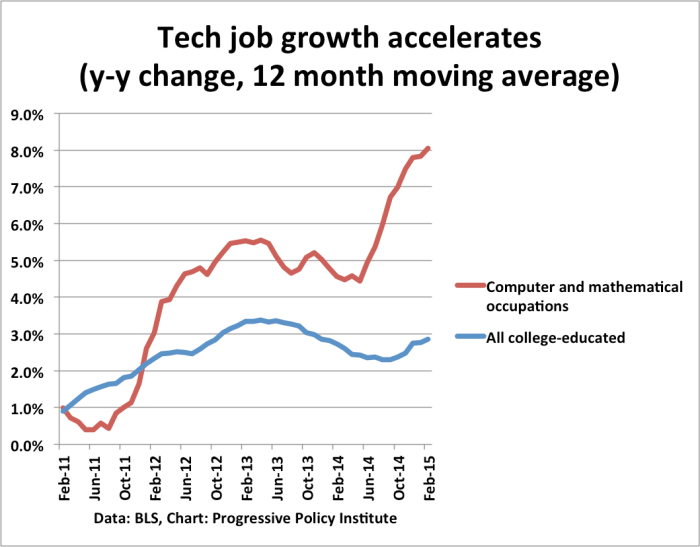
High-Tech Jobs A Booming Landscape
The burgeoning high tech employment landscape is exploding with opportunities, and this is the perfect time to dive into the details. From the current state of high-tech employment to the future of work, we’ll explore the diverse sectors, key trends, and the skills needed to succeed in this dynamic environment. We’ll also investigate the challenges and opportunities, and the impact of automation and AI on the job market.
This overview will examine the growth projections for different high-tech sectors over the next five years, outlining the key drivers behind these developments. We’ll delve into the essential skills and experience needed for specific high-tech roles, and analyze the salary trends and compensation packages for various positions within the industry.
Defining the High-Tech Employment Landscape
The high-tech employment landscape is a dynamic and rapidly evolving space, characterized by constant innovation and a high degree of specialization. This sector is no longer confined to Silicon Valley but has spread globally, impacting various aspects of modern life. Understanding its current state, key characteristics, and future trends is crucial for navigating this ever-changing terrain.The high-tech sector is defined by its reliance on technology, innovation, and a culture of rapid development.
This translates into high-growth potential for companies and employees alike, alongside the inherent challenges of adapting to continuous change and the need for constant upskilling.
Current State of High-Tech Employment
The high-tech employment landscape is currently experiencing significant growth, fueled by increased demand for technological solutions across numerous industries. This includes sectors such as software development, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, cybersecurity, and data analytics. The rapid advancements in these fields create a high demand for skilled professionals with specialized knowledge.
Key Characteristics of the Landscape
The dynamism of the high-tech landscape is a defining characteristic. This sector is characterized by a high degree of innovation, rapid technological advancements, and a constant need for adaptation. Growth is driven by factors such as globalization, increased consumer demand for technology-driven products and services, and the development of new markets. The high-tech landscape is also notable for its entrepreneurial spirit and the frequent emergence of startups and disruptive technologies.
Various Sectors Comprising the Landscape
The high-tech employment landscape encompasses a wide range of sectors, each with its own unique requirements and specializations. These sectors include:
- Software Development: This sector encompasses the creation and maintenance of software applications for various purposes, from mobile apps to enterprise-level systems. Demand for skilled developers is consistently high.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The development and application of AI technologies are key drivers in the high-tech sector. Roles range from machine learning engineers to AI ethicists, reflecting the importance of responsible technology development.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud infrastructure and services are crucial for many businesses. The demand for professionals with expertise in cloud architecture, security, and management is very strong.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting digital assets from cyber threats is essential. The need for cybersecurity experts is steadily growing with the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks.
- Data Analytics: The analysis and interpretation of large datasets are vital for informed decision-making. This sector requires professionals with strong analytical and statistical skills.
Comparison to Previous Eras
The high-tech employment landscape differs significantly from previous eras in employment. Prior eras often saw more stable, predictable industries with slower rates of technological change. The high-tech sector is marked by rapid advancements, demanding continuous learning, and an emphasis on agility and adaptability.
Major Trends Shaping the Landscape
Several major trends are shaping the high-tech employment landscape. These include:
- Automation: Automation is increasingly impacting various roles, leading to both job displacement and the creation of new roles requiring specialized skills to manage and maintain automated systems.
- Remote Work: The adoption of remote work models is altering the traditional workplace, with companies embracing flexibility and employees seeking work-life balance.
- Globalization: The global nature of the high-tech sector fosters opportunities for collaboration and innovation, but also presents challenges in terms of managing diverse teams and international regulations.
Projected Growth of High-Tech Sectors
The following table projects the growth of various high-tech sectors over the next five years, highlighting key drivers of this growth.
| Sector | Current Employment | Projected Growth | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Development | Estimated 5 million | 15-20% | Demand for applications, mobile apps, and enterprise software |
| Artificial Intelligence | Estimated 1.5 million | 25-30% | Growth in AI applications, machine learning, and deep learning |
| Cloud Computing | Estimated 2 million | 10-15% | Increased adoption of cloud services by businesses, data storage, and security |
| Cybersecurity | Estimated 1 million | 18-22% | Rise in cyber threats, need for advanced security measures |
| Data Analytics | Estimated 1.2 million | 12-18% | Growing need for data-driven decision making, business intelligence |
Skills and Talent Requirements
The high-tech sector is constantly evolving, demanding a dynamic skillset from its workforce. Adaptability, continuous learning, and a proactive approach to acquiring new knowledge are crucial for success. This rapid evolution necessitates a focus on emerging technologies and the ability to apply these skills in innovative ways. The most in-demand talents are those who can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.The future of high-tech employment hinges on individuals who can not only master core technical skills but also develop essential soft skills, such as collaboration, communication, and problem-solving.
The ability to learn and adapt quickly to new technologies and methodologies is paramount.
In-Demand Skills in High-Tech
The high-tech sector demands a diverse range of skills, spanning technical expertise, problem-solving abilities, and the capacity for collaboration. Core technical skills, including programming languages like Python and Java, data analysis tools, and cloud computing platforms, are essential. Furthermore, proficiency in software development methodologies and project management techniques is highly sought after.
Evolving Skillsets for Success
The skillsets required for success in high-tech roles are constantly evolving. The ability to learn and adapt quickly to new technologies and methodologies is paramount. This includes a proactive approach to acquiring new knowledge and a willingness to embrace new challenges. Furthermore, strong analytical and critical thinking skills are vital for navigating complex problems and developing innovative solutions.
Importance of Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for staying relevant in the high-tech landscape. The rapid pace of technological advancement necessitates a proactive approach to skill development. This involves actively seeking out new learning opportunities, such as online courses, workshops, and conferences. Furthermore, professionals should engage in peer-to-peer learning and mentorship programs to stay ahead of the curve.
The ability to adapt to changing industry trends and technological advancements is essential for long-term success.
Comparing Skillsets Across High-Tech Roles
Different high-tech roles demand distinct skill sets. Software engineers, for example, require strong programming and problem-solving skills. Data scientists, on the other hand, need expertise in statistical modeling, data visualization, and machine learning. Similarly, cybersecurity professionals need in-depth knowledge of network security protocols and threat detection methods. The key is to identify the specific skills and experience necessary for the chosen role and to continuously develop these competencies.
High-Tech Role Skillset Table
| Role | Essential Skills | Required Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Software Engineer | Programming languages (Java, Python, C++), software development methodologies, problem-solving | 1-3 years of experience in software development, understanding of software design principles |
| Data Scientist | Statistical modeling, data visualization, machine learning algorithms, data analysis tools (e.g., R, Python), programming languages | 2-5 years of experience in data analysis, familiarity with data warehousing and data mining techniques |
| Cybersecurity Analyst | Network security protocols, threat detection, cryptography, security software, incident response | 2-4 years of experience in IT security, familiarity with security policies and regulations |
| Cloud Architect | Cloud computing platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP), virtualization, security best practices, system design | 3-5 years of experience in IT infrastructure, familiarity with cloud deployment models |
Employment Opportunities and Challenges in the High-Tech Sector

The high-tech sector is a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape, presenting a plethora of employment opportunities for skilled individuals. However, navigating this environment comes with unique challenges, particularly for those new to the field. Understanding these opportunities and challenges is crucial for anyone looking to enter or advance within this sector.
Types of Employment Opportunities
The high-tech sector offers a diverse range of employment opportunities, spanning various roles and specializations. These roles can be categorized broadly into software development, data science, cybersecurity, and hardware engineering. Within these categories, sub-specializations are numerous and constantly emerging.
| Opportunity | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Software Engineer | High competition for entry-level positions, requiring strong coding skills and practical experience. |
| Data Scientist | Evolving skillset demands; staying current with the latest tools and techniques is crucial. |
| Cybersecurity Analyst | Rapidly changing threat landscape requires continuous learning and adaptation. |
| Hardware Engineer | Specialized knowledge and practical skills in circuit design, fabrication, and testing are often required. |
Emerging Roles and Specializations
The high-tech sector is characterized by constant innovation, leading to the emergence of new roles and specializations. Machine learning engineers, AI ethicists, and quantum computing specialists are just a few examples of these emerging roles. These roles often require a combination of technical expertise and soft skills, such as communication and problem-solving.
- Machine Learning Engineers: These professionals are crucial in developing and implementing machine learning algorithms across various applications. They require a strong understanding of algorithms, statistical modeling, and programming languages.
- AI Ethicists: With the increasing use of AI in decision-making processes, the need for professionals to evaluate and mitigate ethical concerns is growing. This role demands a deep understanding of AI, ethics, and societal impact.
- Quantum Computing Specialists: The field of quantum computing is rapidly expanding, creating new opportunities for professionals with expertise in quantum algorithms, hardware development, and theoretical physics.
Challenges Faced by Job Seekers
Navigating the high-tech employment landscape can be challenging for job seekers. Competition for desirable roles is often fierce, and maintaining up-to-date technical skills is crucial. The constant evolution of technologies and tools can also present difficulties for individuals seeking to stay current.
- Competition: The demand for skilled professionals in the high-tech sector often exceeds the available supply, leading to intense competition for positions. This is especially true for entry-level roles.
- Skill Gaps: The rapid pace of technological advancement often results in skill gaps between the knowledge required for a job and the actual skills possessed by job seekers. Continuous learning and skill development are essential to overcome this.
- Keeping Up with the Pace of Change: The constant evolution of technologies and tools can be challenging for individuals to keep up with, necessitating continuous learning and adaptation.
Barriers to Entry
Several barriers exist for individuals seeking high-tech employment. A lack of formal education or relevant experience can hinder entry into certain roles. Additionally, the high cost of specialized training and certifications can pose a financial challenge for some.
The high-tech job market is booming, offering tons of exciting opportunities. However, a significant hurdle exists: the digital divide separating rural and urban internet users. This disparity in access to reliable internet is a major roadblock for rural communities seeking to participate fully in the burgeoning high-tech employment landscape. This digital divide separates rural urban internet users means that many talented individuals in rural areas are effectively shut out of these lucrative positions.
Bridging this gap is crucial to truly fostering a diverse and inclusive high-tech sector.
- Lack of Formal Education: While many high-tech roles value practical skills over a traditional degree, a formal education can still provide a strong foundation and often serve as a prerequisite for specific roles.
- Limited Practical Experience: Gaining hands-on experience is crucial in the high-tech sector. Internships, personal projects, and volunteer work can help build a strong foundation and demonstrate practical skills.
- High Cost of Training: Specialized training and certifications, particularly in emerging technologies, can be expensive. Exploring alternative learning methods like online courses or boot camps can mitigate this cost.
Overcoming Challenges in Finding High-Tech Employment
Overcoming challenges in finding high-tech employment requires proactive strategies. Building a strong online presence through a professional portfolio and networking with industry professionals can be beneficial. Continuous learning and skill development are essential to stay competitive in the dynamic high-tech job market. Additionally, actively seeking internships or entry-level positions can provide valuable practical experience.
The high-tech job market is exploding, with tons of new roles popping up constantly. It’s amazing to see how many opportunities are emerging, especially in areas like the insane world of home electronics 2 media distribution, the insane world of home electronics 2 media distribution. This rapid growth is really shaping the future of technology and creating exciting career paths for those willing to adapt and learn.
The demand for skilled professionals in this sector is only going to increase.
The Impact of Technology on Employment: The Burgeoning High Tech Employment Landscape
The high-tech sector is experiencing rapid transformation, driven by automation and artificial intelligence. This technological evolution is reshaping the very fabric of employment, creating both opportunities and challenges for workers and companies alike. The impact extends beyond simple job displacement, influencing skill requirements, career paths, and the future of work itself.The integration of automation and AI is fundamentally altering the nature of work in the high-tech sector.
The high-tech job market is exploding, creating tons of exciting opportunities. Thinking about the holidays, finding unique presents for the tech-savvy people in your life can be tricky, but there are some truly cool and unusual gifts out there! Check out some ideas for the tech enthusiasts in your life at cool and unusual gifts for christmas.
Ultimately, this vibrant employment landscape offers a wealth of options for those seeking fulfilling careers in the tech sector.
From software development to customer service, these technologies are automating tasks previously performed by humans. This process, while potentially leading to efficiency gains and cost reductions, also presents the challenge of adapting to the evolving job market.
Automation and AI’s Impact on Roles
The rise of automation and AI is impacting various roles in the high-tech sector. Some roles, particularly those involving repetitive or predictable tasks, are experiencing increased automation. This is evident in areas like data entry, basic customer service interactions, and even some software testing.
Creation of New Roles
While some roles are being displaced, the high-tech sector is also creating entirely new roles. The demand for specialists in AI development, machine learning, data science, and cybersecurity is soaring. These roles require expertise in advanced technologies and problem-solving skills, highlighting the evolving skillset needed in the modern workforce.
Adapting to the Evolving Landscape
High-tech companies are proactively adapting to these changes. Many are investing in training programs to upskill their existing workforce and equip them with the skills needed for the future. Companies are also actively recruiting talent with the specialized skills demanded by the evolving job market.
Implications for Workers
The impact of these transformations on workers varies. Some workers may find themselves displaced from their current roles, requiring retraining or a career shift. Others may find their roles augmented by technology, allowing them to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their jobs. This requires continuous learning and adaptation to remain competitive in the evolving job market.
Examples include companies providing internal training programs or offering certifications to employees to acquire new skills, enabling them to transition to roles in emerging technologies. This adaptation is crucial for both individual career growth and the overall success of the high-tech sector.
Examples of High-Tech Company Adaptations
Companies are actively responding to the impact of automation and AI. For example, some companies are investing heavily in training programs, offering courses and certifications to upskill their employees in emerging technologies. Others are adopting new recruitment strategies, focusing on candidates with specific skills in AI and data science. This proactive approach demonstrates a commitment to fostering a workforce equipped to handle the challenges and opportunities of the future.
Companies like Google and Amazon have dedicated internal training programs and initiatives to equip their employees with the skills needed for future roles in emerging technologies.
Industry Leader Perspectives
“The future of work will be significantly different. The key will be adaptability and a focus on skills development to prepare for the changing landscape.”
[Name of Industry Leader]
Geographic Distribution and Location
The high-tech sector is not uniformly distributed across the globe. Instead, it exhibits significant clustering in specific geographic areas, creating vibrant tech hubs. Understanding these concentrations is crucial to grasping the dynamics of the modern employment landscape and the opportunities they present. This concentration is not accidental but a result of a complex interplay of factors, which will be explored below.The global map of high-tech employment density reveals a fascinating pattern.
Concentrations are not random, but are often found in regions with a strong confluence of factors such as a skilled workforce, robust venture capital funding, and supportive government policies. These clusters act as engines of innovation, attracting talent and driving economic growth.
Geographic Concentration of High-Tech Employment
The concentration of high-tech employment is most pronounced in North America, particularly in the Silicon Valley region of California and the Boston area of Massachusetts. These regions boast a rich history of technological innovation, coupled with a dense network of universities, research institutions, and venture capital firms. Europe also displays significant high-tech clusters, with prominent hubs in the Netherlands, Switzerland, and the UK, each with its own unique advantages and strengths.
Factors Contributing to Geographic Concentrations
Several factors contribute to the clustering of high-tech employment in specific regions. These include:* Availability of Skilled Labor: Regions with strong educational institutions and a tradition of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education often produce a pool of skilled workers that are crucial for innovation and development.
Robust Venture Capital Funding
The presence of active venture capital firms provides crucial financial support for startups and emerging companies, enabling them to grow and scale their operations.
Supportive Government Policies
Policies that encourage innovation, investment, and talent attraction can significantly influence the location of high-tech employment. Incentives such as tax breaks, grants, and streamlined regulatory environments attract companies and individuals.
Presence of Research Institutions and Universities
A strong network of research institutions and universities provides access to cutting-edge research and fosters a culture of innovation. Collaboration between academia and industry is vital for the advancement of technology.
Infrastructure
Reliable and efficient infrastructure, including transportation networks and communication systems, facilitates the movement of people, goods, and information, further contributing to the concentration of activity in specific regions.
Emerging Tech Hubs and Their Potential
Emerging tech hubs are rapidly gaining prominence. These areas, while often smaller in size compared to established hubs, possess significant potential for growth and innovation. Examples include:* Bengaluru, India: The city’s vibrant startup ecosystem and growing talent pool are positioning it as a key player in the global tech scene.
Tel Aviv, Israel
Known for its entrepreneurial spirit and robust innovation ecosystem, Tel Aviv is becoming a major hub for technology and startups.
Shenzhen, China
This city has a significant manufacturing base, providing a critical foundation for the development of hardware-focused technologies.
Comparison of Different Regions
Comparing different regions reveals varying strengths and weaknesses in the high-tech landscape. For example, while Silicon Valley is known for its venture capital prowess, other regions might excel in specific areas like software development or cybersecurity.
High-Tech Employment Distribution Map
 The map illustrates the global distribution of high-tech employment. Denser concentrations are visible in specific regions, highlighting the clustering effect. Variations in color or shading represent different levels of employment density, allowing for visual comparison of various areas.
The map illustrates the global distribution of high-tech employment. Denser concentrations are visible in specific regions, highlighting the clustering effect. Variations in color or shading represent different levels of employment density, allowing for visual comparison of various areas.
Salary and Compensation Trends
The high-tech sector boasts a dynamic compensation landscape, with salaries often exceeding those in other industries. Understanding these trends is crucial for both job seekers and employers. Competitive compensation packages are essential for attracting and retaining top talent, while also driving innovation and productivity.
Average Salaries for High-Tech Roles
Data on average salaries for various high-tech roles consistently demonstrates a wide range, influenced by factors such as experience, skills, company size, and location. Recent surveys indicate that roles requiring specialized technical expertise, such as machine learning engineers and cybersecurity specialists, often command higher salaries than more generalist roles.
Compensation Packages and Benefits
High-tech compensation packages extend beyond base salary. They frequently include comprehensive benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and generous stock options or profit-sharing schemes. These benefits are often significant motivators for employees, particularly in attracting and retaining top talent in a competitive market.
Factors Influencing Salary Disparities, The burgeoning high tech employment landscape
Several factors contribute to the salary disparities within the high-tech sector. Location plays a crucial role, with major tech hubs like Silicon Valley, the Bay Area, and Seattle consistently offering higher salaries compared to other regions. Specialized skills, such as those in artificial intelligence or blockchain development, are highly valued and command premium compensation. Years of experience, demonstrable accomplishments, and unique contributions to the industry are also influential factors.
Salary Ranges for Specific High-Tech Roles
| Role | Average Salary | Factors Influencing |
|---|---|---|
| Software Engineer (Junior) | $60,000 – $80,000 | Years of experience, specific programming languages, location |
| Data Scientist | $80,000 – $120,000 | Specific tools and techniques, degree level, project experience, industry specialization |
| Machine Learning Engineer | $90,000 – $150,000 | Specific machine learning algorithms and frameworks, research publications, experience with big data |
| Cybersecurity Analyst | $70,000 – $110,000 | Certifications, industry experience, location, expertise in specific security domains |
| Cloud Architect | $90,000 – $160,000 | Specific cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP), certifications, project experience |
Last Recap

In conclusion, the high-tech employment landscape is a dynamic and rapidly evolving environment, demanding adaptability and continuous learning. The future of work in this sector is shaped by technological advancements and a constant need for specialized skills. While challenges exist in navigating this terrain, the opportunities for growth and advancement are substantial. This exploration provides a snapshot of the present and future of the burgeoning high-tech employment landscape.