Vista Launches, Dells Back, Zunes Leadership
Vista launches dell is back zune gets right leadership – Vista launches, Dell is back, Zune gets right leadership – a fascinating look at the highs and lows of tech history. This journey delves into the past, examining the rise and fall of iconic products like Vista and Zune, alongside Dell’s remarkable comeback. We’ll analyze the strategies, leadership, and technological advancements that shaped these products’ fates, ultimately revealing valuable lessons for the future of product development.
From Vista’s market reception to Dell’s resurgence, we’ll unpack the factors behind their success and failures. The Zune’s story offers a unique perspective on what it takes to navigate a rapidly evolving tech landscape. This analysis provides a comparison of these products and the industry dynamics that impacted them, providing valuable insights into product design and market trends.
Vista’s Legacy and Dell’s Resurgence

The launch of Microsoft Vista, while heralded with some innovative features, faced a largely negative reception in the market. Early adopters and critics alike found its performance sluggish and its interface clunky compared to its predecessor, Windows XP. This early reception profoundly impacted Vista’s market share, and it struggled to gain significant traction against competitors like Mac OS and other versions of Windows.
Meanwhile, Dell, a once-dominant player in the PC market, experienced a period of decline due to factors like intense competition and changing consumer preferences. However, recent years have witnessed a resurgence in Dell’s fortunes, driven by strategic adjustments and innovative product offerings. This analysis delves into the contrasting fates of Vista and Dell, examining the factors that contributed to their respective trajectories and the impact of technological advancements on both.Vista’s initial release, with its promise of advanced features, ultimately fell short of user expectations, and this directly influenced the market share of the operating system.
Dell, meanwhile, had to adapt to the changing technological landscape, re-evaluate its strategies, and embrace new approaches to maintain its market presence.
Vista’s Reception and Market Impact
Vista’s initial reception was largely negative, with critics and users citing performance issues, a complex interface, and significant resource consumption. These criticisms led to lower-than-expected adoption rates, impacting Microsoft’s market share and potentially delaying the widespread adoption of some of Vista’s more advanced features. The initial marketing and launch strategies may not have adequately addressed the concerns of the target user base, contributing to the overall negative perception.
This ultimately contributed to the platform’s relatively short-lived period of dominance in the market.
Factors Contributing to Dell’s Comeback
Dell’s resurgence is a testament to its ability to adapt to changing market dynamics. Factors such as increased focus on customer service, the development of innovative products like laptops and desktops that aligned with the demands of mobile and remote work, and a comprehensive understanding of the evolving needs of consumers played a key role in Dell’s turnaround. Furthermore, strategic partnerships and the ability to effectively leverage emerging technologies were also instrumental in the company’s success.
It’s fascinating to see Vista launch, Dell back in the game, and Zune finally getting strong leadership. However, with all this tech excitement, it’s crucial to remember that older browsers like Internet Explorer can have significant security vulnerabilities. For a safer online experience, consider exploring browser alternatives like those highlighted in this informative guide on internet explorer security concerns and browser alternatives.
Ultimately, staying up-to-date with security is key, and this doesn’t change the exciting developments in the tech world like Vista, Dell, and Zune.
Strategies Employed by Vista and Dell
Microsoft’s strategy behind Vista was heavily focused on incorporating new features and technologies, but potentially at the cost of user-friendliness and initial performance. Dell, in contrast, adopted a more customer-centric approach, emphasizing quality, service, and adaptability to changing demands in the market. Vista’s strategy was geared toward future-proofing the operating system, while Dell focused on immediate user satisfaction and market responsiveness.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, particularly in processing power, storage, and networking, significantly impacted both Vista and Dell. Vista’s resource-intensive design, while aiming to capitalize on advancements, may have been outpaced by the actual performance capabilities of available hardware at the time. Dell, in response, adapted its product offerings to leverage these advancements, offering more powerful machines at more accessible price points. Technological shifts were fundamental in shaping the trajectory of both entities.
Key Features and Shortcomings of Vista Operating Systems, Vista launches dell is back zune gets right leadership
| Feature | Description | Shortcoming |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Security Features | Vista introduced several security improvements over XP. | Some users found these security features overly restrictive or disruptive to normal use. |
| Improved User Interface | Vista introduced new visual elements and themes. | The interface was perceived by many as being too complex and difficult to navigate compared to XP’s simplicity. |
| Support for 64-bit processors | Vista supported 64-bit processors, enabling more powerful processing. | Not all hardware was ready to fully take advantage of these advancements. |
| DirectX 10 | Vista supported the latest version of DirectX, providing better graphics performance. | Some games and applications struggled to adapt to the changes. |
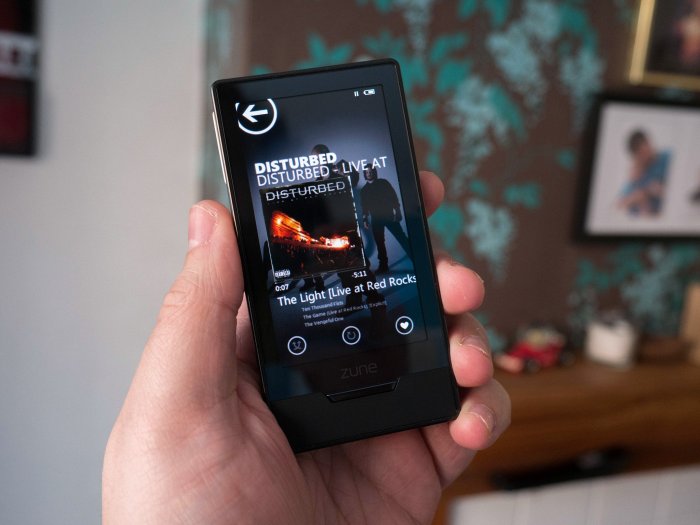
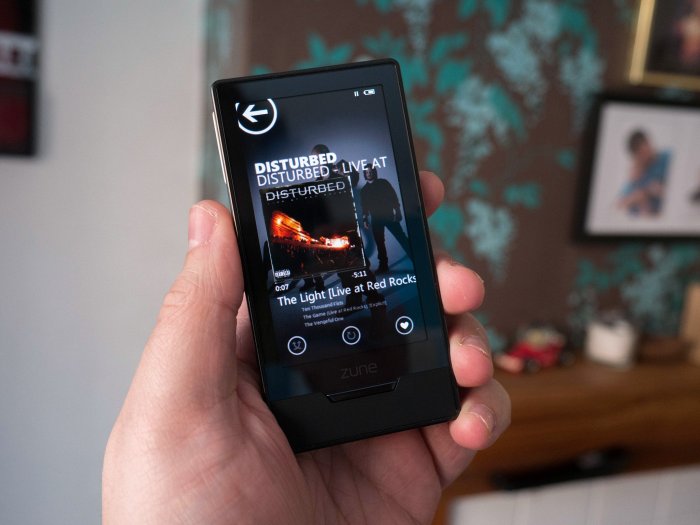
The Zune’s Short-Lived Run and Leadership Lessons: Vista Launches Dell Is Back Zune Gets Right Leadership
The Zune, Microsoft’s foray into the portable music player market, presented a compelling vision but ultimately fell short of expectations. This analysis delves into the factors that contributed to its demise, examining the initial market positioning, consumer reception, and ultimately, the leadership and strategic missteps that led to its discontinuation. Understanding these failures can provide valuable lessons for future product development.The Zune’s initial market positioning aimed to be a compelling alternative to Apple’s iPod, promising a user-friendly experience with a focus on integration with other Microsoft products.
Early reviews highlighted the device’s sleek design and intuitive interface, and Microsoft marketed it heavily, emphasizing the ease of transferring music from their ecosystem. However, the Zune’s eventual failure reveals that initial promise wasn’t enough to sustain market share against a dominant competitor.
Initial Market Positioning and Consumer Reception
The Zune initially garnered attention with its unique design and emphasis on seamless integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem. Early adopters appreciated the intuitive interface and the promise of a comprehensive music management solution. However, the Zune’s attempt to differentiate itself from the established iPod faced a significant challenge. Consumers were already deeply entrenched in the iPod ecosystem, and the Zune struggled to overcome this established preference.
The perception of the Zune as a ‘Microsoft product’ was a complex one, impacting consumer choice.
Factors Leading to Discontinuation
Several factors contributed to the Zune’s eventual demise. Apple’s dominant market position and extensive user base, coupled with the iPod’s established features and user experience, proved a formidable obstacle. The Zune’s reliance on Microsoft’s ecosystem integration, while initially promising, also presented challenges for users outside that realm. Furthermore, the Zune’s price point, though competitive in certain segments, never truly stood out in a market already flooded with options.
Leadership and Strategic Missteps
The Zune’s failure can be attributed, in part, to strategic missteps by Microsoft leadership. A lack of aggressive marketing to counteract Apple’s entrenched dominance and a failure to innovate beyond the initial design contributed significantly. The Zune’s limited appeal beyond the core Microsoft user base was another crucial weakness. Microsoft’s leadership may have underestimated the importance of addressing consumer preferences beyond their existing user base.
The absence of significant product differentiation beyond its core features proved problematic in a highly competitive market.
Successful Product Launches and Comparison
Comparing the Zune’s launch to successful product launches offers valuable insights. Successful products often prioritize features that directly address consumer needs and pain points, differentiating themselves in a competitive landscape. Apple’s meticulous attention to design, user experience, and ecosystem integration, exemplified by the iPod and later the iPhone, offers a valuable lesson in market positioning. Companies like Sony and others have successfully launched products by focusing on innovation and superior technological features.
Key Takeaways for Future Product Development
The Zune’s failure highlights the importance of understanding the consumer needs and market dynamics before launching a new product. Successful product development necessitates rigorous market research and the creation of a product that offers significant value proposition and features beyond existing offerings. Moreover, effective marketing and strategic positioning are critical to securing market share and establishing a successful product launch.
Vista launches, Dell’s back, and Zune’s getting its leadership right – it’s all exciting tech news. But alongside this, the Liberty Alliance is working hard to ensure privacy in phone transactions, a critical element in the modern digital world. This initiative, detailed in their recent work, highlights the need for secure phone interactions and underscores the importance of ongoing innovation in the tech sector, which is a positive step forward.
Ultimately, the focus is still on Vista, Dell, and Zune’s comeback, but the Liberty Alliance’s work on phone privacy is a crucial part of the larger tech landscape. liberty alliance to create privacy for phone transactions is a fascinating development that’s worth checking out.
Building a strong brand identity and user community through effective communication and engagement with the target audience is also essential.
Zune’s Key Features and Competitors
| Feature | Zune | iPod | Other Competitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Music Storage | Up to 120 GB | Up to 160 GB | Various capacities, depending on the model |
| Playback Quality | High-quality audio | High-quality audio | Varied, depending on the model and technology |
| User Interface | Intuitive and integrated with Windows Media Player | Simple and user-friendly | Varied interfaces and navigation |
| Pricing | Competitive, but not a significant differentiator | Competitive, often with a strong value proposition | Varied pricing, depending on the model and features |
| Integration | Strong integration with Microsoft ecosystem | Integration with iTunes and Mac OS | Varied integrations, depending on the platform |
Dell, Vista, and Zune
The tech landscape is a dynamic stage, where triumphs and setbacks are often intertwined. Three prominent entities – Dell, Vista, and Zune – each embarked on their journeys with hopes of market dominance, yet their trajectories diverged. This analysis explores the similarities and differences in their paths, examining their strategies and the impact of evolving consumer preferences.Understanding the challenges faced by these entities provides valuable insights into the intricacies of product development, market positioning, and adapting to shifting consumer demands.
The story of each reveals valuable lessons about the forces that shape the tech industry.
Similarities in Approach
The initial strategies of Dell, Vista, and Zune, though focused on different markets, exhibited some common ground. All three aimed to leverage their strengths to establish a dominant position in their respective segments. Dell focused on direct-to-consumer sales and customizable products, Vista on a comprehensive operating system, and Zune on a cohesive music ecosystem. This proactive approach, although ultimately not successful in all cases, highlighted the desire to capitalize on a perceived market need.
Differences in Business Models
Dell’s business model was characterized by its direct-sales approach and customizable hardware. Vista, conversely, was a platform-based operating system, reliant on partnerships with hardware manufacturers for distribution. Zune, an MP3 player, focused on a curated music experience and integration with Microsoft services. The differing models exposed the varied challenges associated with different product types and distribution channels.
Vista launching, Dell back in the game, and Zune finally getting strong leadership – it’s all very exciting. This renewed focus on tech giants might be a sign of things to come. Companies are increasingly looking to broaden their brand identity by offering cellular services, like mobile phones or data plans, a trend explored further in this great article about companies look to broaden brand identity with cellular services.
This suggests a wider strategy for these tech companies beyond their core products, and a push into more integrated services. It all points to a fascinating future for Vista, Dell, and Zune.
Dell’s model, for example, allowed for greater control over the customer experience, but also increased the need for robust supply chains.
Impact of Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences and market trends played a significant role in the trajectory of each entity. Dell’s customizable approach initially resonated with customers seeking tailored solutions. Vista, with its extensive features, aimed to cater to the diverse needs of users. Zune, however, faced competition from more user-friendly and feature-rich music players and services. Ultimately, each entity struggled to adapt quickly enough to evolving consumer tastes.
The rise of smartphones, for example, significantly impacted Zune’s market share as consumers increasingly turned to mobile devices for music consumption.
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Dell | Vista | Zune |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Type | PC Hardware | Operating System | MP3 Player |
| Business Model | Direct sales, customizable | Platform-based, partnerships | Integrated music ecosystem |
| Target Audience | Home users, businesses | PC users | Music enthusiasts |
| Success Factors | Customization, direct interaction | Comprehensive features, broad compatibility | Curated music, integration |
| Failure Factors | Competition, evolving needs | Lack of adoption, competitor strength | Evolving market, lack of innovation |
This table provides a concise overview of the key characteristics of each entity, highlighting the crucial factors that shaped their respective fates. It reveals the complex interplay between product features, business strategies, and market forces.
The Technological Landscape and Product Evolution
The years surrounding the launch of Vista, the Zune, and Dell’s resurgence witnessed a dynamic shift in the technological landscape. Advancements in computing power, storage, and connectivity profoundly impacted consumer expectations and product design. This period marked a crucial juncture where innovation collided with market demands, influencing the success or failure of products like the Zune and Vista’s reception.
Technological Advancements Shaping the Landscape
The early 2000s saw a surge in consumer electronics, with faster processors, larger hard drives, and improved graphics capabilities becoming increasingly common. The rise of broadband internet further connected consumers to a global network of information and entertainment. Mobile devices, while not as prevalent as today, were beginning to influence computing paradigms, foreshadowing the future of portable computing.
These advancements created both opportunities and challenges for companies like Dell, and the software giants that were vying for consumer attention.
Evolution of Computing Technology
The period between Vista’s release and the Zune’s demise saw a significant evolution in computing technology. From the early days of desktop computing, users transitioned to more portable laptops and the beginnings of mobile devices. The shift towards increasingly powerful processors and more sophisticated operating systems was evident. Vista, for all its flaws, represented an attempt to incorporate these advances into a consumer-friendly package.
Dell, meanwhile, adjusted its product lines to leverage these improvements in hardware and software, aiming to provide affordable and capable computing solutions for consumers.
Key Technological Milestones
- 2000s: Rise of Broadband Internet: Broadband internet connections became more widespread, enabling faster downloads and online experiences, which directly influenced the design of devices like the Zune and the Vista operating system. Users could access more information and entertainment than ever before, driving the need for faster and more efficient technology. This development influenced the consumer’s desire for quicker downloads and a more fluid online experience.
- 2000s: Increasing Mobile Computing: The concept of mobile computing started to take root. Portable laptops and handheld devices were gaining popularity, setting the stage for the proliferation of smartphones and tablets in later years. This trend reflected the growing need for portability and convenience in the computing experience, directly impacting Dell’s efforts to offer laptops as a primary computing device.
- 2006: Vista Release: Microsoft’s Vista operating system introduced new features, but it also faced criticism for performance issues. This exemplifies how technological advancements, while promising, can sometimes be challenging to integrate smoothly into existing frameworks, particularly in consumer-facing products.
- 2006-2008: Emergence of Portable Media Players: Devices like the Zune, along with iPods, signified a growing demand for portable media consumption. This trend reflected the desire to enjoy music, video, and other forms of digital content on the go, pushing manufacturers to innovate in hardware and software to meet this need.
Impact on Consumer Preferences
Technological advancements directly influenced consumer preferences during this era. Consumers, increasingly accustomed to faster processors and more intuitive interfaces, demanded similar experiences in their computing and entertainment devices. The Zune, for example, attempted to leverage these trends by offering a seamless music experience. Dell’s focus on offering affordable and powerful laptops responded to the rising demand for personal computers with enhanced capabilities.
The increased speed and storage capacity of computers led to an increased demand for faster and more reliable storage devices, like external hard drives and flash drives.
Technological Changes Timeline
| Year | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2000s | Rise of Broadband Internet | Faster downloads, more online access, increased demand for faster devices. |
| 2000s | Increasing Mobile Computing | Desire for portability and convenience in computing; rise of laptops. |
| 2006 | Vista Release | New features, but performance issues; showcased challenges of integrating advancements. |
| 2006-2008 | Emergence of Portable Media Players | Increased demand for portable entertainment; influence on Zune design. |
Emerging Market Trends and Product Design
The landscape of consumer electronics and technology has undergone a dramatic evolution since the Vista era. Understanding the shifting needs and preferences in emerging markets is crucial for successful product design. This evolution, driven by factors like globalization, rising incomes, and changing communication patterns, has profoundly impacted how products are conceived, developed, and ultimately, perceived.The rise of the internet and mobile devices fundamentally altered the way people interacted with technology.
This transformation, coupled with economic shifts, played a critical role in shaping consumer expectations and preferences, impacting the success of products like Vista, Zune, and Dell’s subsequent comeback. The ability to adapt to these changes is paramount for companies seeking to thrive in the modern market.
Consumer Preferences During Key Periods
The consumer landscape during the Vista era, the Zune’s short-lived reign, and Dell’s resurgence was significantly different from today’s. Understanding these nuances is vital for appreciating the challenges and opportunities presented by the evolving market. A detailed understanding of these distinct periods allows for a richer appreciation of product design considerations during each era.
- Vista Era (Early 2000s): Consumers were primarily focused on desktop computing. Internet access was becoming more widespread, but mobile devices were less prevalent. Performance, reliability, and user-friendly interfaces were paramount. Basic features and compatibility were prioritized over advanced functionalities.
- Zune Era (Early 2000s): The rise of portable media players was a defining trend. Consumers were seeking devices that could easily store and play music. Battery life, storage capacity, and music quality became key purchasing drivers. The emphasis was on portability and user experience, a shift from the more static desktop-centric computing.
- Dell’s Resurgence: Dell, having faced challenges in the early 2000s, adapted to changing market conditions. The emphasis shifted towards affordability, customization, and greater accessibility. The market demanded options and configurations to suit diverse needs. The importance of after-sales service and reputation also emerged as key factors.
Market Research and Consumer Feedback
Effective product development relies heavily on market research and consumer feedback. Gathering insights from diverse consumer groups is crucial for understanding the evolving needs and preferences in the market. This allows companies to tailor products to meet specific demands.
- Importance of Market Research: Market research provides critical data to understand consumer behavior, identifying unmet needs and preferences. Analyzing trends, analyzing competitive products, and understanding the market’s overall dynamics are critical steps in successful product design.
- Value of Consumer Feedback: Direct feedback from consumers, obtained through surveys, focus groups, and online communities, provides valuable insights into product usability, design preferences, and functionality. Understanding the user experience is paramount for creating products that consumers find valuable and easy to use.
Evolving Consumer Needs and Preferences
Consumer expectations are dynamic and constantly evolving. The demands and preferences for technology products shift as consumer needs and desires change. Understanding these evolving patterns is essential for product development and market adaptation.
| Period | Key Consumer Needs | Key Consumer Preferences |
|---|---|---|
| Vista Era | Reliable performance, ease of use, basic functionality | Desktop-centric, high-quality components, stable systems |
| Zune Era | Portability, music storage and playback, battery life | Easy-to-use interfaces, sleek designs, compact size |
| Dell’s Resurgence | Affordability, customization options, accessibility | Wide range of configurations, robust after-sales support, trusted brand reputation |
| Present/Future | Integration with other devices, personalized experiences, sustainability | Intuitive interfaces, seamless transitions, eco-friendly design, affordability in developing markets |
Industry Analysis and Market Shifts

The years surrounding Vista’s launch, Zune’s brief run, and Dell’s resurgence were periods of significant change in the technology industry. Shifting consumer preferences, evolving competitive landscapes, and global economic factors all played pivotal roles in shaping product success and market share. Understanding these forces is crucial for analyzing the challenges faced by each product and the industry as a whole.The technological landscape during this era was marked by a transition from traditional PC dominance to the rise of mobile devices.
Consumers were becoming increasingly reliant on portable computing and entertainment options, which created both opportunities and threats for established players like Dell and Microsoft. The economic climate of the time also played a critical role, impacting consumer spending habits and the overall market demand.
Competitive Pressures Faced by Vista, Zune, and Dell
The period saw intense competition across multiple fronts. Microsoft, with Vista, faced pressure from Apple’s innovative user experience and the growing popularity of open-source operating systems. Dell, competing against HP, Acer, and other established players, had to differentiate its offerings to maintain market share. Zune, trying to capture a market segment within the burgeoning music player market, confronted competition from iPods, as well as the increasing accessibility of music streaming services.
The rivalry was fierce, forcing each company to adapt and innovate rapidly to remain competitive.
Impact of Market Forces and Economic Conditions
The economic climate significantly impacted consumer spending. During periods of economic uncertainty, consumers were more likely to prioritize essential products, potentially impacting sales of higher-priced items like Vista-powered PCs. The recessionary climate of the time might have also encouraged a preference for budget-friendly options and alternative solutions. This created a competitive landscape where cost-effectiveness and affordability were significant factors.
Impact of Global Events on the Tech Industry
Global events like financial crises or political instability could significantly affect consumer confidence and spending patterns. This could have led to reduced demand for certain products and forced companies to re-evaluate their strategies and priorities. Such events can disrupt supply chains and impact production, which could impact pricing and availability of products.
Key Players and Market Share (Estimated)
| Company | Product | Estimated Market Share (Vista Era) | Estimated Market Share (Zune Era) | Estimated Market Share (Dell Resurgence Era) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft | Vista | 50-60% | N/A | N/A |
| Apple | Mac OS X/iPod | 30-40% | Significant | Significant |
| Dell | PCs | 15-20% | N/A | 15-25% (depending on period) |
| HP | PCs | 10-15% | N/A | 10-15% |
| Other | Various | 5-10% | N/A | Various |
Note: Market share estimations are approximate and vary depending on the specific time period within each era. Factors like region and product categories can further influence these figures.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the story of Vista, Dell, and Zune highlights the complexities of the tech industry. While Vista’s legacy is somewhat shadowed, Dell’s comeback demonstrates the importance of adapting to change. The Zune’s failure, while painful, reveals crucial lessons in leadership and market analysis. By examining these products through a comparative lens, we gain a richer understanding of product development, market trends, and the ever-shifting technological landscape.