role in the industry, newer platforms like VMware and Microsoft Hyper-V have become more prevalent. The key differentiators lie in the breadth of features, integration with other tools, and the sheer market dominance of some competitors. Sun’s solutions, while innovative for their time, often lacked the extensive ecosystem and support that later platforms developed.
Sun Virtualization Products and Functionalities
| Product | Key Features | Target Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Sun xVM | Hypervisor-based virtualization, resource management, improved server utilization. | Server consolidation, improved resource utilization, cost reduction, and increased availability. |
| Sun xVM Server | Enhanced server management features, including dynamic resource allocation and scaling. | Businesses seeking greater server efficiency, reduced infrastructure costs, and enhanced operational flexibility. |
Services Support in Sun Virtualization
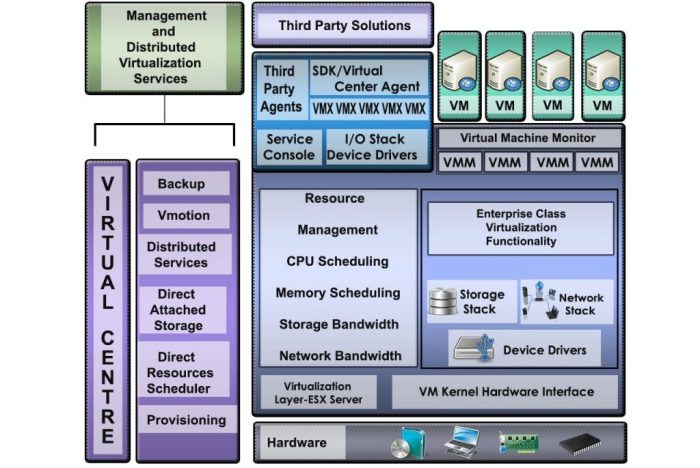
Sun’s virtualization platform offers a robust ecosystem for running diverse applications and services. Beyond the fundamental virtualization technology, effective support for various services is crucial for a successful implementation. This includes crucial areas like storage, networking, and security, each requiring careful integration and management. Understanding the specific services supported by Sun’s virtualization solutions, along with the associated challenges, is key to optimizing performance and reliability.
Supported Services Overview
Sun’s virtualization platform, while primarily focused on virtual machine creation and management, extends its capabilities to support a range of essential services. These services are integral to the smooth operation and scalability of virtualized environments. They ensure consistent access to resources, data integrity, and enhanced security. This includes provisioning, managing, and securing various resources like storage, networking, and security.
Sun’s virtualization plan to include services support is a significant move, potentially impacting the ongoing Linux vs. Longhorn battle. This plan, in a way, mirrors the growing need for robust storage solutions within a virtualized environment. The debate surrounding Linux and Longhorn, as seen in articles like linux vs longhorn the battle is joined , highlights the complexities of this transition.
Ultimately, Sun’s plan should offer a compelling alternative for managing storage within their virtualization platform.
Effective integration between these services and the virtualization platform is paramount for optimizing performance and reliability.
Storage Services
Storage management is critical within a virtualized environment. Sun’s virtualization solutions, such as XVM, integrate with various storage technologies. This integration allows for dynamic allocation of storage resources to virtual machines (VMs) based on demand. Different storage types, including local disks, SANs, and cloud storage, are often supported. The integration approach commonly involves storage drivers and protocols to enable efficient data transfer and access.
Storage solutions are often crucial for performance and scalability. The ability to scale storage resources is important for adapting to changing demands.
Sun’s virtualization plan to include services support is a smart move, especially considering the intense competition in the voice market. Wireless carriers are feeling the pinch as competition in the voice market squeezes wireless carriers , and this could potentially impact their reliance on existing infrastructure. This new plan will likely be crucial for Sun to stay competitive in the long run.
Networking Services
Networking services are essential for connectivity within a virtualized environment. Sun’s virtualization platform usually supports various networking protocols and technologies. This allows VMs to communicate with each other and the physical network. Network configurations, such as VLANs and firewalls, can be applied to individual VMs or groups of VMs. This granular control is essential for isolating and securing virtualized environments.
The integration with external networks is often crucial for application access.
The Sun virtualization plan, aiming to include services support, is a crucial step for companies. However, mobile devices are creating significant security challenges for businesses, as highlighted in this insightful article about mobile devices create security challenge for companies. Addressing this requires a robust security strategy alongside the Sun virtualization plan to ensure seamless operations and data protection.
Security Services
Security services are vital for protecting virtualized environments from threats. Sun’s virtualization solutions often include built-in security features, such as access controls and intrusion detection systems. These features are designed to enhance security postures and prevent unauthorized access to VMs and data. Security is often integrated into the virtualization layer, offering a layered approach to protecting virtualized resources.
The integration of security services with storage and networking is important for complete protection.
Integration Methods
Various methods are employed for integrating services into Sun’s virtualization platform. These methods vary depending on the specific service and product. For example, storage integration often involves storage drivers and protocols. Networking integration usually utilizes virtualization-aware network devices and protocols. Security integration may include specialized security modules or APIs.
The integration process is critical for seamless service provision and optimized resource utilization. A well-integrated system ensures reliable and secure operations.
Challenges in Service Support, Sun virtualization plan to include services support
Several challenges exist in providing service support within a Sun virtualization environment. One challenge is ensuring compatibility between different services and the virtualization platform. Another challenge is managing and monitoring the performance of integrated services. Security is another concern, as virtualized environments can be vulnerable to various threats. Scalability can be an issue as the virtualized environment grows.
Addressing these challenges is essential for maximizing the benefits of Sun’s virtualization platform.
Supported Services Across Sun Virtualization Products
| Service Type | Supported Products | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | XVM, ZVM | Supports various storage protocols and technologies, including local disks, SANs, and cloud storage. Provides dynamic allocation of storage resources. |
| Networking | XVM, ZVM | Supports various networking protocols and technologies, enabling communication between VMs and the physical network. Allows for VLANs and firewalls to be applied to VMs. |
| Security | XVM, ZVM | Includes built-in security features like access controls and intrusion detection systems. Offers a layered approach to protecting VMs and data. |
Plan for Sun Virtualization Services: Sun Virtualization Plan To Include Services Support
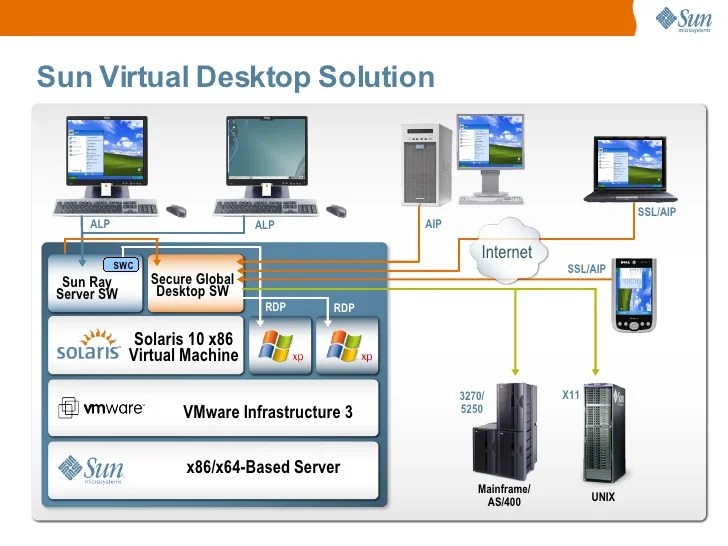
Sun virtualization presents a powerful platform for deploying and managing IT services. A well-defined plan for these services is crucial for maximizing efficiency, scalability, and reliability. This plan encompasses not only the implementation and management strategies but also the procedures for support, deployment, and maintenance. It ensures a smooth transition to virtualization and continued optimal performance.Effective service management in a virtualized environment requires a proactive approach.
This plan details the steps involved in ensuring consistent service levels and a robust troubleshooting process. The strategies discussed here will guide the implementation and ongoing maintenance of Sun virtualization services, enabling businesses to leverage the benefits of this technology fully.
Strategies for Implementing and Managing Sun Virtualization Services
A successful Sun virtualization implementation requires a well-defined strategy encompassing service level agreements (SLAs), resource allocation, and ongoing monitoring. Careful planning is crucial for avoiding bottlenecks and ensuring optimal performance. This includes defining roles and responsibilities within the IT team and establishing communication protocols. Prioritizing tasks and establishing clear timelines are key to successful deployment and ongoing maintenance.
Methods for Deploying and Scaling Sun Virtualization Services
Deployment strategies for Sun virtualization services need to consider the specific needs of the organization. A phased approach, deploying services in stages, allows for testing and validation before full-scale implementation. This iterative approach minimizes risk and ensures smooth integration. Careful consideration should be given to the infrastructure’s capacity to handle increased load and the necessary resources required for scaling.
Planning for Virtualization Service Support
Service support planning for Sun virtualization must include proactive monitoring and maintenance. This includes setting up alerts for potential issues and establishing a clear escalation process for resolving problems. Comprehensive documentation is essential for supporting both existing and new users. The documentation should clearly Artikel procedures for troubleshooting and resolving common issues. A dedicated support team, equipped with the necessary training and tools, is vital to ensure rapid response times and high-quality service.
Maintaining Service Levels within a Sun Virtualization Environment
Maintaining service levels in a Sun virtualization environment requires a continuous monitoring process. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established and tracked to ensure that service levels are met consistently. Regular performance assessments will identify potential bottlenecks or areas needing optimization. Proactive maintenance, including patching and updates, is crucial for preventing service disruptions.
Troubleshooting and Resolving Issues Related to Sun Virtualization Services
A comprehensive troubleshooting procedure is essential for quickly resolving issues. This involves establishing a standardized approach to identifying and isolating problems. Detailed logs and monitoring tools provide valuable insights for diagnosing the root cause of any issues. A structured approach for escalation, involving escalation paths and contact procedures, is critical for efficient issue resolution.
Process for Deploying a New Service in a Sun Virtualization Environment
A well-defined flow chart outlining the process for deploying a new service is vital for maintaining consistency and minimizing errors.
- Assessment and Planning: Identify the requirements of the new service, including resources, dependencies, and potential impacts on existing services. Thoroughly document these requirements.
- Resource Allocation: Ensure sufficient virtual resources are allocated for the new service. Consider factors such as CPU, memory, and storage capacity. A clear resource allocation plan is necessary.
- Configuration and Deployment: Configure the virtual environment according to the service’s specifications. Carefully test the deployment process to ensure smooth integration.
- Testing and Validation: Rigorously test the new service to ensure it meets the required performance and functional specifications. Test cases should be designed to cover various scenarios.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Deploy the service to the production environment. Implement monitoring tools to track performance and identify potential issues.
- Documentation and Support: Document the deployment process and create user guides. Establish support procedures for users of the new service.
Virtualization Services Implementation
Bringing Sun virtualization services online requires a meticulous implementation plan. This involves not just setting up the virtual machines but also configuring the underlying infrastructure, implementing security protocols, and establishing robust support mechanisms for the services. A well-executed implementation ensures smooth transitions, optimized resource utilization, and a secure environment.
Best Practices for Implementing Virtualization Services
A successful virtualization service implementation follows key best practices. These include thorough planning, careful selection of hardware and software components, and a phased approach to migration. Thorough documentation and clear communication throughout the process are critical for success. Understanding the specific needs of the applications and workloads to be virtualized is essential for optimal performance.
Potential Pitfalls and Mitigation Strategies
Implementing virtualization services can encounter various pitfalls. Compatibility issues between different components, such as hypervisors and guest operating systems, can cause problems. Insufficient capacity planning can lead to performance bottlenecks. Data migration errors and network configuration issues can also disrupt service. Mitigation strategies include thorough testing, meticulous planning, and having contingency plans in place.
Regular monitoring and performance tuning are crucial to prevent and resolve issues proactively.
Security Considerations for Sun Virtualization Services
Security is paramount in any virtualization implementation. Ensuring the security of virtual machines is critical. Protecting against unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious software is vital. Implementing strong access controls, regularly updating software, and using intrusion detection systems are essential steps. Furthermore, regularly auditing the security posture of the virtualized environment is critical for ongoing security maintenance.
Tools and Technologies Supporting Sun Virtualization Services
Implementing Sun virtualization services relies on several supporting tools and technologies. These tools automate tasks, manage resources, and monitor performance. A comprehensive suite of tools streamlines the entire virtualization lifecycle, from initial setup to ongoing maintenance.
Tools for Sun Virtualization Services Implementation
| Tool | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| VMware vCenter | A centralized management platform for VMware virtualization environments. It provides a single pane of glass for managing multiple virtual machines, hosts, and networks. | Centralized management of virtual machines, monitoring of performance, and automation of tasks. |
| Microsoft Hyper-V Manager | A management tool for Microsoft Hyper-V virtual environments. It provides a graphical user interface for managing virtual machines, hosts, and networks. | Managing and monitoring virtual machines within a Microsoft environment. |
| Oracle VM Manager | A centralized management platform for Oracle VirtualBox and other Oracle virtualization products. It enables centralized management of virtual machines, storage, and networking. | Management and monitoring of virtual machines within an Oracle environment. |
| VMware vSphere | A suite of products for building and managing large-scale virtualized environments. It encompasses vCenter Server, ESXi hypervisors, and other components. | Creating and managing large-scale, complex virtual environments. |
| VirtualBox | A free and open-source virtualization platform. It is suitable for smaller deployments and testing. | Development, testing, and prototyping in a virtual environment. |
Illustrative Example
Sun virtualization services offer a powerful platform for deploying and managing diverse applications and services. This example demonstrates a specific implementation, highlighting the benefits and challenges encountered. We will focus on a scenario involving a web application deployment.A web application, “E-commerce Store,” requires scaling to handle increasing user traffic during peak seasons. Traditional server infrastructure would involve significant hardware upgrades and potentially lead to downtime during transitions.
Sun virtualization presents a more efficient and adaptable solution.
Web Application Deployment Scenario
The “E-commerce Store” application is deployed on a Sun virtualization platform. Multiple virtual machines (VMs) are created, each representing a specific function of the application. For instance, one VM handles user authentication, another manages product catalogs, and a third handles order processing. These VMs are allocated resources dynamically based on real-time demands. This allows for efficient resource utilization and scaling.
Deployment Steps
- Planning and Design: The architecture of the web application is designed with virtualization in mind. Resource allocation for each VM is determined based on anticipated peak loads. This includes memory, CPU, and storage requirements. Network configurations are also established to ensure optimal communication between VMs.
- VM Creation: Virtual machines are created using a Sun virtualization tool, utilizing templates for efficiency. Each VM is configured with the specific software and application components required for its function. This involves installing the operating system and relevant software packages on each VM. This configuration ensures the application is isolated and protected from disruptions from other virtual machines.
Moreover, the VMs are provisioned based on the design specifications for performance and stability.
- Application Deployment: The “E-commerce Store” application is deployed across the virtual machines. The application is configured to access resources on other VMs as required. Deployment is automated, enabling quick and reliable updates.
- Monitoring and Management: Real-time monitoring tools track performance metrics such as CPU utilization, memory consumption, and network traffic. This allows for dynamic resource allocation and proactive issue resolution. Virtualization management tools facilitate easy monitoring and control over all VMs.
- Scalability: During peak seasons, additional VMs are provisioned automatically. This is triggered by pre-defined scaling rules, ensuring that the application can handle increased traffic loads without performance degradation. The system automatically adjusts resource allocation for each VM, maximizing efficiency and responsiveness.
Benefits and Challenges
- Benefits: Improved resource utilization, increased scalability, faster deployment, reduced hardware costs, and enhanced flexibility. The virtualization approach significantly reduces the cost and complexity of scaling the application to meet seasonal demands. Moreover, it provides isolation for different components of the application, reducing the risk of conflicts and improving overall system stability. The ability to quickly provision and scale virtual machines provides a significant competitive advantage.
- Challenges: Initial setup and configuration can be complex. Ensuring compatibility between the application and the virtualization platform requires careful planning. Proper monitoring and management are crucial to avoid performance bottlenecks and ensure smooth operation. Understanding the limitations of the virtualization environment is critical to avoid performance degradation or unexpected issues during peak loads.
Virtualization Service Management
Sun virtualization services, like any complex system, demand meticulous management to ensure optimal performance, security, and resource utilization. Effective management involves a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simply deploying virtual machines. It necessitates a proactive strategy encompassing monitoring, optimization, and maintenance. This section delves into the key processes and tools required for successful Sun virtualization service management.Effective management of Sun virtualization services requires a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between various components and the impact of resource allocation on overall system performance.
This involves monitoring key metrics, proactively identifying potential bottlenecks, and implementing strategies for optimizing performance.
Monitoring Tools and Techniques
Monitoring Sun virtualization services is crucial for maintaining stability and identifying potential issues early. Various tools and techniques can be employed to achieve this.
- Sun’s built-in monitoring tools provide valuable insights into resource consumption and system health. These tools often offer real-time dashboards and alerts, enabling administrators to respond quickly to potential problems.
- Third-party monitoring solutions provide comprehensive views of the virtualization environment. They can aggregate data from multiple sources, allowing for a holistic understanding of the entire system. Some tools offer advanced analytics and predictive capabilities to anticipate potential issues.
- Performance metrics such as CPU utilization, memory consumption, disk I/O, and network traffic are critical indicators of system health. Monitoring these metrics allows administrators to pinpoint resource bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
- Logging mechanisms capture events and errors, providing detailed information about system activity. This data can be analyzed to identify patterns and trends, helping in diagnosing and resolving issues.
Performance Optimization Strategies
Optimizing performance in a Sun virtualization environment is essential for ensuring smooth operation and user satisfaction. Strategies can focus on resource allocation, workload management, and virtual machine configuration.
- Resource allocation should be optimized based on the demands of each virtual machine. Over-provisioning can lead to wasted resources, while under-provisioning can cause performance degradation. Dynamic resource allocation allows for adjustments based on real-time needs.
- Workload management strategies aim to distribute tasks efficiently across virtual machines. Scheduling algorithms can ensure that tasks are allocated to the appropriate virtual machines based on their current resource utilization and performance requirements.
- Virtual machine configuration plays a significant role in performance. Proper configuration of virtual machines, including CPU and memory settings, can dramatically impact performance. Tuning these settings based on application needs is essential.
Service Usage and Resource Allocation Monitoring
Monitoring service usage and resource allocation allows administrators to identify areas needing adjustment. This involves analyzing patterns in resource consumption and identifying potential bottlenecks.
| Metric | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Utilization | Percentage of CPU time used by virtual machines. | A virtual machine consistently exceeding 90% CPU utilization might indicate a need for additional resources or optimization of the application running within it. |
| Memory Consumption | Amount of memory used by virtual machines. | High memory consumption might suggest that a virtual machine is using more memory than necessary or that the application requires more memory. |
| Disk I/O | Rate of disk read/write operations. | High disk I/O can be indicative of inefficient storage utilization, or potential problems with the virtual hard drive configuration. |
Maintenance and Updates
Regular maintenance and updates are crucial for the stability and security of Sun virtualization services.
- Regular patching of the virtualization platform addresses security vulnerabilities and ensures the platform’s ongoing stability.
- Maintaining the virtual machine configurations prevents unexpected issues and ensures the desired performance levels are consistently met.
- Implementing a robust backup and recovery strategy is vital for disaster recovery and data protection. This is especially important in a virtualization environment where data loss can have significant consequences.
Future Trends and Considerations
Sun virtualization services are poised for significant evolution. Emerging technologies and changing business needs will reshape the landscape of virtualization support. Understanding these trends is crucial for proactively adapting Sun virtualization services to meet future demands and maintain a competitive edge. This section explores key future considerations and potential challenges.
Emerging Trends in Sun Virtualization Technology
The virtualization landscape is dynamic, with several key trends impacting Sun’s approach. Cloud-native architectures, serverless computing, and advancements in AI are driving substantial changes. These trends are influencing the way applications are developed, deployed, and managed. The increasing demand for flexibility and scalability in IT infrastructure further propels these trends.
- Cloud-Native Architectures: Cloud-native applications are designed to leverage the benefits of cloud environments, like scalability and elasticity. This shift demands virtualization platforms that seamlessly integrate with cloud infrastructure services. For instance, containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes are gaining significant traction, influencing the need for virtualization platforms that can efficiently manage containerized workloads.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing removes the need for managing servers, providing on-demand resources. This model necessitates virtualization platforms that dynamically provision and de-provision resources based on application needs. This trend significantly reduces operational overhead, making it attractive for applications with fluctuating demand.
- AI-Driven Optimization: Artificial intelligence can optimize resource allocation and performance within Sun’s virtualization environment. AI-powered tools can proactively identify and resolve potential issues, ensuring high availability and optimal resource utilization. Examples of this include predicting resource needs and dynamically adjusting allocation in real-time.
Potential Impact on Sun Virtualization Services
These emerging trends will substantially impact Sun virtualization services. The demand for more automated and intelligent management systems will increase. The ability to seamlessly integrate with cloud-native architectures and support serverless applications will be crucial. Addressing these changes will require a shift in service offerings and a focus on proactive support and optimization.
Future Directions for Sun Virtualization Service Development
Sun virtualization services must evolve to keep pace with the rapid changes in technology. This includes enhancing support for cloud-native applications and serverless deployments. A critical component will be developing tools that facilitate the integration of Sun virtualization with existing cloud platforms. The development of proactive monitoring and automated management tools is also essential.
Potential Future Challenges in Managing Sun Virtualization Services
Managing a dynamic virtualization environment presents several challenges. Maintaining security in a complex and ever-changing environment is paramount. The increasing complexity of applications and the integration with various cloud platforms will demand highly skilled personnel. The ability to handle fluctuating workloads and unpredictable demands will be critical for optimal performance.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the Sun virtualization plan to include services support provides a robust framework for integrating and managing services within a Sun virtualization environment. It offers a practical approach to implementation, management, and future considerations, ensuring smooth deployment and optimal performance. This comprehensive plan addresses the technical aspects and potential challenges, offering a clear path forward for organizations looking to leverage Sun virtualization.