Tech Companies Rally Around Ethernet A Deep Dive
Tech companies rally around ethernet, signaling a significant shift in network infrastructure. This renewed focus on Ethernet reflects a growing recognition of its advantages in data centers and cloud computing. From high-speed data transfer to enhanced reliability, ethernet offers a compelling alternative to traditional technologies. This in-depth look explores the reasons behind this surge in interest, examining the benefits, applications, future trends, challenges, and the key players driving this evolution.
The current state of ethernet adoption in the tech industry shows a noticeable increase in recent years. Factors like the escalating demands for higher bandwidth and lower latency are pushing companies towards ethernet solutions. The rise of cloud computing and the need for seamless data transfer across geographically dispersed locations have also played a significant role. This article delves into the specific benefits, detailed applications, and the future implications of this trend.
Introduction to Ethernet Rally
The tech industry is witnessing a resurgence of interest in Ethernet, a networking technology that has been a cornerstone of data transmission for decades. While fiber optics have gained prominence in recent years, Ethernet’s reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness are driving a renewed focus, particularly in data centers and enterprise networks. This renewed interest signifies a shift from purely fiber-centric solutions towards a more integrated approach leveraging the strengths of both technologies.The increasing demand for high-bandwidth, low-latency connections in cloud computing, AI, and high-performance computing is a key factor in this resurgence.
Ethernet’s ability to support these demanding applications, with its adaptable speeds and cost-effective infrastructure, is driving this movement. This shift isn’t just about upgrading existing infrastructure; it’s about recognizing Ethernet’s potential as a vital component in future-proof network architectures.
Current State of Ethernet Adoption
Ethernet’s ubiquitous presence in consumer and enterprise networks is undeniable. Its versatility across a wide spectrum of applications, from home networking to data centers, demonstrates its enduring strength. However, recent years have seen a trend toward fiber optics for high-bandwidth applications. This has been partially driven by the sheer bandwidth capacity fiber optics can provide.
Factors Driving the Recent Increase in Interest
Several key factors are driving the current surge in interest in Ethernet technologies. Firstly, the ever-increasing demand for high-bandwidth and low-latency connections in cloud computing and data centers necessitates solutions that can scale efficiently. Ethernet, with its established infrastructure and readily available expertise, is proving to be an attractive solution to meet these demands. Secondly, the cost-effectiveness of Ethernet, especially when compared to more specialized high-bandwidth technologies in certain situations, makes it an attractive option for businesses looking to upgrade or expand their networks.
Finally, the continued development of higher-speed Ethernet standards is enabling a seamless transition to faster, more efficient data transmission.
Key Reasons Behind the Renewed Focus
Ethernet’s robust ecosystem, coupled with its adaptability, plays a crucial role in its renewed focus. The existing infrastructure and skilled workforce familiar with Ethernet technology make the transition smoother and more cost-effective than migrating to entirely new, often more complex, networking technologies. The inherent reliability and stability of Ethernet, proven over decades, provide a foundation of trust for organizations looking for secure and predictable data transmission.
This reliability, combined with its proven scalability, makes Ethernet an attractive option for future-proofing network infrastructure.
Ethernet Technologies and Applications
The evolution of Ethernet technologies has kept pace with the increasing demand for faster data transfer rates. This evolution has led to a range of technologies, each optimized for specific applications.
Tech companies are clearly rallying around ethernet, and for good reason. The speed and reliability are undeniable. But, as we’ve seen with the ongoing debate surrounding the Supreme Court, the underlying infrastructure is a critical part of the battle over the internet’s future. This conflict, detailed in the battle over supreme court already raging on the net , highlights the growing need for a robust and secure network infrastructure, making the tech community’s focus on ethernet even more relevant in the long run.
| Ethernet Technology | Speed (Gbps) | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 10GbE | 10 | High-performance computing, enterprise networking, storage area networks |
| 40GbE | 40 | Data centers, high-bandwidth applications, high-performance computing clusters |
| 100GbE | 100 | Data centers, high-performance computing, large-scale storage networks |
| 200GbE | 200 | High-bandwidth data centers, large-scale cloud computing, high-performance computing |
| 400GbE | 400 | Ultra-high-bandwidth data centers, next-generation cloud infrastructure, high-performance computing clusters |
Ethernet, with its diverse range of speeds and adaptable infrastructure, provides a robust solution for a wide spectrum of needs.
Benefits of Ethernet for Tech Companies: Tech Companies Rally Around Ethernet
Ethernet, a cornerstone of modern networking, offers significant advantages for tech companies operating data centers and cloud computing environments. Its robust performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make it a superior choice compared to many alternative technologies. This detailed look at ethernet’s benefits will explore how it enhances network performance and reliability, and why it often represents a more economical solution.
Data Centers and Cloud Computing
Ethernet’s adaptability and high-speed capabilities make it ideal for the demanding environments of data centers and cloud computing. Its ability to handle massive amounts of data with low latency allows for smooth operations and efficient processing. The reliable connections facilitate seamless data transfer, crucial for applications like cloud storage and high-performance computing. Modern data centers rely heavily on Ethernet’s ability to support a wide range of devices and applications, allowing for scalability and flexibility as needs evolve.
Enhanced Network Performance and Reliability
Ethernet’s structured cabling system contributes to a highly reliable network. This structured approach allows for organized connections and reduced errors, minimizing disruptions. The standardized protocols ensure consistent performance, while the use of dedicated physical connections avoids the interference and unpredictable behavior often associated with wireless technologies like Wi-Fi. Ethernet’s predictable performance is vital for applications that demand consistent speed and reliability, such as financial transactions and online gaming.
Cost-Effectiveness
While initial investment might seem higher than some alternatives, ethernet’s long-term cost-effectiveness shines through. The lower maintenance and troubleshooting costs, coupled with the reduction in downtime, significantly offset the potential higher upfront expense. The longevity of ethernet infrastructure and its ability to scale with growing needs translate into substantial savings over time. For example, companies with high data traffic volumes may find ethernet’s consistent speed and reliability outweigh the short-term cost advantage of less robust technologies.
Ethernet vs. Other Networking Technologies
| Feature | Ethernet | Wi-Fi | Fiber Optic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed (Gbps) | 1-100+ | 1-10 (variable) | 10-100+ |
| Latency (ms) | Low (sub-millisecond) | High (millisecond) | Low (sub-millisecond) |
| Cost (per connection) | Moderate | Low | High |
| Security | High, with appropriate measures | Lower than Ethernet (vulnerable to interception) | High, with appropriate measures |
| Scalability | Excellent | Moderate | Excellent |
Ethernet offers a robust and scalable solution for demanding network environments. While Wi-Fi provides convenience for mobile devices, its latency and security vulnerabilities make it less suitable for mission-critical applications. Fiber optic technology provides extremely high bandwidth but comes with a higher initial cost. Ethernet, often a middle ground, strikes a balance between cost, speed, and reliability. It allows for efficient scaling to meet future network demands and offers significant advantages in security, latency, and performance.
Specific Applications and Use Cases
Ethernet’s versatility extends far beyond basic connectivity. It’s a crucial backbone for high-performance computing, cloud infrastructure, and countless other applications across diverse tech sectors. From gaming to finance, the speed and reliability of ethernet are transforming how businesses operate and how consumers experience technology.
Ethernet in High-Performance Computing (HPC)
High-performance computing (HPC) relies heavily on the ability to transfer massive amounts of data quickly and reliably. Ethernet’s low latency and high throughput make it ideal for the demanding needs of HPC clusters. These clusters often consist of thousands of interconnected processors and storage devices, each requiring seamless communication. The ability of ethernet to handle these high data rates and maintain consistent performance is critical for scientific simulations, complex modeling, and data analysis in fields like genomics and climate research.
Ethernet’s Role in Cloud Services
Cloud services rely on the ability to rapidly transmit vast quantities of data to and from servers. Ethernet’s high bandwidth allows cloud providers to deliver significantly faster data transfer speeds. This translates to quicker response times for users accessing cloud-based applications, faster uploads and downloads, and a more responsive user experience. For example, a real-time video streaming service on the cloud benefits enormously from high-speed ethernet connections to ensure seamless video delivery.
Ethernet Use Cases Across Tech Sectors, Tech companies rally around ethernet
Ethernet’s importance transcends specific sectors. Its adaptability and high performance make it a vital component in various tech industries.
| Tech Sector | Specific Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Gaming | Ethernet enables low-latency, high-bandwidth connections for online gaming, crucial for smooth gameplay and avoiding lag. High-speed ethernet connections allow for seamless streaming and downloading of game assets and updates. |
| Finance | In financial institutions, ethernet is essential for high-speed transactions, ensuring that critical data is processed and transferred rapidly and securely. This includes trading platforms, risk management systems, and data warehousing. |
| Healthcare | Hospitals and medical research facilities use ethernet to transmit medical images, patient records, and other sensitive data. High-speed ethernet connections facilitate real-time monitoring of patients and quick access to critical information, potentially impacting patient outcomes. |
| Manufacturing | Ethernet is integral to the automation and data collection processes in modern manufacturing facilities. Connecting various machines and sensors through ethernet allows for real-time data analysis, optimized production processes, and efficient resource management. |
Future Trends and Projections

Ethernet, a foundational technology for data transmission, is poised for continued evolution. The increasing demand for faster, more reliable, and efficient network connections across various industries fuels innovation in this area. This evolution will significantly impact data centers and cloud infrastructure, shaping the future of how we access and utilize data.The next few years promise substantial advancements, driven by technological breakthroughs and industry needs.
Expect to see ethernet playing a crucial role in the continued expansion of cloud services and data-intensive applications. This is due to its adaptability and scalability, which makes it a key element in the infrastructure of the future.
Potential Future Developments in Ethernet Technology
Ethernet technology is constantly evolving, driven by the relentless pursuit of higher bandwidth and lower latency. Future developments will focus on leveraging new materials and innovative transmission techniques to achieve these goals. These developments will involve improvements in optical technologies for long-haul connections, advancements in signal processing to reduce errors, and exploring alternative transmission mediums like microwave or millimeter-wave frequencies.
Impact on Data Centers and Cloud Infrastructure
Ethernet’s role in modern data centers and cloud infrastructure is paramount. Its scalability and flexibility make it an ideal choice for supporting the ever-growing demands of cloud services. Future developments will enable even greater density and efficiency in data centers. This will allow for more powerful and cost-effective cloud computing resources, further driving cloud adoption across various industries.
Examples include faster cloud deployments, improved responsiveness of applications, and better resource utilization.
Growth Projections for Ethernet Adoption
Ethernet adoption is expected to continue its upward trajectory in the next five years. The ongoing expansion of data-intensive applications, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and high-performance computing, is a significant driver. Moreover, the need for reliable and high-speed connections in industries like finance and healthcare fuels the demand. These factors, combined with the continuous development of new ethernet standards, are expected to fuel the adoption of ethernet.
Tech companies are seemingly rallying around Ethernet, recognizing its robust and reliable performance. This resurgence in interest is intriguing, especially given the recent DOJ call for Microsoft to open more code, doj calls on microsoft to open more code. Perhaps this push for greater code openness will unlock new possibilities for Ethernet, boosting its already impressive capabilities and further solidifying its place in the tech world.
Future Ethernet Standards and Capabilities
The following table Artikels projected future ethernet standards and their anticipated capabilities. These standards are critical to meeting the growing demands of data-intensive applications and supporting the future of cloud computing.
| Standard | Anticipated Release Date | Data Rate (Gbps) | Latency (µs) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethernet 400GbE | 2024-2026 | 400 | 1.5-2.5 | High-performance computing, data centers |
| Ethernet 800GbE | 2027-2029 | 800 | 1.0-1.8 | Cloud infrastructure, supercomputers |
| Ethernet 1.6TbE | 2029-2031 | 1600 | 0.8-1.5 | Ultra-high-bandwidth data transfer |
Challenges and Considerations
The increasing adoption of Ethernet presents exciting opportunities for tech companies, but also introduces a range of challenges. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial for successful implementation and avoiding potential pitfalls. From complex deployments to security concerns, navigating these hurdles is vital for realizing the full benefits of Ethernet.
Potential Challenges Associated with Increasing Adoption
Ethernet’s widespread adoption, while promising, faces several hurdles. Compatibility issues between different Ethernet standards and devices can lead to unexpected performance problems or even system failures. Migrating existing infrastructure to support Ethernet can be costly and time-consuming, particularly in large organizations with extensive legacy systems. The sheer scale of a comprehensive Ethernet deployment requires significant planning, budgeting, and skilled personnel.
Technical Hurdles in Implementing Ethernet in Complex Environments
Deploying Ethernet in intricate environments, like data centers or industrial settings, presents unique technical challenges. Dealing with varying network topologies, diverse device types, and complex cabling requirements can be daunting. Ensuring high bandwidth and low latency across multiple floors or even across geographically dispersed locations requires meticulous planning and careful selection of networking equipment. Interoperability issues between different vendors’ equipment can also hinder the implementation process.
Comparison of Ethernet Deployment Complexities with Other Technologies
While Ethernet offers compelling advantages, its implementation complexity varies depending on the specific network environment. Deploying a wireless network, for instance, might involve fewer physical cabling requirements, but can face challenges with signal interference and security vulnerabilities. Fiber optic networks, while offering extremely high bandwidth, often necessitate specialized equipment and expertise for deployment and maintenance. Each technology has its own set of trade-offs, making a thorough analysis of the specific needs and constraints of the environment crucial.
Security Implications of Widespread Ethernet Use
The increasing reliance on Ethernet for critical infrastructure necessitates robust security measures. Vulnerabilities in the Ethernet network can expose sensitive data to unauthorized access or malicious attacks. Malicious actors could exploit weaknesses in the network infrastructure or devices to disrupt services or steal confidential information. Ensuring data integrity and confidentiality is paramount in a network environment that is increasingly interconnected.
Security Measures and Protocols for Secure Ethernet Implementations
Robust security protocols are essential for mitigating the security risks associated with Ethernet implementations.
| Security Measure | Protocol/Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | 802.1X | Verifies the identity of devices attempting to access the network. |
| Access Control | VLANs | Segment the network into smaller, isolated groups to restrict access to specific resources. |
| Data Encryption | IPsec, TLS | Encrypts data transmitted over the network to protect it from unauthorized interception. |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention | IDS/IPS systems | Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and prevent attacks. |
| Regular Audits and Security Assessments | Security Audits | Periodically evaluate the network security posture to identify and address vulnerabilities. |
Industry Players and Partnerships

The ethernet ecosystem thrives on collaboration and innovation. Numerous tech companies are actively involved in developing, implementing, and promoting ethernet technologies, fostering a dynamic and interconnected market. This section explores key players, their partnerships, and the impact of these collaborations on the future of ethernet.The evolution of ethernet is intrinsically linked to the strategic partnerships forged between companies.
These alliances enable the sharing of resources, expertise, and market reach, ultimately accelerating the adoption and improvement of ethernet solutions. Strong collaborations are critical for overcoming technical challenges and meeting the growing demands of high-performance networking.
Tech companies are clearly recognizing the benefits of ethernet, boosting its adoption across the board. This renewed focus on wired connections, however, doesn’t overshadow the exciting console market shakeup as Nintendo prepares to enter the fray. Their recent push into the console battle, as detailed in nintendo nudges into console battle , could potentially influence consumer choices and, in turn, impact the overall demand for high-speed ethernet solutions.
Ultimately, though, the fundamental appeal of ethernet for high-performance computing remains strong, ensuring its continued growth within the tech sector.
Key Companies Actively Promoting Ethernet
Several prominent tech companies are significant drivers of ethernet advancements. Their investments and strategic initiatives contribute significantly to the evolution and wider adoption of ethernet technologies.
- Cisco Systems: A global leader in networking, Cisco plays a pivotal role in developing and deploying ethernet solutions for various industries. Their extensive product portfolio, coupled with a strong commitment to research and development, positions them as a key player in the ethernet market.
- Juniper Networks: Juniper Networks is a significant player in the ethernet arena, specializing in high-performance networking equipment. Their expertise in advanced routing and switching technologies makes them a crucial contributor to ethernet infrastructure development.
- Intel Corporation: Intel’s involvement extends beyond CPUs to networking chips. Their development of ethernet network interface cards (NICs) is crucial for enabling fast and reliable data transmission. Intel’s influence is felt throughout the entire computing ecosystem.
- Broadcom Inc.: Broadcom is a significant semiconductor company with a strong presence in the ethernet chipset market. Their chipsets are foundational to many ethernet devices, highlighting their role in the broader ecosystem.
Key Partnerships and Collaborations
Strategic partnerships are essential for driving innovation and expanding market reach in the ethernet industry.
- Cloud Providers and Ethernet Vendors: Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud often collaborate with ethernet equipment manufacturers to ensure seamless network integration within their cloud infrastructures. This synergy enables efficient data transfer and optimized performance for their customers.
- Telecom Operators and Ethernet Vendors: Telecom operators are partnering with ethernet vendors to upgrade their network infrastructure and provide high-speed connectivity services. This collaboration is crucial for the deployment of next-generation fiber optic networks.
- Data Centers and Ethernet Equipment Manufacturers: Data centers are actively engaging with ethernet equipment manufacturers to design and deploy highly scalable and reliable networks. This partnership focuses on optimizing performance and capacity for handling increasing data volumes.
Impact of Collaborations on the Market
The collaborations between industry players have a significant impact on the ethernet market.
- Driving Innovation: Joint research and development efforts accelerate the introduction of new ethernet technologies and standards. This collaborative environment promotes innovation and the creation of cutting-edge solutions.
- Expanding Market Reach: Partnerships enable vendors to reach a wider customer base and penetrate new markets. This expanded reach fosters a more competitive environment and benefits consumers.
- Reducing Development Costs: Sharing resources and expertise through partnerships allows companies to reduce development costs and accelerate time to market. This translates into more affordable and accessible ethernet solutions.
Roles of Industry Players
Different industry players have distinct roles in shaping the ethernet landscape.
- Component Manufacturers: Companies focused on components, such as chipsets and cables, are fundamental to the ethernet ecosystem. Their contributions ensure the availability of reliable and high-performing building blocks for ethernet devices.
- Equipment Manufacturers: These companies design, build, and market the complete ethernet devices, from switches to routers. Their role is critical in bringing ethernet solutions to market.
- System Integrators: System integrators specialize in integrating ethernet solutions into complex systems. Their expertise is crucial in implementing and optimizing ethernet networks for specific applications.
Market Share and Influence of Key Companies
The following table provides a snapshot of the market share and influence of key companies in the ethernet industry. Note that precise market share data is often proprietary and not publicly available.
| Company | Market Share (Estimated) | Influence/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco Systems | Significant | Dominant player in networking equipment and standards |
| Juniper Networks | Significant | Strong presence in high-performance networking |
| Intel Corporation | Significant | Crucial role in networking chipsets and NICs |
| Broadcom Inc. | Significant | Key player in semiconductor solutions for ethernet |
Illustrative Examples
Ethernet’s versatility shines through in diverse tech company implementations. From streamlining data centers to enhancing specific applications, its efficiency is demonstrably impactful. This section delves into practical examples, highlighting both hypothetical and real-world scenarios.
Hypothetical Data Center Utilizing Ethernet
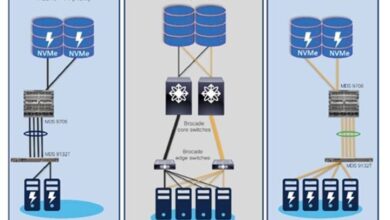
A modern data center designed for optimal performance leverages the speed and reliability of Ethernet. Imagine a facility housing thousands of servers. High-speed 100 Gigabit Ethernet connections are strategically deployed to connect servers, storage arrays, and network equipment. These connections are redundant, ensuring uninterrupted operations even in case of a failure. This redundancy is critical to maintain uptime and avoid service disruptions.
Fiber optic cables are extensively used to minimize signal degradation over longer distances. The network architecture employs advanced network management tools, which allow for real-time monitoring and proactive troubleshooting. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and maximizes resource utilization.
Real-World Example of Ethernet Adoption
A leading e-commerce company, experiencing escalating transaction volumes, saw significant improvements in website responsiveness and order processing speed after migrating to a high-performance Ethernet network. The old network, based on older technologies, struggled to handle the increased data traffic. The switch to Ethernet significantly reduced latency and increased bandwidth, leading to a demonstrably improved user experience. This improvement translated to higher customer satisfaction and, ultimately, increased sales.
Ethernet Case Study in a Specific Application
A financial institution leveraged Ethernet to improve transaction processing speed in its high-frequency trading (HFT) department. This application required extremely low latency and high bandwidth to execute trades rapidly and accurately. The institution implemented a high-performance Ethernet network with low-latency fiber optic connections. The implementation resulted in a significant reduction in trade execution time, allowing for more profitable transactions.
The success of this project proved Ethernet’s effectiveness in demanding applications requiring minimal latency.
Different Ethernet Implementations
| Implementation Category | Description | Typical Use Case | Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Ethernet Network | Basic Ethernet setup using standard Cat5e or Cat6 cables for connecting computers and devices in a small office or home office (SOHO). | Small offices, home offices, and light network traffic environments. | Lower bandwidth and latency compared to advanced implementations. |
| High-Performance Ethernet Network | Utilizes high-speed Ethernet connections, such as 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GbE) and 40 Gigabit Ethernet (40GbE), typically using fiber optic cables. | Data centers, large enterprises with heavy data traffic, and high-performance computing (HPC) environments. | Higher bandwidth and lower latency than simple implementations, enabling faster data transfer rates and reduced delays. |
| Redundant Ethernet Network | Employing multiple paths for data transmission, ensuring continuous operation even if one connection fails. Typically using redundant switches and routers. | Mission-critical applications, data centers, and financial institutions where network downtime is unacceptable. | High availability and reliability due to redundancy. May include advanced network management tools. |
Last Point
The renewed focus on ethernet by tech companies is a testament to its enduring power and versatility. Its cost-effectiveness, high performance, and reliability make it a compelling choice for a wide range of applications. While challenges remain in complex deployments and security considerations, the future of ethernet looks bright, with exciting developments and a predicted surge in adoption over the next few years.
The collaborative efforts of industry leaders, coupled with ongoing advancements in technology, position ethernet to remain a dominant force in the future of networking.