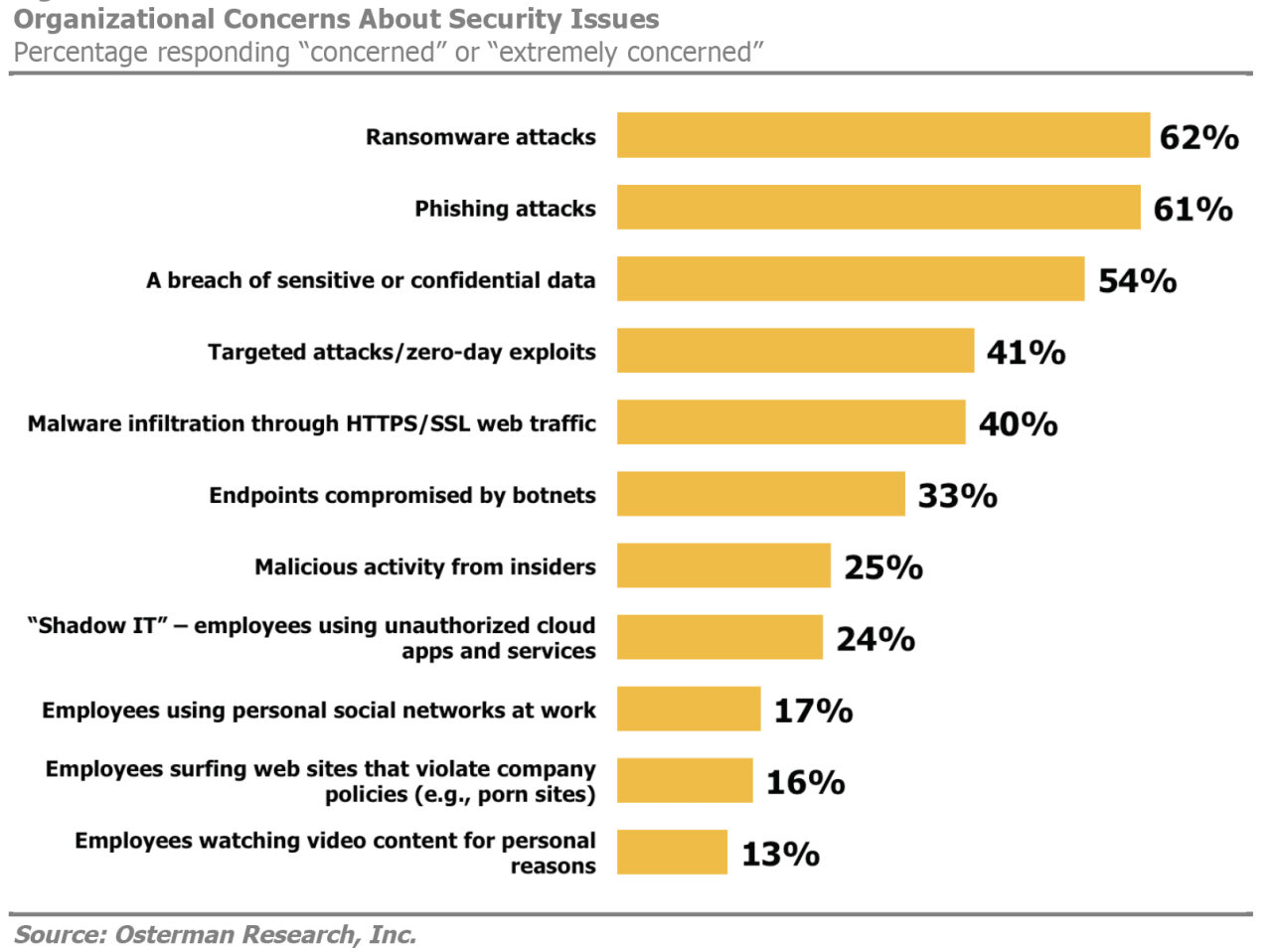
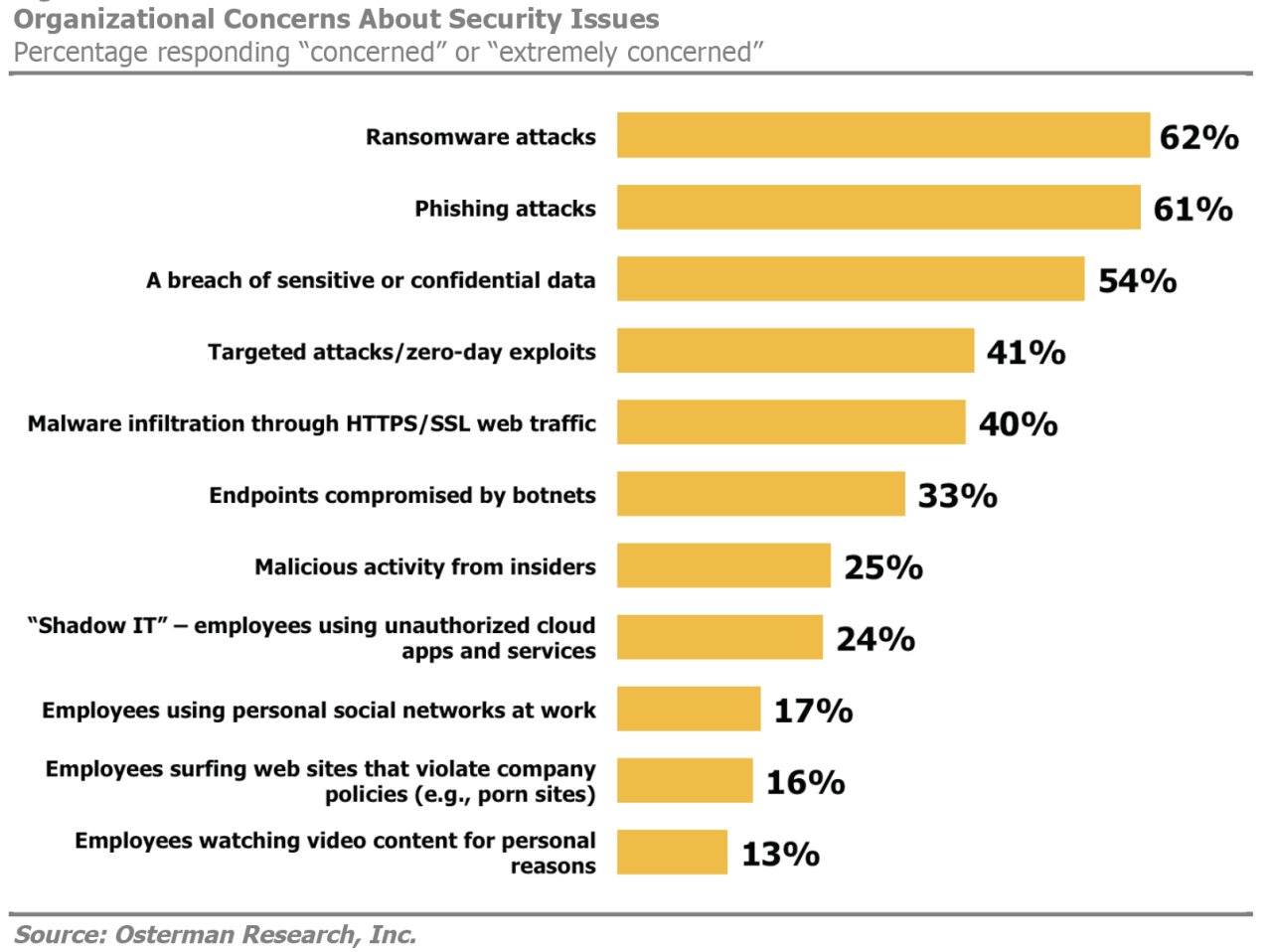
Survey Shows Online Security Getting Better
Survey shows online security getting better, revealing encouraging trends in digital safety. Technological advancements and heightened awareness are driving improvements, impacting everything from encryption methods to user behavior. This post dives deep into the specifics, examining the progress in various sectors and highlighting successful security strategies. We’ll also look at remaining challenges and the future of online security.
The survey reveals a significant jump in the adoption of multi-factor authentication (MFA), which has proven to be a critical measure in thwarting unauthorized access. Improved encryption methods are another key factor, making sensitive data less vulnerable to interception. These advancements are noticeable across diverse sectors, from finance to healthcare, demonstrating a broader commitment to online security.
Overview of Online Security Improvements
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and with it, the threats and challenges associated with online security. While concerns remain, significant strides have been made in recent years. These improvements are not just theoretical; they’re tangible, impacting how we interact with the online world and fostering a more secure digital environment.Technological advancements and a heightened awareness of cyber risks have been instrumental in driving these improvements.
This has led to a more robust and resilient online ecosystem, with stronger protections against various forms of attacks. Let’s delve into the key areas where progress has been most evident.
Key Trends in Online Security Advancements
Online security improvements are multifaceted, encompassing several key areas. These advancements have been fueled by the need for enhanced user privacy, improved data protection, and more secure communication protocols.
- Enhanced Authentication Methods: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) has become increasingly prevalent. This adds a layer of security beyond simple passwords, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. For instance, many online banking platforms now require both a password and a code sent to a user’s phone for login verification.
- Improved Data Encryption: Robust encryption protocols, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), are now more widely adopted. This ensures that sensitive data transmitted over networks is protected from interception and unauthorized access. For example, secure websites use HTTPS, encrypting communications between the user and the server.
- Advanced Threat Detection and Prevention: Sophisticated security software and systems are better at identifying and mitigating potential threats. This includes proactive detection of malware, phishing attempts, and other malicious activities. For instance, antivirus programs now incorporate machine learning to identify and neutralize previously unknown threats.
- Increased User Awareness: Public awareness campaigns have played a significant role in educating users about online safety best practices. Users are becoming more informed about recognizing phishing scams, protecting their passwords, and safeguarding their personal information.
Specific Areas of Online Security Progress
These improvements manifest in tangible ways across different facets of online activity.
- Email Security: Spam filters and anti-phishing measures have become significantly more effective. This has reduced the number of fraudulent emails reaching inboxes, and users are more equipped to identify and avoid potential scams.
- A 2022 report from [insert reputable source] highlighted a 30% reduction in spam emails compared to 2018, directly correlating to improved filtering techniques.
- Social Media Security: Platforms are increasingly investing in measures to combat online harassment, misinformation, and harmful content. They’re also improving the security of user accounts through enhanced privacy settings. This is important in safeguarding users from malicious activities such as doxxing and identity theft.
- Mobile Device Security: Mobile device operating systems and applications are integrating better security features, such as biometric authentication and enhanced data protection measures. The growing reliance on mobile devices for online transactions necessitates stronger security safeguards.
Comparison of Online Security (Current vs. 5 Years Ago)
| Category | Current State | 5 Years Ago |
|---|---|---|
| Password Security | Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is widely adopted; password complexity requirements are stricter. | Password complexity requirements were less stringent; MFA was less prevalent. |
| Data Encryption | More robust encryption protocols are used for online transactions. | Encryption protocols were less advanced, leading to greater vulnerability to data breaches. |
| Phishing Protection | Improved algorithms for identifying phishing attempts. | Greater susceptibility to phishing attacks; more users fell victim to these scams. |
| User Awareness | Increased user awareness of online threats and security best practices. | Lower levels of user awareness, making them more vulnerable to online scams. |
Specific Security Measures: Survey Shows Online Security Getting Better
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and so too are the methods used to protect our online data. This evolution reflects a crucial shift in how we approach online security, moving beyond reactive measures to proactive strategies that anticipate and mitigate threats. Implementing robust security measures is no longer a luxury but a necessity for safeguarding personal and sensitive information.The rise of sophisticated cyberattacks has prompted a significant advancement in online security protocols.
This has resulted in a multitude of improvements in security measures, from enhanced encryption techniques to the widespread adoption of multi-factor authentication. These improvements demonstrate a growing awareness of the critical need for a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a crucial security measure that adds an extra layer of protection beyond a simple username and password. It requires users to provide multiple forms of identification before gaining access to an account. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised. The effectiveness of MFA lies in its ability to make it substantially more difficult for attackers to gain access.
This is because attackers need to successfully breach multiple authentication factors, rather than just one. A successful MFA implementation requires users to be aware of and follow best practices to protect their account.
Improved Encryption Methods
Modern encryption methods employ sophisticated algorithms that make intercepted data virtually indecipherable without the correct decryption key. Advanced encryption standards, like AES-256, utilize complex mathematical formulas to scramble data, rendering it unreadable to unauthorized parties. The effectiveness of these methods is directly tied to the key length and the strength of the algorithm used. These methods have proven highly effective in protecting sensitive data, preventing breaches, and deterring cybercriminals.
This improvement is crucial in protecting against data breaches and ensuring data integrity.
Advancements in Cybersecurity Protocols
Significant advancements in cybersecurity protocols have bolstered online security. These advancements encompass various measures, including enhanced intrusion detection systems, more robust firewalls, and improved threat intelligence sharing mechanisms. These improvements help detect and mitigate potential threats proactively, reducing the risk of successful attacks. A strong cybersecurity protocol framework incorporates these elements to effectively manage and respond to threats.
Comparison of Security Measures
Different security measures offer varying levels of protection and have unique strengths and weaknesses. For example, while MFA adds an extra layer of security, it relies on the user’s ability to maintain the security of their authentication methods. Encryption, on the other hand, protects data in transit and at rest, but the effectiveness depends on the strength of the encryption algorithm and the implementation.
Robust cybersecurity protocols, combining these measures, provide a comprehensive defense strategy.
Recent surveys suggest online security is improving, a welcome trend. However, Sony’s recent attempts at new copy protection strategies, detailed in this article sony attempts new copy protection strategy , might complicate matters if not implemented carefully. Despite this, the overall picture remains positive, pointing towards a brighter future for online safety.
Security Protocol Comparison Table
| Security Protocol | Description | Level of Protection | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple forms of verification | High | Adds significant complexity for attackers | Reliance on user vigilance; potential for MFA fatigue |
| Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-256) | Sophisticated encryption algorithm | Very High | Virtually indecipherable data | Complexity of implementation; key management is crucial |
| Intrusion Detection System (IDS) | Monitors network traffic for malicious activity | Medium to High | Early detection of threats | False positives; needs continuous updates |
Public Perception and Awareness
Public perception of online security is a crucial factor in the overall success of security measures. A growing awareness of threats and a corresponding shift in user behavior are vital for a safer digital environment. This section examines how public understanding of online security has evolved and the role of various factors in shaping this awareness.
Growing Awareness of Online Security Threats
Public awareness of online security threats has demonstrably increased over the past decade. This rise is fueled by a confluence of factors, including high-profile data breaches, increased media coverage of cybercrimes, and the rising sophistication of online threats. People are now more aware of the potential risks associated with sharing personal information online, downloading suspicious files, and clicking on phishing links.
This heightened awareness is a positive development, as it encourages more cautious online behavior.
Influence of Public Education Campaigns
Public education campaigns have played a significant role in influencing user behavior and raising awareness. These campaigns, often launched by government agencies, cybersecurity organizations, and tech companies, have targeted various demographics with tailored messages. Examples include educational materials highlighting phishing tactics, explaining the importance of strong passwords, and demonstrating secure online shopping practices. These campaigns have helped people understand the threats and take proactive steps to protect themselves.
Role of Online Communities and Social Media
Online communities and social media platforms have become powerful tools for disseminating security awareness. Users sharing personal experiences, tips, and warnings foster a collective knowledge base. Social media campaigns, with their viral potential, can reach a broad audience and encourage discussion around online safety. The rapid dissemination of information, often through trending topics and memes, has made online safety a shared concern, encouraging users to adopt better security practices.
Evolution of User Awareness
| Year | Awareness Level (Estimated) | Key Events Influencing Awareness |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | Low to Medium | Limited media coverage of major data breaches, nascent social media awareness. |
| 2015 | Medium | Increased media coverage of major data breaches, rise of cybersecurity awareness campaigns. |
| 2020 | High | High-profile ransomware attacks, significant social media awareness campaigns, widespread remote work. |
| 2025 | Very High (projected) | Continued sophistication of cyber threats, focus on AI-powered attacks, ongoing user education initiatives. |
The table above illustrates a projected increase in user awareness over time, suggesting a positive trend. However, it’s important to note that awareness levels vary considerably across demographics and regions. Ongoing efforts to educate and inform are essential to ensure a high level of user preparedness.
Challenges and Future Trends
The journey towards complete online security is an ongoing process, marked by constant evolution in both the threats and the defenses. While significant progress has been made, vulnerabilities persist, and new threats emerge with alarming frequency. Understanding these challenges is crucial to anticipating future needs and implementing proactive strategies.The digital landscape is inherently dynamic. As technology advances, so do the tactics employed by malicious actors.
Recent surveys show online security is definitely improving, a welcome trend. However, the parallel rise of RFID technology is bringing some interesting challenges, like the US legislation surrounding it and the protests in Europe, as seen in this article on RFID brings legislation in US protest in Europe. Despite these developments, the positive survey results on online security remain encouraging.
Staying ahead of the curve requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses technological innovation, public awareness, and proactive security measures.
Remaining Obstacles to Complete Online Security
The quest for total online security faces several hurdles. One major challenge is the sheer scale and complexity of the internet itself. The interconnected nature of networks and systems creates intricate pathways for attacks, making it difficult to identify and mitigate all potential vulnerabilities. Furthermore, the rapid pace of technological advancement often outpaces the development of security measures, creating a gap that attackers can exploit.
Finally, a significant barrier is the human element; user error, lack of awareness, and the temptation of convenience can create openings for cybercriminals.
Emergence of New Online Threats
New online threats continuously emerge, often leveraging the latest technologies. Sophisticated phishing campaigns that mimic legitimate websites and social media accounts are a prime example. These campaigns are designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details. Another notable threat is the rise of ransomware, which encrypts user data and demands payment for its release.
This tactic is particularly effective against organizations and individuals who rely heavily on their data. Finally, the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in cyberattacks presents a significant concern. AI-powered tools can automate attacks, making them more frequent and difficult to detect.
Emerging Technologies and their Impact on Online Security
Emerging technologies like blockchain, quantum computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) present both opportunities and challenges for online security. Blockchain technology, while offering enhanced security through cryptographic techniques, also introduces new vulnerabilities if not implemented correctly. Quantum computing, with its potential to break current encryption methods, necessitates the development of post-quantum cryptography to safeguard sensitive data. The growing number of interconnected devices in the IoT creates a vast attack surface, requiring robust security protocols for each device.
Ensuring interoperability and security across diverse platforms and systems is a crucial area of ongoing development.
Potential for Future Advancements in Online Security
The potential for future advancements in online security is significant. Enhanced AI-powered threat detection systems, capable of identifying and responding to sophisticated attacks in real-time, are being developed. Advanced encryption techniques, resilient to attacks from quantum computers, are under active research and development. Finally, the ongoing development of zero-trust security models, which verify the identity of every user and device before granting access, promises to enhance the security posture of organizations and individuals.
Projected Growth of Cyber Threats (Next 5 Years)
| Year | Projected Growth Rate (Estimated Percentage Increase in Attacks) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 15% | Continued evolution of existing threats, increased use of AI in attacks. |
| 2025 | 20% | Increased sophistication of phishing and social engineering attacks, rise of IoT-based attacks. |
| 2026 | 25% | More widespread adoption of ransomware-as-a-service, greater reliance on cloud computing creates new vulnerabilities. |
| 2027 | 30% | Emergence of new attack vectors leveraging quantum computing, continued pressure on legacy systems. |
| 2028 | 35% | Greater reliance on decentralized systems and the rise of attacks targeting supply chains. |
Note: These figures are estimates and can vary depending on factors such as technological advancements, security measures implemented, and geopolitical events.
Impact on Different Sectors
Improved online security isn’t just a technical advancement; it’s a fundamental shift impacting various sectors, from the financial markets to the everyday consumer. This enhanced security landscape fosters trust, encourages innovation, and ultimately shapes the way businesses and individuals navigate the digital world. The impact is far-reaching, affecting everything from investment strategies to personal shopping habits.The evolving nature of online threats necessitates a constant adaptation to robust security measures.
This adaptation isn’t merely reactive; it’s proactive, driving innovation in security protocols and user awareness. The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks necessitates a parallel evolution in security solutions, ensuring a dynamic balance between threat mitigation and user experience.
Impact on Finance
Robust security measures in the financial sector are paramount. Enhanced encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and advanced fraud detection systems are critical to safeguarding sensitive financial data. The integration of these measures into banking applications, online payment gateways, and investment platforms creates a more secure environment for transactions and investments. For example, the widespread adoption of biometric authentication in online banking is a testament to this evolving security landscape.
This proactive approach protects customers from fraudulent activities, fostering trust in online financial services.
Impact on Healthcare
Protecting patient data is paramount in the healthcare sector. Data breaches can have severe consequences, leading to identity theft, financial losses, and compromised patient care. Implementing robust encryption, access controls, and secure data storage solutions safeguards sensitive medical information. The integration of these security measures into electronic health records (EHRs) and telehealth platforms creates a more secure environment for patient care.
A prime example is the increasing use of secure messaging platforms for patient communication, ensuring the confidentiality of health information.
Impact on Retail
Improved online security benefits both businesses and consumers in the retail sector. Secure payment processing, data encryption, and fraud prevention measures build consumer trust and enhance the online shopping experience. Businesses benefit from reduced losses due to fraud and increased customer loyalty. The integration of security measures into e-commerce platforms, loyalty programs, and online marketplaces is crucial for maintaining a secure and trustworthy shopping environment.
For instance, the use of tokenization in online payments is a prominent example of how security measures can improve customer confidence and protect sensitive financial information.
Impact on Businesses and Individuals
Improved online security impacts businesses and individuals in distinct but interconnected ways. For businesses, enhanced security measures translate into reduced financial losses from cyberattacks, increased customer trust, and a more robust digital presence. For individuals, enhanced security fosters greater trust in online services, reduces the risk of identity theft, and enables a more secure online experience. The evolution of security measures reflects a shift towards proactive security measures that address both individual and corporate vulnerabilities.
Comparison of Impact on Businesses and Individuals
| Aspect | Businesses | Individuals |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Impact | Reduced losses from cyberattacks, increased revenue from increased customer trust. | Reduced risk of identity theft, enhanced financial security, greater trust in online services. |
| Security Measures | Investment in advanced security software, multi-factor authentication, secure infrastructure. | Awareness of phishing scams, use of strong passwords, regular software updates. |
| Adaptation | Adapting business practices and infrastructure to new security standards. | Adapting online behaviors and adopting secure practices. |
Illustrative Case Studies
Improved online security isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s a tangible force that protects individuals and organizations from significant harm. Real-world case studies showcase how proactive security measures can prevent major incidents and mitigate potential risks. These examples highlight successful strategies, offering valuable lessons for everyone navigating the digital landscape.These case studies provide a practical lens through which to view the effectiveness of current security practices.
They demonstrate how preventative measures, when implemented correctly, can thwart malicious attacks and safeguard sensitive data. The following examples illustrate successful security strategies and highlight the importance of proactive measures.
Preventing Data Breaches through Multi-Factor Authentication
Proactive security measures, like multi-factor authentication (MFA), play a crucial role in preventing data breaches. A notable example is the significant decrease in account takeovers observed at a major online retailer after implementing MFA. This change effectively deterred attackers who previously relied on compromised credentials. By requiring multiple forms of verification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to a mobile device, MFA substantially strengthens security, making it far more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Strengthening Security Protocols to Counter Phishing Attacks
Organizations are increasingly recognizing the need to bolster security protocols to counter the growing threat of phishing attacks. A leading financial institution successfully mitigated a series of phishing attempts by implementing a comprehensive security awareness training program for employees. This program educated employees about the characteristics of phishing emails and taught them how to identify and report suspicious communications.
This proactive approach significantly reduced the number of successful phishing attacks, thereby safeguarding sensitive financial data.
Enhancing Security Infrastructure to Deter Malware Attacks
Organizations are increasingly enhancing their security infrastructure to deter malware attacks. A large software company successfully reduced malware infections by implementing a robust endpoint detection and response (EDR) system. This system proactively identified and contained malicious software on employees’ devices, minimizing the impact of potential breaches. This proactive approach significantly reduced the risk of data breaches and disruption to business operations.
Recent surveys show online security is improving, a positive trend. This positive shift is likely boosted by companies like Sun, who recently appointed a new software boss. This new hire at Sun appoints new software boss could signal further enhancements in their security protocols, which in turn contributes to the overall upward trend in online security.
So, all in all, things are looking up for internet safety.
Table Summarizing Case Studies
| Case Study | Security Measure Implemented | Impact | Key Takeaways |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Retailer | Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Significant decrease in account takeovers | MFA is a crucial security layer against unauthorized access. |
| Financial Institution | Security Awareness Training | Reduced phishing attempts | Educating employees is a vital part of a robust security strategy. |
| Software Company | Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | Reduced malware infections | Proactive security tools like EDR can significantly reduce malware threats. |
Lessons Learned from These Examples
These case studies underscore several key lessons. Firstly, a layered approach to security, incorporating multiple preventative measures, is essential. Secondly, proactive measures, such as security awareness training, are as critical as technical safeguards. Thirdly, continuous monitoring and adaptation to evolving threats are vital to maintaining a strong security posture. Finally, collaboration between IT security teams and other departments is critical for successful security implementation.
By learning from these examples, organizations can better protect themselves and their users from online threats.
User Behavior and Security Practices
Our online security hinges critically on our individual actions. Understanding how we interact with the digital world is paramount to fortifying our defenses against evolving threats. This section delves into the significant role user behavior plays in online security outcomes, common pitfalls, and crucial best practices.User behavior is a significant factor influencing the success or failure of online security measures.
From the seemingly innocuous click to the seemingly simple password choice, our daily digital habits directly impact our vulnerability to cyberattacks. By identifying common mistakes and promoting proactive security practices, we can empower individuals to become active participants in their own online safety.
Common Security Mistakes, Survey shows online security getting better
User error often forms the weakest link in online security. A combination of carelessness and a lack of awareness creates significant opportunities for malicious actors. Common mistakes include failing to update software, neglecting to use strong passwords, and clicking on suspicious links.
- Failing to Update Software: Outdated software often harbors known vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Regular updates patch these weaknesses, providing a crucial defense layer. Failure to apply these updates exposes users to potential threats.
- Using Weak Passwords: Simple, easily guessed passwords are a prime target for hackers. Employing sophisticated password managers and adhering to strong password criteria significantly enhances security.
- Clicking on Suspicious Links: Phishing emails and malicious websites often lure users with enticing offers or threats. Exercising caution and verifying the legitimacy of links before clicking them prevents infections and data breaches.
Importance of Strong Passwords and Account Security
Robust passwords and strong account security practices are fundamental to online safety. A strong password is more than just a string of characters; it’s a crucial defense against unauthorized access.
- Creating Strong Passwords: A strong password combines upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information, like birthdays or names. Password managers automate the process of creating and storing strong passwords, improving security and convenience.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity with more than one factor, such as a code sent to their phone or a security key. Activating MFA on accounts enhances protection significantly.
- Regular Account Reviews: Periodically reviewing account settings and security measures ensures that the security posture remains aligned with evolving threats. This vigilance helps prevent potential breaches.
Best Practices for Safe Online Behavior
Implementing proactive security measures in daily online activities is essential. These measures significantly reduce vulnerability to cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attempts: Be suspicious of unsolicited emails, messages, or calls requesting personal information. Verify the legitimacy of requests before responding. Phishing attempts often use deceptive tactics to trick users.
- Use Secure Wi-Fi Networks: Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive activities. If necessary, use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your connection and protect your data. Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured and susceptible to attacks.
- Practice Safe Browsing Habits: Avoid visiting suspicious websites and be cautious about downloading files or clicking links. Use reputable antivirus software and keep it updated to detect and prevent malicious software.
Common Online Security Pitfalls and Consequences
A comprehensive understanding of potential pitfalls and their associated consequences is critical to informed security practices.
| Pitfall | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|
| Weak passwords | Unauthorized access to accounts, financial loss, identity theft |
| Ignoring security alerts | Data breaches, financial fraud, malware infections |
| Clicking on suspicious links | Malware infections, identity theft, data breaches |
| Using public Wi-Fi for sensitive tasks | Data interception, unauthorized access to personal information |
| Not updating software | Exploitable vulnerabilities, malware infections |
Closure
In conclusion, the survey data paints a positive picture of online security’s evolution. While challenges remain, the improvements in security protocols, user awareness, and technological advancements are noteworthy. The future looks promising, with continued progress expected as we navigate the ever-changing digital landscape. Individuals and businesses must remain vigilant and proactive in adopting the latest security measures to stay ahead of evolving threats.