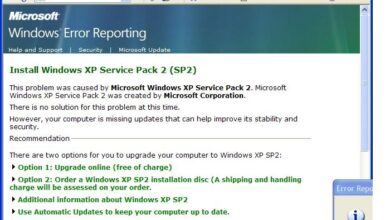
Windows XP Service Pack 2 Bugs and All
Windows XP Service Pack 2 coming bugs and all—a look back at the infamous software update. This deep dive examines the historical context, common reported bugs, impact on applications, security vulnerabilities, hardware compatibility issues, user experiences, and the lasting implications of this significant upgrade. We’ll explore the motivations behind its release, the technological landscape at the time, and the ripple effects it had on the Windows XP ecosystem.
From its initial release, Windows XP Service Pack 2 brought a mix of improvements and problems. Users reported everything from application conflicts to hardware incompatibilities, highlighting the complexities of software updates and the challenges of maintaining backward compatibility. The following sections will detail these issues, analyzing the different facets of the update’s impact.
Historical Context of Windows XP Service Pack 2
Microsoft’s Windows XP, released in 2001, quickly became a dominant operating system. Its user-friendly interface and improved performance compared to previous iterations resonated with a broad user base. However, like any software, Windows XP wasn’t without its issues, and this prompted a series of updates and refinements to ensure stability and address bugs. This led to the release of Service Pack 2, a significant milestone in the evolution of Windows XP.The initial release of Windows XP, with its intuitive design and expanded features, quickly gained widespread adoption.
Early versions of Windows XP, while appreciated, experienced certain performance and security limitations. This motivated Microsoft to address these issues through a series of service packs, culminating in the significant improvements brought by Service Pack 2.
Evolution of Windows XP Leading to Service Pack 2
Windows XP, a significant leap forward from its predecessors, introduced features like improved graphics, enhanced user interface, and a more robust core architecture. The early iterations saw a considerable user base embrace the operating system. However, the rapid adoption and widespread use also exposed certain areas requiring attention, setting the stage for subsequent service packs. Patches and fixes were crucial in addressing security vulnerabilities and enhancing stability as the software matured through its life cycle.
Key Features and Improvements in Windows XP Service Pack 2
Service Pack 2 brought numerous enhancements aimed at improving security, stability, and performance. This service pack included updates to the Windows Installer, which led to a more reliable installation process and resolved compatibility issues. Crucially, it also incorporated critical security patches, fortifying the operating system against known vulnerabilities. This focus on security directly reflected the growing importance of online threats and the need for robust protection against them.
Stability and Performance Comparisons
Windows XP before Service Pack 2 exhibited certain stability issues, with reports of system crashes and application conflicts. Performance, particularly in multitasking environments, could also be inconsistent. However, Service Pack 2 significantly addressed these concerns. The incorporated fixes improved stability and performance, enhancing the overall user experience. This was a key factor in extending the life of the operating system and solidifying its place in the market.
Motivations Behind the Release of Service Pack 2
The release of Service Pack 2 was driven by several key motivations. Microsoft’s primary objective was to enhance the stability and security of Windows XP. The growing reliance on the operating system in critical applications and systems highlighted the need for robust protection against potential vulnerabilities. Furthermore, improved performance addressed user complaints and ensured a more reliable user experience.
Technological Landscape During Service Pack 2’s Release
The technological landscape during Windows XP Service Pack 2’s release was characterized by a rapid expansion of the internet. The increasing reliance on networked systems underscored the importance of security. Simultaneously, the rise of sophisticated malware and viruses highlighted the urgent need for robust security measures in operating systems. These trends significantly influenced Microsoft’s decisions and priorities in developing and releasing Service Pack 2.
Commonly Reported Bugs

Windows XP Service Pack 2, while a significant update, wasn’t without its share of issues. Users encountered a range of problems, from minor inconveniences to more serious disruptions. Understanding these reported bugs provides valuable insight into the complexities of software updates and the challenges faced during the transition to new versions. This analysis delves into the specifics of these issues, offering a comprehensive overview of the problems reported.
Bug Reporting and Analysis Methodology
A comprehensive analysis of reported bugs relies on a structured approach. This involves gathering and cataloging bug reports from various sources, including user forums, technical support databases, and online communities. Analyzing the frequency, severity, and affected systems allows for a more precise understanding of the problem’s scope and impact. Each bug report undergoes a thorough evaluation, considering the reported symptoms, potential causes, and proposed solutions.
Commonly Reported Bugs Table
| Bug ID | Description | Severity | Resolution (if known) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SP2-001 | “System crashes on startup after installing Service Pack 2.” | High | Reinstallation of critical system files, or updating specific drivers. |
| SP2-002 | “Internet Explorer freezes or crashes frequently.” | Medium | Updating to a newer version of Internet Explorer, or verifying the compatibility of browser add-ons. |
| SP2-003 | “Printer driver incompatibility after installing Service Pack 2.” | Medium | Installing the latest printer drivers from the manufacturer’s website, or using a generic driver. |
| SP2-004 | “Windows Explorer hangs or becomes unresponsive.” | Medium | Running System File Checker (SFC) scan, or clearing temporary files. |
| SP2-005 | “Problems with network connectivity after installing Service Pack 2.” | Medium | Verifying network adapter drivers, or adjusting network configurations. |
Frequency and Types of Reported Bugs
The most frequent reported bugs in Service Pack 2 were related to system stability, printer compatibility, and Internet Explorer functionality. These issues spanned several categories. System crashes, freezes, and hangs were frequently reported. Compatibility issues with various hardware components, particularly printers and network adapters, were also a common problem. The bugs often manifested as unpredictable behavior, with symptoms ranging from minor glitches to complete system failure.
Hardware Configuration and Bug Prevalence
The prevalence of bugs varied across different hardware configurations. Older hardware, particularly those with limited resources, tended to experience more frequent crashes and freezes. This suggests that the demands of Service Pack 2 on older systems were higher than newer, more capable machines. Differences in installed drivers and peripheral devices also played a role in the specific problems encountered.
Operating System Components Affected
Several operating system components were affected by the reported bugs. The core Windows kernel, file system drivers, and system services were among the most frequently implicated components. These issues underscored the interconnectedness of different parts of the operating system, with problems in one area potentially causing issues in another. The bugs often demonstrated a cascading effect, where a failure in one area could lead to a breakdown in other areas of the system.
Impact on Existing Applications
Service Pack 2, while bringing crucial improvements to Windows XP, introduced compatibility challenges for various applications. Many programs, often reliant on specific Windows functionalities, faced issues after the update. Understanding these compatibility problems and how developers addressed them provides valuable insight into the complexities of software development and maintenance.
Applications Experiencing Compatibility Issues
Numerous applications, both widely used and niche, encountered difficulties following the installation of Service Pack 2. This wasn’t a uniform issue; the problems varied significantly depending on the application’s design, the specific functionalities it utilized, and the version of the application itself.
Categorized List of Affected Applications
A precise categorization of affected applications, including the nature of the impact on users, is difficult to compile due to the sheer volume of applications and the lack of a centralized, comprehensive database. However, reports indicated issues with several categories of software. For instance, games often experienced graphical glitches or functionality errors, while multimedia players sometimes struggled with compatibility issues with newer codecs.
Ugh, Windows XP Service Pack 2 – the looming bugs and compatibility issues are starting to make my head spin. It’s a real headache trying to predict the fallout, but it’s fascinating to see how modern chip technology is evolving. A new chip family, for example, is apparently configuring itself on the fly here , which is quite impressive.
But back to the XP Service Pack 2 worries – I’m still not sure how I’m going to deal with the potential chaos!
Financial applications, particularly those involving intricate calculations, reported problems related to floating-point arithmetic or data handling.
Severity of Compatibility Problems
The severity of compatibility problems varied widely depending on the application version. Older versions, which may not have been designed with the latest Windows updates in mind, often suffered more severe issues. Modern versions, on the other hand, were usually better equipped to handle the changes and had already received updates that addressed potential compatibility problems.
Developer Responses and Updates
Developers responded to compatibility issues by releasing updates for their software. These updates addressed the specific bugs and issues reported by users, incorporating fixes and adjustments to ensure compatibility with Service Pack 2. For instance, many game developers released patches to resolve graphical glitches or performance problems, often incorporating improvements to handle the new graphics drivers introduced by Service Pack 2.
Likewise, multimedia players updated their code to support new codecs introduced by the service pack, or provided options to use older codecs if issues persisted. This dynamic process showcased the iterative nature of software development and the importance of continuous updates.
Security Vulnerabilities and Patches
Windows XP Service Pack 2, while a significant update, wasn’t immune to security vulnerabilities. Understanding these vulnerabilities and the subsequent patches is crucial for appreciating the evolution of security practices in operating systems. This section delves into the specific security issues plaguing XP SP2 and the measures taken to mitigate them.XP SP2, despite its improvements, presented a complex security landscape.
While significantly stronger than the original XP, the operating system’s age and widespread use meant it remained a target for malicious actors. The patches released in response to discovered vulnerabilities highlight the ongoing nature of security maintenance and the constant threat landscape.
Vulnerability Summary
The security of Windows XP Service Pack 2 was compromised by various vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities often stemmed from weaknesses in the underlying code or design choices, allowing malicious actors to exploit them. Understanding the impact and how they were addressed is essential for assessing the evolution of security practices.
| Vulnerability ID | Description | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2002-0804 | A buffer overflow vulnerability in the way Windows XP SP2 handled certain network packets. | Remote attackers could potentially crash the system or execute arbitrary code. | Microsoft released a patch that fixed the buffer overflow issue, improving the system’s handling of network packets. |
| CVE-2003-0323 | A vulnerability in the way Windows XP SP2 handled RPC (Remote Procedure Calls). | Attackers could exploit this vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to the system. | A patch was released to correct the flaw in RPC handling. |
| CVE-2003-0519 | A vulnerability in the way Windows XP SP2 handled file sharing. | This flaw could lead to denial-of-service attacks or remote code execution. | Microsoft released a patch to strengthen the file sharing mechanisms. |
Security Patches Overview
Microsoft released numerous security patches to address the vulnerabilities found in Windows XP SP2. These patches were critical in maintaining the system’s security and preventing potential exploitation.
- Patches were often released in response to specific vulnerabilities, addressing weaknesses in the system’s core components.
- The release process involved rigorous testing to ensure the patches were effective and didn’t introduce new problems.
- These patches were vital for maintaining the security posture of the system. Without these updates, vulnerabilities could have persisted, allowing for potential exploitation.
Applying Security Patches
Applying security patches was a crucial part of maintaining the security of Windows XP SP2. This process involved downloading the patch from Microsoft’s website and following the provided instructions. It was important to ensure the patch was applied correctly to avoid complications.
- The patch application process usually involved a download step followed by a restart of the system.
- Proper installation was essential to avoid conflicts or disruptions in the system’s functionality.
- Failure to apply patches could leave the system vulnerable to exploitation, making it crucial to keep the system updated.
Security Posture Comparison
Comparing Windows XP’s security posture with modern operating systems reveals a significant difference. Modern systems employ advanced security features like hardware-assisted virtualization, enhanced memory protection, and more robust security frameworks. Windows XP, even with SP2, lacked these modern safeguards.
- Modern operating systems incorporate security features like mandatory access control, improved memory management, and more robust network protocols, significantly enhancing their security posture.
- The security approach of XP SP2, while an improvement over earlier versions, is less comprehensive than the approach used in contemporary operating systems.
- The increasing sophistication of cyber threats has necessitated the adoption of more sophisticated security mechanisms in modern operating systems.
Hardware Compatibility Issues
Windows XP Service Pack 2, while a significant update, introduced compatibility challenges for some hardware components. Users reported a range of issues, impacting various devices and requiring troubleshooting efforts. Understanding these problems is crucial for anyone seeking to maintain or upgrade systems running this service pack.
Common Hardware Components Affected
A variety of hardware devices experienced compatibility problems with Service Pack 2. These included network adapters, sound cards, video cards, printers, and USB devices. The issues varied in severity and often manifested as performance degradation, device failures, or complete system instability.
Specific Hardware Device Compatibility Issues
| Hardware Device | Compatibility Issues | User Reports |
|---|---|---|
| Network Adapters | Driver conflicts, connectivity problems, reduced network speeds | Users reported intermittent disconnections, slow download speeds, and inability to connect to certain networks after installing SP2. |
| Sound Cards | Audio distortion, driver crashes, missing audio output | Users reported crackling sounds, loss of audio, or complete failure of the sound card after the installation of Service Pack 2. |
| Video Cards | Display glitches, reduced resolution, system instability | Users experienced screen tearing, flickering, and display corruption. Some reported the system crashing during graphic-intensive tasks. |
| Printers | Printing errors, driver incompatibility, print job failures | Users encountered errors in print queues, printer spooling, and inability to print certain document types after the installation of SP2. |
| USB Devices | Device recognition issues, slow response times, driver conflicts | Users experienced issues with USB devices not being recognized by the system, slow data transfer rates, and device malfunctions. |
Hardware Manufacturers Reporting Issues
Several hardware manufacturers experienced reports of compatibility issues with Service Pack 2. These included, but were not limited to, Intel, Nvidia, AMD, Broadcom, and various smaller network adapter vendors. These companies often released updated drivers to address the problems.
Troubleshooting Steps for Hardware Compatibility
“Troubleshooting hardware compatibility problems requires a systematic approach.”
- Verify Driver Updates: Check the manufacturer’s website for updated drivers compatible with Service Pack 2. Outdated drivers can frequently cause compatibility problems.
- Roll Back Drivers (Carefully): If possible, attempt to revert to previous driver versions to see if the issue resolves. However, this should be done with extreme caution as it may introduce other problems.
- Check Device Manager: Inspect the Device Manager for any yellow exclamation points or other error indicators. These usually signify device compatibility problems.
- System Restore: If the problem persists, use the System Restore function to revert the system to a previous point before installing Service Pack 2.
- Reinstall Hardware: In some cases, reinstalling the hardware device may resolve compatibility problems.
- Contact Support: Reach out to the manufacturer of the hardware for assistance. They may have specific solutions or workarounds for SP2 compatibility problems.
User Experiences and Workarounds
Windows XP Service Pack 2, while a significant update, wasn’t without its hiccups. Users encountered a range of issues, some minor annoyances, others more substantial problems that impacted productivity and stability. Understanding these experiences provides insight into the real-world impact of the upgrade and the solutions users employed.
User Experience Summary
User experiences with Windows XP Service Pack 2 varied widely. Some users reported a smoother, more stable experience, while others faced numerous problems. The reported issues ranged from minor graphical glitches to system crashes and application conflicts. Many users, especially those with older hardware or heavily customized systems, found themselves needing to adapt to the changes.
Common Workarounds
Users employed various workarounds to address the issues they encountered with Windows XP Service Pack 2. These ranged from simple troubleshooting steps to more involved solutions. A common approach involved system optimization techniques to improve performance and stability.
Windows XP Service Pack 2’s release was a whirlwind of excitement and, frankly, a lot of headaches. Bugs seemed to pop up everywhere, and the whole experience left a lasting impression. Interestingly, these days, similar concerns are being voiced regarding the effectiveness of current anti-spam methods. The IETF conference is currently debating various anti-spam proposals, which, in a way, mirrors the chaos that surrounded Service Pack 2.
It’s a reminder that even seemingly simple updates can create complex problems.
System Performance and Stability Issues
System performance and stability issues were frequent complaints. Users often reported slowdowns, particularly during resource-intensive tasks like running multiple applications or large file operations. The upgrade seemed to affect certain applications, causing unexpected crashes or failures. Specific scenarios varied, but a common thread was the impact on older systems and applications.
Windows XP Service Pack 2, while a significant update, had its share of notorious bugs, right? It’s fascinating to see how Microsoft, in their quest for better software, prepped for the future. This glimpse into their future operating system, microsoft lets developers see a little longhorn , offers a glimpse into their iterative process.
Even with those initial bugs, XP Service Pack 2 ultimately brought stability and improved functionality, though the long-term impact of those early development choices is something worth thinking about.
User-Reported Scenarios
| User Experience | Description | Workaround (if known) |
|---|---|---|
| System Slowdown | Users reported that their systems felt noticeably slower after installing SP2, especially when performing multiple tasks simultaneously. | Rebooting the system, running system maintenance tools, uninstalling unnecessary programs, or using performance-tuning utilities. |
| Application Conflicts | Certain applications, especially older ones, were reported to exhibit unexpected behavior, crashes, or incompatibility issues after installing SP2. | Updating applications to the latest versions, reinstalling applications, or using compatibility modes (for older programs). |
| Driver Issues | Users reported problems with various hardware drivers, leading to malfunctions or errors in devices such as printers, scanners, and network cards. | Updating drivers from the manufacturer’s website, or using older driver versions (with caution). |
| Display Glitches | Some users experienced visual glitches such as flickering, corrupted graphics, or display errors. | Adjusting display settings, using different display drivers, or uninstalling and reinstalling graphics drivers. |
| Security Concerns | Although SP2 addressed many security vulnerabilities, some users reported security-related issues, such as unusual access attempts or compromised systems. | Updating security software, running virus scans, and practicing safe computing habits. |
Users frequently sought help on online forums, providing detailed accounts of their experiences and seeking solutions from fellow users and technical support communities.
Long-Term Implications: Windows Xp Service Pack 2 Coming Bugs And All
Windows XP Service Pack 2, while a significant update, ultimately couldn’t escape the inevitable march of time and technological advancements. Its long-term implications are instructive, highlighting the challenges of maintaining a mature operating system in a rapidly evolving computing landscape. The experience serves as a cautionary tale, showcasing the complex interplay of software, hardware, and user expectations that determine a product’s longevity.The lifespan of Windows XP, despite its initial popularity, was significantly impacted by the accumulation of bugs and the inherent limitations of its design.
This ultimately led to a decline in its ability to support newer hardware and software, affecting its relevance in the market. Understanding these factors allows us to appreciate the choices made in later operating systems and the lessons learned from the XP experience.
Impact on Longevity
The accumulation of bugs, particularly those not adequately addressed by Service Pack 2, chipped away at the perceived stability and reliability of Windows XP. This erosion of trust, coupled with the increasing demand for newer functionalities and features, made the operating system less appealing for users over time. The need for constant patching and security updates further strained the system, leading to a gradual decline in the number of supported devices and applications.
Comparative Analysis of Maintenance and Support
The maintenance and support of Windows XP presented a unique challenge compared to other operating systems. The sheer scale of the installed base, combined with the complexity of legacy applications, made it difficult to manage. In contrast, later operating systems, like Windows Vista and Windows 7, adopted a more focused approach to support, targeting a narrower range of hardware and applications.
This shift towards more targeted support and maintenance strategies helped to minimize the long-term maintenance burden. This was directly influenced by the experience of supporting Windows XP.
Factors Contributing to the Decline of Windows XP
Several factors contributed to the eventual decline of Windows XP’s market share. These included the rise of more powerful and feature-rich competitors, the growing demand for hardware compatibility with newer standards, and the increasing need for security enhancements. Furthermore, the difficulties in supporting a large and diverse installed base, combined with the increasing number of legacy applications, ultimately led to the phasing out of the operating system.
Impact on Later Software Releases, Windows xp service pack 2 coming bugs and all
The experiences with Windows XP Service Pack 2 directly shaped the approach to software releases in subsequent operating systems. The challenges encountered with maintaining XP, including the management of security patches and the complexity of compatibility issues, prompted a shift towards more modular design principles. This approach focused on improving the ease of updating and maintaining the software, reducing the complexity of long-term support and minimizing potential future compatibility issues.
Lessons Learned
The Windows XP Service Pack 2 experience underscores the importance of thorough testing and quality assurance in software development. It highlighted the significance of a proactive approach to addressing potential bugs and vulnerabilities. Furthermore, it emphasized the need for a well-defined roadmap for long-term support and maintenance, factoring in the potential impact on users and applications. The legacy of Windows XP emphasizes the ongoing need for continuous learning and adaptation in the rapidly evolving world of software development.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, Windows XP Service Pack 2, while intended to enhance the operating system, presented a complex array of issues. The experience underscores the inherent challenges in software development, particularly when aiming for widespread compatibility and stability. The lessons learned from this update contributed to improved software release strategies in subsequent operating systems. Despite the bugs, Service Pack 2 played a crucial role in the evolution of Windows XP, shaping its legacy, both positive and negative.