Symantec Exec Named U.S. Internet Security Chief A New Era
Symantec exec named u s internet security chief – Symantec exec named U.S. internet security chief signals a significant shift in national cybersecurity strategy. This appointment, bringing a wealth of experience from the private sector, promises to shape the future of internet protection in the US. The new chief’s responsibilities will encompass a wide range of duties, from addressing current threats to developing long-term strategies.
The appointment comes at a crucial time for U.S. internet security, with evolving threats and vulnerabilities demanding innovative solutions. The new chief’s background and expertise in the private sector are poised to bring a fresh perspective and potential solutions to the challenges facing the nation’s digital infrastructure.
Contextual Background: Symantec Exec Named U S Internet Security Chief
The appointment of a U.S. internet security chief represents a critical step in bolstering national cybersecurity defenses. This role, though not entirely new in concept, signifies a heightened awareness of the increasingly complex and pervasive threats facing the digital infrastructure of the nation. The position requires a deep understanding of the current landscape of cyber vulnerabilities, the organizational structure of relevant government agencies, and the historical context of previous efforts in this domain.The current state of U.S.
internet security is characterized by a multitude of sophisticated threats, demanding a comprehensive and coordinated response. From ransomware attacks crippling critical infrastructure to nation-state-sponsored cyber espionage, the dangers are diverse and ever-evolving. Understanding these evolving threats and vulnerabilities is essential to developing effective countermeasures.
Current State of U.S. Internet Security
The U.S. faces a complex web of cyber threats. Sophisticated nation-state actors are actively seeking to penetrate critical infrastructure, steal sensitive data, and disrupt operations. Ransomware attacks, often targeting businesses and government agencies, have become increasingly prevalent, causing significant financial and operational disruption. Vulnerabilities in software, outdated systems, and human error remain persistent weak points.
Significance of the U.S. Internet Security Chief
The U.S. internet security chief plays a pivotal role in coordinating and directing national cybersecurity efforts. This individual serves as a focal point for interagency collaboration, fostering a cohesive approach to tackling threats. This position is critical for driving policy changes, allocating resources, and ensuring a strategic alignment across various government departments.
Historical Context of Previous Appointees
The role of a national cybersecurity coordinator, while evolving, has roots in previous efforts. Examining the impact of previous appointees reveals a spectrum of successes and challenges. Some appointees have focused on specific legislative initiatives, while others have concentrated on improving interagency collaboration. Evaluating the outcomes of these prior efforts offers insights into the efficacy of various strategies and their long-term implications.
Organizational Structure of Relevant Government Agencies
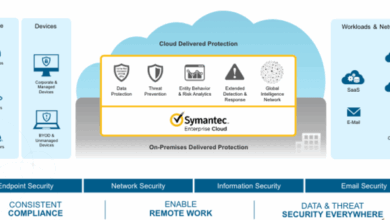
Understanding the structure of the government agencies involved in cybersecurity is essential. The Department of Homeland Security (DHS), the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the National Security Agency (NSA), and the FBI all play critical roles in defending the U.S. digital infrastructure. Their interconnected responsibilities and overlapping mandates require clear lines of communication and collaboration to avoid duplication and ensure optimal resource allocation.
| Agency | Primary Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| DHS | Oversight of domestic security, including cybersecurity aspects |
| CISA | Focus on national cybersecurity and infrastructure protection |
| NSA | National intelligence gathering and analysis, including cybersecurity |
| FBI | Investigation of cybercrimes and threats |
Potential Implications
The appointment of a U.S. internet security chief at Symantec signals a significant shift in the landscape of cybersecurity. This move reflects a growing recognition of the critical need for a unified and proactive approach to internet security, particularly in the face of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. This appointment has the potential to reshape policies, regulations, and international collaborations in the field.This strategic appointment promises to have a profound impact on the cybersecurity ecosystem, influencing everything from government regulations to private sector practices.
The specific implications of this appointment will likely depend on the specific policies and initiatives championed by the new leader, as well as the evolving cyber threat landscape.
Impact on Cybersecurity Policies and Regulations
The appointment will likely encourage the development of more comprehensive and stringent cybersecurity policies and regulations. This is especially true given the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks and the growing reliance on interconnected digital systems. Existing policies might be updated to reflect the changing threat environment and the need for enhanced security measures. For example, recent data breaches have highlighted the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to cyberattacks, leading to calls for more robust regulatory frameworks.
A Symantec executive taking on the US internet security chief role is certainly a big deal. However, recent developments like the Scos evidence raising questions about the case are definitely casting a shadow over the whole situation. This raises interesting questions about the larger picture of cybersecurity, especially given the potential impact on the new chief’s approach and responsibilities.
For more details on the Scos evidence, check out this article: scos evidence raises questions about case. Regardless, it’s still a significant appointment for the US internet security landscape.
A dedicated security chief can drive this process, leading to potentially significant changes in policy.
Impact on International Relations and Cooperation
The appointment could significantly influence international relations and cooperation in cybersecurity. A unified U.S. approach, spearheaded by a dedicated security chief, can encourage greater collaboration with international partners. This could lead to shared intelligence, best practices, and joint efforts to combat transnational cybercrime. Such collaborations are crucial given the global nature of cyber threats.
Symantec’s new exec named US internet security chief is a big deal, especially considering the rapidly evolving landscape of digital threats. This appointment highlights the critical need for robust security measures, but the rise of RFID technology, like in the case of RFID emerging to threaten the bar code , might just change how we approach physical security too.
Ultimately, it’s all part of the ongoing digital transformation, and Symantec’s new leader will have their work cut out for them.
For instance, the recent ransomware attacks targeting critical infrastructure have highlighted the need for international cooperation to share information and develop coordinated responses.
With a Symantec exec now heading up US internet security, it’s interesting to consider the broader tech landscape. The recent news about Intel focusing on broadband wireless chips, like intel to focus on broadband wireless chips , highlights the interconnectedness of these sectors. Ultimately, strong internet security is crucial, especially as reliance on wireless connections grows.
This new appointment seems timely and relevant given these developments.
Influence on Future Cybersecurity Strategies
The appointment might shape future cybersecurity strategies by focusing on proactive measures, rather than just reactive ones. This proactive approach could involve identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities before they are exploited, fostering greater collaboration between government and private sectors, and investing in advanced threat detection and response capabilities. A key component of this strategy could involve developing a more comprehensive understanding of the interconnected nature of digital systems and the vulnerabilities they present.
Potential Effects on the Private Sector
The appointment could encourage a more proactive and unified approach to cybersecurity within the private sector. Businesses will likely be encouraged to adopt stronger security measures, such as enhanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and improved incident response plans. The potential for increased regulatory scrutiny will also motivate private sector investments in cybersecurity infrastructure. For instance, companies operating in critical infrastructure sectors might face stricter regulations, leading to significant investments in security enhancements.
This will have a cascading effect on other sectors as they strive to maintain similar levels of security.
Analysis of the Role
Stepping into the role of US Internet Security Chief at Symantec presents a significant shift for the executive. This position demands a deep understanding of the evolving cyber landscape, the ability to navigate complex regulatory environments, and a strategic vision for proactively addressing emerging threats. Analyzing the executive’s prior experience provides crucial insight into their preparedness for this demanding leadership role.The analysis below delves into a comparison between the executive’s previous responsibilities and their new role at Symantec.
This comparative assessment will highlight key similarities and differences, illuminating the strengths and potential areas for development within this new leadership capacity.
Comparison of Previous and Current Roles
This section Artikels a comparative analysis of the executive’s previous role and their current role at Symantec. Understanding the nuances between these positions is critical to assessing the executive’s suitability for the new role.
| Category | Previous Role | Current Role |
|---|---|---|
| Responsibilities | Likely focused on a specific aspect of cybersecurity, such as threat intelligence, incident response, or product development within a smaller or mid-sized team. Potential responsibilities included developing and implementing security strategies, managing budgets, and collaborating with internal and external stakeholders. | Responsibilities encompass the entire US internet security landscape for Symantec. This includes developing and implementing national security strategies, managing budgets across multiple security sectors, and coordinating with government agencies, industry peers, and other stakeholders. |
| Experience | Likely includes practical experience in a specific cybersecurity area, with experience in managing teams, projects, or products. Experience might range from technical expertise to leadership roles, depending on the prior role. | Requires experience in leading complex, large-scale initiatives and building strong relationships with various stakeholders. A proven track record in developing and implementing cybersecurity strategies at a national level is paramount. Furthermore, the ability to influence policy and navigate complex political landscapes is crucial. |
Prior Experience and New Role Alignment
The executive’s prior experience is a key factor in assessing their readiness for this new role. A successful transition hinges on the alignment between past accomplishments and the demands of the current position. For example, if the executive has a strong background in incident response, this experience could be leveraged to develop effective incident response strategies at a national level.
Key Differences and Similarities
The table below summarizes the key differences and similarities between the executive’s previous role and their current role. Understanding these contrasts is crucial for a comprehensive evaluation.
- Differing Scope: The new role encompasses a significantly broader scope, moving from a departmental or divisional focus to a national-level responsibility. This demands a higher level of strategic thinking, policy expertise, and inter-agency collaboration.
- Increased Complexity: Navigating the complexities of the US internet security landscape, with its intricate regulatory frameworks and numerous stakeholders, is substantially more challenging than the previous role. The new role necessitates a deep understanding of geopolitical factors and their impact on cybersecurity initiatives.
- Enhanced Leadership Requirements: The current role necessitates a more substantial leadership role, including the ability to influence policy, collaborate with diverse teams, and represent Symantec effectively in high-level discussions and negotiations.
Future Outlook
The appointment of a new U.S. Internet Security Chief signals a crucial shift in the nation’s approach to cybersecurity. This role carries significant responsibility for proactively addressing the ever-evolving threat landscape, and the future success of this new position hinges on a strategic focus on both policy and technological advancements. The chief will play a vital role in shaping the future of digital security, especially concerning critical infrastructure.
Potential Areas of Focus, Symantec exec named u s internet security chief
The new security chief will likely focus on several key areas. These include strengthening existing cybersecurity frameworks, bolstering international partnerships, and spearheading innovative technological solutions to combat emerging threats. Crucially, the chief will need to bridge the gap between policy and implementation, ensuring that security measures are effectively integrated across various sectors.
Potential Future Challenges and Opportunities
The following table Artikels potential future challenges and opportunities in U.S. internet security. These issues demand a comprehensive and multifaceted approach to cybersecurity, requiring constant adaptation and innovation.
| Area | Challenge | Opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| Policy | Balancing national security interests with individual privacy rights in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. This requires meticulous policy revisions and public-private collaborations to address evolving threats. Examples include the potential for overreach in surveillance or the challenges in regulating emerging technologies like artificial intelligence. | Developing robust and adaptable cybersecurity policies that proactively address emerging threats while respecting fundamental rights. This can be achieved by incorporating international best practices, promoting transparency, and fostering collaboration between government agencies, industry, and academia. The success of such an approach could be observed in the response to ransomware attacks, fostering industry-government partnerships. |
| Technology | Keeping pace with the rapid advancement of malicious technologies. Maintaining an effective defense against sophisticated cyberattacks requires constant innovation in detection, prevention, and response capabilities. The rise of quantum computing and AI pose significant challenges for current security protocols. | Harnessing emerging technologies, like artificial intelligence and machine learning, to enhance security systems. These technologies can be used to develop more sophisticated detection systems, predict and prevent attacks, and rapidly respond to breaches. This can be seen in the development of AI-powered intrusion detection systems. |
Impact on Critical Infrastructure Security
The appointment of a dedicated security chief for the U.S. internet will have a profound impact on the security of critical infrastructure. The chief will be responsible for coordinating cybersecurity efforts across various sectors, from energy and transportation to finance and healthcare. This centralized approach can help prevent widespread disruptions caused by cyberattacks. This means bolstering defenses across these sectors, particularly for systems and networks that are vital to the nation’s infrastructure.
This will require a multi-layered approach, including advanced threat detection, robust incident response plans, and regular vulnerability assessments. The potential impact is significant; a successful strategy can protect against catastrophic disruptions to essential services.
Strategies to Address Future Cybersecurity Threats
Developing and implementing effective strategies to address future cybersecurity threats in the digital age is crucial. These strategies must be proactive, adaptable, and inclusive. A comprehensive strategy will include:
- Investing in advanced cybersecurity technologies: This includes investing in research and development for new detection and response tools, as well as fostering partnerships with private sector innovators to develop and deploy these tools quickly.
- Strengthening international cooperation: This involves collaborating with other nations to share intelligence, best practices, and resources to combat cyber threats that transcend borders. International cooperation is essential to address the global nature of cybercrime.
- Promoting cybersecurity education and awareness: This includes educating the public and private sectors on how to identify and mitigate cyber threats, thereby reducing the vulnerability of systems and networks to malicious actors.
Visual Representation

Visual representations are crucial for understanding complex topics like the evolution of internet security threats, organizational structures, and the impact of appointments on various sectors. These visualizations can effectively communicate intricate relationships and potential outcomes in a concise and easily digestible format. They facilitate a deeper comprehension of the dynamics involved, promoting a clearer understanding of the subject matter.
Evolution of Internet Security Threats
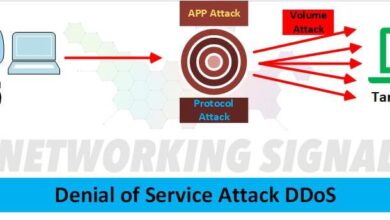
The evolution of internet security threats mirrors the ever-evolving landscape of technology. Initially, threats were predominantly focused on individual systems and networks. As the internet expanded and interconnected systems became more complex, attacks diversified and increased in sophistication.
A timeline graph depicting the evolution would show a gradual increase in the frequency and complexity of attacks. Early threats could be represented by a small, steady rise in the line graph. As time progressed, a steeper upward trend would represent the increasing sophistication of malware, phishing campaigns, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. The graph would also highlight key events like the rise of ransomware, cryptojacking, and social engineering tactics.
Each new threat type could be marked on the timeline, allowing for a clear visualization of how threats have become more sophisticated and widespread.
Organizational Structure of Relevant Government Agencies
Visualizing the structure of relevant government agencies involved in cybersecurity provides a clear understanding of the roles, responsibilities, and interdependencies.
A hierarchical organizational chart would be most effective. The chart should depict the structure of the relevant agencies, including the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), and the National Security Agency (NSA). This structure could be visualized by different levels and branching out of departments and sub-agencies. Relationships between these agencies could be shown using connecting lines, indicating collaborative efforts or areas of shared responsibility.
This visual representation would facilitate a clear understanding of how these agencies work together.
Potential Impact of the Appointment on Different Sectors
The appointment of a new US internet security chief can have a wide range of impacts across various sectors. A visual representation is essential to understand the potential ramifications for these sectors.
A matrix would be suitable. The matrix’s rows could represent different sectors (e.g., finance, healthcare, critical infrastructure) while the columns could represent potential impacts (e.g., enhanced security posture, increased compliance requirements, new regulations, economic benefits, economic risks). Each cell could contain a descriptive summary of the potential impact. For example, the cell for “finance” and “enhanced security posture” could describe the potential for improved fraud prevention measures.
A color-coded system (e.g., green for positive impact, red for negative impact) would further enhance the visual appeal and clarity of the matrix.
Potential Future Trends in Cybersecurity
Predicting the future of cybersecurity requires analyzing current trends and potential developments. A visual representation can help illustrate potential future directions.
A mind map would be ideal for illustrating future trends. The central idea could be “Future Cybersecurity Trends.” Branches could represent emerging technologies (e.g., AI, quantum computing), evolving attack vectors (e.g., supply chain attacks, zero-day exploits), and defensive strategies (e.g., advanced threat detection, zero trust architecture). Each branch could be further expanded with examples of specific trends, such as the increasing use of AI for both offense and defense, or the rise of sophisticated attacks targeting cloud environments.
This visual representation would aid in understanding the interconnectedness of these trends.
Final Summary

This appointment of a Symantec executive as the U.S. internet security chief marks a pivotal moment in the nation’s approach to cybersecurity. The implications for policy, international cooperation, and the private sector are significant. Looking ahead, the new chief’s focus and the evolving threat landscape will shape the future of digital security in the U.S. and beyond.